Abstract
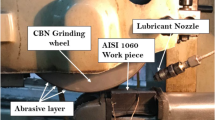
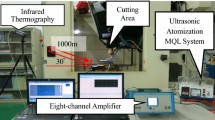
This study proposed the application of a nanofluid/ultrasonic atomization minimum quantity lubrication (MQL) method to grind Inconel 718 alloys. This is a grinding manufacturing innovation on lubrication technology. Multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) and molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanoparticles were used as the nanofluid additives. Specifically, MWCNTs exhibit excellent thermophysical properties to effectively remove the heat generated by cutting and reduce the friction coefficient, and MoS2 has excellent lubricating properties to generate film layers with high wear resistance to protect the workpiece and avoid plowing. The parameters of multiple performance characteristics were optimized through applications of the Taguchi robust design method, grey relational analysis, and a fuzzy inference system. The control parameters comprised nozzle angle, distance of the nozzle, type of nanoparticle, fraction of the nanofluid, value of atomization, tangential velocity, table rate, and air pressure. Subsequently, the optimized result was compared with basefluid/ultrasonic atomization MQL and nanofluid MQL. The results revealed that nanofluid/ultrasonic atomization MQL yields the optimal grinding force ratio, grinding temperature, and surface roughness.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Smith, G.T.: Cutting Tool Technology: Industrial Handbook. Springer, New York (2008)
Klocke, F., Eisenblätter, G.: Dry cutting. CIRP Ann. 46(2), 519–526 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60877-4
Brinksmeier, E., Heinzel, C., Wittmann, M.: Friction, cooling and lubrication in grinding. CIRP Ann. 48(2), 581–598 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)63236-3
Brinksmeier, E., Walter, A., Janssen, R., Diersen, P.: Aspects of cooling lubrication reduction in machining advanced materials. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. B 213(8), 769–778 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1243/0954405991517209
Tschätsch, I.H., Reichelt, D.I.A.: Cutting Fluids (Coolants and Lubricants). Applied Machining Technology, pp. 349–352. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Weinert, K., Inasaki, I., Sutherland, J.W., Wakabayashi, T.: Dry machining and minimum quantity lubrication. CIRP Ann. 53(2), 511–537 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-8506(07)60027-4
Huang, W.T., Liu, W.S., Wu, D.H.: Investigations into lubrication in grinding processes using MWCNTs nanofluids with ultrasonic-assisted dispersion. J. Cleaner Prod. 137, 1553–1559 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.06.038
Huang, W.T., Wu, D.H., Lin, S.P., Liu, W.S.: A combined minimum quantity lubrication and MWCNT cutting fluid approach for SKD 11 end milling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. 84, 1697–1704 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7770-2
Huang, W.T., Chen, J.T.: Application of intelligent modeling methods to enhance the effectiveness of nanofluid/micro lubrication in microdeep drilling holes machining. J. Adv. Mech. Des. Syst. Manuf. 14(7), 01–26 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1299/jamdsm.2020jamdsm0099
Nath, C., Kapoor, S.G., DeVor, R.E., Srivastava, A.K., Iverson, J.: Design and evaluation of an atomization-based cutting fluid spray system in turning of titanium alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 14(4), 452–459 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2012.09.002
Geoff, B., Chan, S.G., Yanqiao, Z., Martin, B.G.: Use of vegetable oil in water emulsion achieved through ultrasonic atomization as cutting fluids in micro-milling. J. Manuf. Process. 16(3), 405–413 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2014.04.005
Rukosuyev, M., Goo, C.S., Jun, M.B.: Understanding the effects of the system parameters of an ultrasonic cutting fluid application system for micro-machining. J. Manuf. Process. 12(2), 92–98 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmapro.2010.06.002
Huang, W.T., Liu, W.S., Tsai, J.T., Chou, J.H.: Multiple quality characteristics of nanofluid/ultrasonic atomization minimum quantity lubrication for grinding hardened mold steel. IEEE Trans. Auto. Sci. Eng. 15(3), 1065–1077 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/tase.2017.2726000
Huang, W.T., Wu, D.H., Chen, J.T.: Robust design of using Nanofluid/MQL in micro-drilling. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 85, 2155–2161 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-015-7382-x
Xu, J., Fang, H., Zeng, F., et al.: Robust observer design and fuzzy optimization for uncertain dynamic systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 1511–1523 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00646-6
Dong, F., Chen, Y.H., Zhao, X.: Optimal design of adaptive robust control for fuzzy swarm robot systems. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 1059–1072 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00626-w
Dourado, A.D., Lobato, F.S., Cavalini, A.A., et al.: Fuzzy reliability-based optimization for engineering system design. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 21, 1418–1429 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00655-5
Liu, J., Chen, Y., Zhou, J., et al.: An exact expected value-based method to prioritize engineering characteristics in fuzzy quality function deployment. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 18, 630–646 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-015-0118-0
Huang, W.T., Chou, F.I., Tsai, J.T., et al.: Application of graphene nanofluid/ultrasonic atomization MQL system in micromilling and development of optimal predictive model for SKH-9 high-speed steel using fuzzy-logic-based multi-objective design. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 22, 2101–2118 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-020-00930-w
Jun, M.B., Joshi, S.S., DeVor, R.E., Kapoor, S.G.: An experimental evaluation of an atomization-based cutting fluid application system for micromachining. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. Trans. ASME 130(3), 031118 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1115/1.2738961
Edwards, E.R., Antunes, E.F., Botelho, E.C., Baldan, M.R., Corat, E.J.: Evaluation of residual iron in carbon nanotubes purified by acid treatments. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(2), 641–648 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.07.032
Gong, H., Kim, S.T., Lee, J.D., Yim, S.: Simple quantification of surface carboxylic acids on chemically oxidized multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Appl. Surf. Sci. 266, 219–224 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.11.152
Liu, G., Li, X., Qin, B., Xing, D., Guo, Y., Fan, R.: Investigation of the mending effect and mechanism of copper nano-particles on a tribologically stressed surface. Tribol. Lett. 17, 961–966 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-004-8109-6
Zhang, B.-S., Xu, B.-S., Xu, Y., Gao, F., Shi, P.-J., Wu, Y.-X.: CU nanoparticles effect on the tribological properties of hydrosilicate powders as lubricant additive for steel contacts. Tribol. Int. 44(7–8), 878–886 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2011.03.002
Rapoport, L., Leshchinsky, V., Lvovsky, M., Nepomnyashchy, O., Volovik, Y., Tenne, R.: Mechanism of friction of fullerenes. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 54(4), 171–176 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1108/00368790210431727
Rapoport, L., Nepomnyashchy, O., Lapsker, I., Verdyan, A., Moshkovich, A., Feldman, Y., Tenne, R.: Behavior of fullerene-like WS2 nanoparticles undersevere contact conditions. Wear 259(1–6), 703–707 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wear.2005.01.009
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, R.O.C., under Grant Numbers MOST 109-2221-E-020-019-MY2. The authors also thank to Researchers Supporting Project number (Grant No. #NPUST-KMU-109-P009), NPUST-KMU JOINT RESEARCHPROJECT and the "Intelligent Manufacturing Research Center" (iMRC) from the Featured Areas Research Center Program within the framework of the Higher Education Sprout Project by the Ministry of Education (MOE) in Taiwan, R.O.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, WT., Tsai, JT., Hsu, C.F. et al. Multiple Performance Characteristics in the Application of Taguchi Fuzzy Method in Nanofluid/Ultrasonic Atomization Minimum Quantity Lubrication for Grinding Inconel 718 Alloys. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 24, 294–309 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01135-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01135-5