Abstract
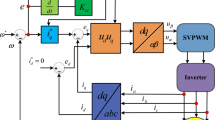
A linear permanent magnet synchronous motor (LPMSM) drive system is keeping in many nonlinear effects such as the external load force, the flux saturation, the cogging force, the column friction and Stribeck force, and the parameters variations. Due to the uncertainty effects the existing linear controllers can not achieve better control performances for the LPMSM drive system. To raise robustness under occurrence of uncertainty, the integral backstepping control system with hitting function is proposed for controlling the LPMSM drive system in accordance with the Lyapunov function. To improve larger chattering phenomenon under uncertainties effects, the integral backstepping control system with revised recurrent fuzzy neural network (RRFNN) and mended particle swarm optimization (MPSO) is proposed to operate the LPMSM drive system to raise robustness of system. The RRFNN is used to estimate the value of the external lumped force uncertainty. Moreover, the error compensation control with the error compensation mechanism is proposed to compensate the minimum reconstructed error of the error estimation law. Besides, four variable learning rates in the weights of the RRFNN are regulated by virtue of MPSO with segment regulation to speed-up parameter’s convergence. Finally, comparative performances through some tentative upshots are verified that the integral backstepping control system by virtue of RRFNN with MPSO has better control performances than those of the proposed methods for the LPMSM drive system.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
16 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01067-0
References
Boldea, I., Nasar, S.A.: Linear Electric Actuators and Generators. Cambridge University Press, London (1997)
Egami, T., Tsuchiya, T.: Disturbance suppression control with preview action of linear DC brushless motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 42(5), 494–500 (1995)
Sanada, M., Morimoto, S., Takeda, Y.: Interior permanent magnet linear synchronous motor for high-performance drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 33(5), 966–972 (1997)
Lin, C.H.: Precision motion control of a linear permanent magnet synchronous machine based on linear optical-ruler sensor and Hall sensor. Sensors 18(10), 3345 (2018)
Kanellakopoulos, I., Kokotovic, P.V., Morse, A.S.: Systematic design of adaptive controller for feedback linearizable system. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 36(11), 1241–1253 (1991)
Bartolini, G., Ferrara, A., Giacomini, L., Usai, E.: Peoperties of a combined adaptive/second-order sliding mode control algorithm for some classes of uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 45(7), 1334–1341 (2000)
Lin, C.H.: A backstepping control of LSM drive systems using adaptive modified recurrent Laguerre OPNNUO. J. Power Electron. 16(2), 598–609 (2016)
Lin, C.H.: Nonlinear backstepping control design of LSM drive system using adaptive modified recurrent Laguerre orthogonal polynomial network. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 15(2), 905–917 (2017)
Wang, X., Song, J.: Synchronization of the fractional order hyperchaos Lorenz systems with activation feedback control. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 14(8), 3351–3357 (2009)
Wang, X., He, Y.: Projective synchronization of fractional order chaotic system based on linear separation. Phys. Lett. A 372(4), 435–441 (2008)
Wang, X., Wang, M.: Dynamic analysis of the fractional-order Liu system and its synchronization. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 17(3), 033106 (2007)
Lin, D., Wang, X.: Observer-based decentralized fuzzy neural sliding mode control for interconnected unknown chaotic systems via network structure adaptation. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 161(15), 2066–2080 (2010)
Wang, X., He, Y., Wang, M.: Chaos control of a fractional order modified coupled dynamos system. Nonlinear Anal. Theory Methods Appl. 71(12), 6126–6134 (2009)
Wang, Y., Zhang, H., Wang, X., Yang, D.: Networked synchronization control of coupled dynamic networks with time-varying delay. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 40(6), 1468–1479 (2010)
Lin, C.H.: Hybrid recurrent wavelet neural network control of PMSM servo-drive system for electric scooter. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 12(1), 177–187 (2014)
Lin, F.J., Lin, C.H.: On-line gain-tuning IP controller using RFNN for linear synchronous motor. IEEE Trans. Aerospace Electron. Syst. 37(2), 655–670 (2001)
Tosunoğlu, N.G., Apaydın, A.: A new spatial algorithm based on adaptive fuzzy neural network for prediction of crustal motion velocities in earthquake research. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(5), 1656–1670 (2018)
Yang, M.C., Wang, J.Z., Sun, T.Y.: EMD-based preprocessing with a fuzzy inference system and a fuzzy neural network to identify kiln coating collapse for predicting refractory failure in the cement process. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(8), 2640–2656 (2018)
Lin, D., Wang, X., Nian, F., Zhang, Y.: Dynamic fuzzy neural networks modeling and adaptive backstepping tracking control of uncertain chaotic systems. Neurocomputing 73(16–18), 2873–2881 (2010)
Lin, D., Wang, X.: Self-organizing adaptive fuzzy neural control for the synchronization of uncertain chaotic systems with random-varying parameters. Neurocomputing 74(12–13), 2241–2249 (2011)
Kim, H.M., Han, S.I., Kim, J.S.: Precision position control of servo systems using adaptive back-stepping and recurrent fuzzy neural networks. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 23(11), 3059–3070 (2009)
Sheng, L.G., Gao, X., Zhang, L.: Robust adaptive backstepping sliding mode control for six-phase permanent magnet synchronous motor using recurrent wavelet fuzzy neural network. IEEE Access 5, 14502–14515 (2017)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization, pp. 1942–1948. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Neural Netw., Perth (1995)
Clerc, M., Kennedy, J.: The particle swarm-explosion, stability, and convergence in a multi-dimensional complex space. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6(1), 58–73 (2002)
Shi, Y., Eberhart, R.C.: A modified particle swarm optimizer, pp. 69–73. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Evol. Comput., Anchorage (1998)
Akbari, R., Ziarati, K.: A rank based particle swarm optimization algorithm with dynamic adaptation. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 235(8), 2694–2714 (2010)
Lin, C.H.: Composite recurrent Laguerre orthogonal polynomials neural network dynamic control for continuously variable transmission system using altered particle swarm optimization. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(3), 1219–1245 (2015)
Chen, C.C.: Optimization of zero-order TSK-type fuzzy system using enhanced particle swarm optimizer with dynamic mutation and special initialization. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 20(5), 1685–1698 (2018)
Lin, C.H., Yu, C.Y.: Blend recurrent Gegenbauer OPNNAPSO control for a SynRM servo-drive CVT system, pp. 1060–1065. Proc. IEEE Conf. Ind. Electron. Appl., Wuhan (2018)
Slotine, J.J.E., Li, W.: Applied Nonlinear Control. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (1991)
Astrom, K.J., Wittenmark, B.: Adaptive control. Addison-Wesley, New York (1995)
Ku, C.C., Lee, K.Y.: Diagonal recurrent neural networks for dynamic system control. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 6(1), 144–156 (1995)
Lin, C.H.: Recurrent modified Elman neural network control of PM synchronous generator system using wind turbine emulator of PM synchronous servo motor drive. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 52, 143–160 (2013)
Lewis, F.L., Campos, J., Selmic R.: Neuro-fuzzy control of industrial systems with actuator nonlinearities. SIAM Front. Appl. Math. (FR), Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia (2002)
Astrom, K.J., Hagglund, T., Controller, P.I.D.: Theory, Design, and Tuning. Instrument Society of America, Research Triangle Park, North Carolina (1995)
Hagglund, T., Astrom, K.J.: Revisiting the Ziegler-Nichols tuning rules for PI control. Asian J. Control 4(2), 364–380 (2002)
Hagglund, T., Astrom, K.J.: Revisiting the Ziegler- Nichols tuning rules for PI control-part II: the frequency response method. Asian J. Control 6(4), 469–482 (2004)
Funding
This research received the financial support of the Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan, R.O.C. through its Grant MOST 107-2221-E-239-021.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that he has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
This article has been retracted. Please see the retraction notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01067-0
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, CH. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Integral Backstepping Control of LPMSM Drive System Using Revised Recurrent Fuzzy NN and Mended Particle Swarm Optimization. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 400–413 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00775-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00775-y