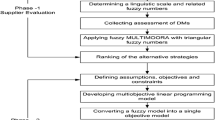
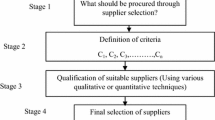
Abstract
One of the serious supply chain management (SCM) challenges is the effective selection of suppliers and the right allocation of orders to achieve an SCM's suitable financial and technical status. This paper introduced a multi-objective linear programming model to prioritize and weigh suppliers using the modified best–worst method (BWM). The proposed model uses evaluation criteria and used fuzzy variables to determine the right numbers of suppliers as well as order quantity of raw materials each supplier should provide. The model has been made up of four objective functions, and the required constraints have been solved using the goal programming method. The proposed model can take a set of opposing goals into account and prioritize the goals to maximize access to each goal. The uncertain concepts such as fuzzy and rough theories in some criteria enabled the proposed model to use the imprecise information in the best possible manner. This study has solved an example using the proposed model through analytic network process and BWM. Then, the obtained results were compared with our findings for adopting interval-valued fuzzy-rough numbers BWM (IVFRN-BWM) and it was shown that the modified BWM approach generates lower costs and better criteria.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 January 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01238-z
References
Gitinavard, H., Ghaderi, H., Pishvaee, M.S.: Green supplier evaluation in manufacturing systems: a novel interval-valued hesitant fuzzy group outranking approach. Soft Comput. 22, 6441–6460 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-017-2697-1
Li, G., Kou, G., Peng, Y.: A group decision making model for integrating heterogeneous information. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 48, 982–992 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2016.2627050
Mousavi, S.M., Foroozesh, N., Zavadskas, E.K., Antucheviciene, J.: A new soft computing approach for green supplier selection problem with interval type-2 trapezoidal fuzzy statistical group decision and avoidance of information loss. Soft Comput. 24, 12313–12327 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-020-04675-4
Duan, L., Ventura, J.A.: A dynamic supplier selection and inventory management model for a serial supply chain with a novel supplier price break scheme and flexible time periods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 272, 979–998 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJOR.2018.07.031
PrasannaVenkatesan, S., Goh, M.: Multi-objective supplier selection and order allocation under disruption risk. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 95, 124–142 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRE.2016.09.005
Liu, P., Hendalianpour, A., Razmi, J., Sangari, M.S.: A solution algorithm for integrated production-inventory-routing of perishable goods with transshipment and uncertain demand. Complex Intell. Syst. 1, 3 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40747-020-00264-y
Hendalianpour, A., Razmi, J., Gheitasi, M.: Comparing clustering models in bank customers: based on fuzzy relational clustering approach. Accounting. 3, 81–94 (2017). https://doi.org/10.5267/j.ac.2016.8.003
Hendalianpour, A.: Optimal lot size and price of perishable goods: a novel game-theoretic model using double interval grey numbers. Comput. Ind. Eng. 149, 106780 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106780
Hendalianpour, A., Razmi, J., Rameshi Sarvestani, A.: Applying decision tree models to SMEs: a statistics-based model for customer relationship management. Manag. Sci. Lett. 509, 520 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5267/j.msl.2016.5.002
Meyer, A., Amberg, B.: Transport concept selection considering supplier milk runs—an integrated model and a case study from the automotive industry. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 113, 147–169 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRE.2017.07.004
Wan, N., Chen, X.: The role of put option contracts in supply chain management under inflation. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 26, 1451–1474 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/itor.12372
Liu, P., Hendalianpour, A., Hamzehlou, M.: Pricing model of two-echelon supply chain for substitutable products based on double-interval grey-numbers. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-201206
Gupta, S., Chatterjee, P., Yazdani, M., Santibanez Gonzalez, E.D.R.: A multi-level programming model for green supplier selection. Manag. Decis. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1108/MD-04-2020-0472
Hendalianpour, A., Razmi, J., Fakhrabadi, M., Kokkinos, K., Papageorgiou, E.I.: A linguistic multi-objective mixed-integer programming model for multi-echelon supply chain network at bio-refinery. EuroMed J. Manag. 2, 329 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1504/emjm.2018.096453
Zailani, S., Jeyaraman, K., Vengadasan, G., Premkumar, R.: Sustainable supply chain management (SSCM) in Malaysia: a survey. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 140, 330–340 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpe.2012.02.008
Amirghodsi, S., Bonyadi Naeini, A., Makui, A.: A dual model for selecting technology and technology transfer method using a combination of the best-worst method (BWM) and goal programing. Sci. Iran. (2020). https://doi.org/10.24200/SCI.2020.53925.3511
Dhouib, D.: An extension of MACBETH method for a fuzzy environment to analyze alternatives in reverse logistics for automobile tire wastes. Omega (United Kingdom). 42, 25–32 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omega.2013.02.003
Zhao, M., Wei, G., Wei, C., Wu, J.: TODIM method for interval-valued pythagorean fuzzy MAGDM based on cumulative prospect theory and its application to green supplier selection. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 46, 1899–1910 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-020-05063-8
Wei, C., Wu, J., Guo, Y., Wei, G.: Green supplier selection based on codas method in probabilistic uncertain linguistic environment. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3846/tede.2021.14078
Mabrouk, N.: Ben: Green supplier selection using fuzzy Delphi method for developing the sustainable supply chain. Decis. Sci. Lett. 10, 63–70 (2020). https://doi.org/10.5267/j.dsl.2020.10.003
Li, X., Ventura, J.A., Venegas, B.B., Kweon, S.J., Hwang, S.W.: An integrated acquisition policy for supplier selection and lot sizing considering total quantity discounts and a quality constraint. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 119, 19–40 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2018.09.003
Cai, Y.J., Choi, T.M.: A United Nations’ sustainable development goals perspective for sustainable textile and apparel supply chain management. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 141, 102010 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tre.2020.102010
Torabi, S.A., Baghersad, M., Mansouri, S.A.: Resilient supplier selection and order allocation under operational and disruption risks. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 79, 22–48 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRE.2015.03.005
Moon, I., Feng, X.: Supply chain coordination with a single supplier and multiple retailers considering customer arrival times and route selection. Transp. Res. Part E Logist. Transp. Rev. 106, 78–97 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRE.2017.08.004
Wu, C.-C., Gupta, J.N.D., Cheng, S.-R., Lin, B.M.T., Yip, S.-H., Lin, W.-C.: Robust scheduling for a two-stage assembly shop with scenario-dependent processing times. Int. J. Prod. Res. 1, 16 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207543.2020.1778208
Pamučar, D., Petrović, I., Ćirović, G.: Modification of the Best-Worst and MABAC methods: a novel approach based on interval-valued fuzzy-rough numbers. Expert Syst. Appl. 91, 89–106 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2017.08.042
Rathi, K., Balamohan, S.: A mathematical model for subjective evaluation of alternatives in fuzzy multi-criteria group decision making using COPRAS method. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 19, 1290–1299 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-016-0256-z
Liu, P., Hendalianpour, A., Hamzehlou, M., Feylizadeh, M.R., Razmi, J.: Identify and rank the challenges of implementing sustainable supply chain blockchain technology using the bayesian best worst method. Technol. Econ. Dev. Econ. (2021). https://doi.org/10.3846/tede.2021.14421
Hendalianpour, A., Fakhrabadi, M., Zhang, X., Feylizadeh, M.R., Gheisari, M., Liu, P., Ashktorab, N.: Hybrid model of IVFRN-BWM and robust goal programming in agile and flexible supply chain, a case study: automobile industry. IEEE Access. 7, 71481–71492 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2915309
Hendalianpour, A., Hamzehlou, M., Feylizadeh, M.R., Xie, N., Shakerizadeh, M.H.: Coordination and competition in a two-echelon supply chain using grey revenue-sharing contracts. Grey Syst. Theory Appl. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1108/GS-04-2020-0056
Hendalianpour, A., Fakhrabadi, M., Sangari, M.S., Razmi, J.: A combined benders decomposition and lagrangian relaxation algorithm for optimizing a multi-product, multi-level omni-channel distribution system. Sci. Iran (2020). https://doi.org/10.24200/sci.2020.53644.3349
Perçin, S.: Use of fuzzy AHP for evaluating the benefits of information-sharing decisions in a supply chain. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 21, 263–284 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1108/17410390810866637
Craighead, C.W., Blackhurst, J., Rungtusanatham, M.J., Handfield, R.B.: The severity of supply chain disruptions: design characteristics and mitigation capabilities. Decis. Sci. 38, 131–156 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5915.2007.00151.x
Deng, X., Jiang, W.: Evaluating green supply chain management practices under fuzzy environment: a novel method based on d number theory. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-019-00639-5
Zhou, Q., Huang, W., Zhang, Y.: Identifying critical success factors in emergency management using a fuzzy DEMATEL method. Saf. Sci. 49, 243–252 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SSCI.2010.08.005
Chen, Y.-H., Wang, T.-C., Wu, C.-Y.: Strategic decisions using the fuzzy PROMETHEE for IS outsourcing. Expert Syst. Appl. 38, 13216–13222 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ESWA.2011.04.137
Hsu, C.-C., Liou, J.J.H.: An outsourcing provider decision model for the airline industry. J. Air Transp. Manag. 28, 40–46 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JAIRTRAMAN.2012.12.009
Routroy, S., Sunil Kumar, C.V.: Analyzing supplier development program enablers using fuzzy DEMATEL. Meas. Bus. Excell. 18, 1–26 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1108/MBE-08-2013-0046
Uygun, Ö., Kaçamak, H., Kahraman, Ü.A.: An integrated DEMATEL and Fuzzy ANP techniques for evaluation and selection of outsourcing provider for a telecommunication company. Comput. Ind. Eng. 86, 137–146 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CIE.2014.09.014
Yu, D., Li, D.-F., Merigó, J.M.: Dual hesitant fuzzy group decision-making method and its application to supplier selection. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 7, 819–831 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-015-0400-3
Lima-Junior, F.R., Carpinetti, L.C.R.: A multicriteria approach based on fuzzy QFD for choosing criteria for supplier selection. Comput. Ind. Eng. 101, 269–285 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CIE.2016.09.014
Ren, J.: Technology selection for ballast water treatment by multi-stakeholders: a multi-attribute decision analysis approach based on the combined weights and extension theory. Chemosphere 191, 747–760 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.053
Rezaei, J., Kothadiya, O., Tavasszy, L., Kroesen, M.: Quality assessment of airline baggage handling systems using SERVQUAL and BWM. Tour. Manag. 66, 85–93 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TOURMAN.2017.11.009
Haeri, S.A.S., Rezaei, J.: A grey-based green supplier selection model for uncertain environments. J. Clean. Prod. 221, 768–784 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.02.193
Wu, L., Chen, Y., Feylizadeh, M.R.: Study on the estimation, decomposition, and application of China’s provincial carbon marginal abatement costs. J. Clean. Prod. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.10.082
Đalić, I., Stević, Ž, Karamasa, C., Puška, A.: A Novel Integrated Fuzzy PIPRECIA–Interval Rough Saw Model: Green Supplier Selection. Decis. Mak. Appl. Manag. Eng. 3, 80–95 (2020). https://doi.org/10.31181/dmame2003114d
Oroojeni Mohammad Javad, M., Darvishi, M., Oroojeni Mohammad Javad, A.: Green supplier selection for the steel industry using BWM and fuzzy TOPSIS: A case study of Khouzestan steel company. Sustain. Futur. 2, 100012 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sftr.2020.100012
Kilic, H.S., Yalcin, A.S.: Modified two-phase fuzzy goal programming integrated with IF-TOPSIS for green supplier selection. Appl. Soft Comput. J. 93, 106371 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106371
Gupta, S., Soni, U., Kumar, G.: Green supplier selection using multi-criterion decision making under fuzzy environment: a case study in the automotive industry. Comput. Ind. Eng. 136, 663–680 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.07.038
Akman, G.: Evaluating suppliers to include green supplier development programs via fuzzy c-means and VIKOR methods. Comput. Ind. Eng. 86, 69–82 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2014.10.013
Demirtas, O.: Evaluating the core capabilities for strategic outsourcing decisions at aviation maintenance industry. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 99, 1134–1143 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SBSPRO.2013.10.587
Kannan, D., Khodaverdi, R., Olfat, L., Jafarian, A., Diabat, A.: Integrated fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making method and multi-objective programming approach for supplier selection and order allocation in a green supply chain. J. Clean. Prod. 47, 355–367 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2013.02.010
Li, D.-F., Wan, S.-P.: Fuzzy linear programming approach to multiattribute decision making with multiple types of attribute values and incomplete weight information. Appl. Soft Comput. 13, 4333–4348 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ASOC.2013.06.019
Pun, H., Sebastian Heese, H.: Outsourcing to suppliers with unknown capabilities. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 234, 108–118 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EJOR.2013.10.068
Li, D.-F.: Notes on “Possibilistic programming approach for fuzzy multidimensional analysis of preference in group decision making.” Comput. Ind. Eng. 73, 1–4 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CIE.2014.04.004
Azadi, M., Jafarian, M., Farzipoor Saen, R., Mirhedayatian, S.M.: A new fuzzy DEA model for evaluation of efficiency and effectiveness of suppliers in sustainable supply chain management context. Comput. Oper. Res. 54, 274–285 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.COR.2014.03.002
Vahidi, F., Torabi, S.A., Ramezankhani, M.J.: Sustainable supplier selection and order allocation under operational and disruption risks. J. Clean. Prod. 174, 1351–1365 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCLEPRO.2017.11.012
Hamdan, S., Cheaitou, A.: Supplier selection and order allocation with green criteria: an MCDM and multi-objective optimization approach. Comput. Oper. Res. 81, 282–304 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cor.2016.11.005
Liu, C., Chen, W., Mu, J.: Retailer’s multi-tier green procurement contract in the presence of suppliers’ reference point effect. Comput. Ind. Eng. 131, 242–258 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2019.03.013
Zhou, F., Chen, T.-Y.: Multiple criteria group decision analysis using a Pythagorean fuzzy programming model for multidimensional analysis of preference based on novel distance measures. Comput. Ind. Eng. 148, 106670 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106670
Wu, Y., Xu, C., Huang, Y., Li, X.: Green supplier selection of electric vehicle charging based on Choquet integral and type-2 fuzzy uncertainty. Soft Comput. 24, 3781–3795 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-019-04147-4
Miranda-Ackerman, M.A., Azzaro-Pantel, C., Aguilar-Lasserre, A.A.: A green supply chain network design framework for the processed food industry: application to the orange juice agro-food cluster. Comput. Ind. Eng. 109, 369–389 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2017.04.031
Sarkar, B., Omair, M., Choi, S.-B.: A multi-objective optimization of energy, economic, and carbon emission in a production model under sustainable supply chain management. Appl. Sci. 8, 1744 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/app8101744
Deveci, M., Özcan, E., John, R., Covrig, C.F., Pamucar, D.: A study on offshore wind farm siting criteria using a novel interval-valued fuzzy-rough based Delphi method. J. Environ. Manag. 270, 110916 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2020.110916
Gorzałczany, M.B.: A method of inference in approximate reasoning based on interval-valued fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 21, 1–17 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1016/0165-0114(87)90148-5
Gao, H., Ran, L., Wei, G., Wei, C., Wu, J.: Vikor method for MAGDM based on Q-rung interval-years, given the advantages of considering the compromise between and its application to supplier selection of medical consumption products. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 17, 525 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17020525
Wan, S., Dong, J., Chen, S.-M.: Fuzzy best-worst method based on generalized interval-valued trapezoidal fuzzy numbers for multi-criteria decision-making. Inf. Sci. (NY). (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.03.038
Ali, A., Rashid, T.: Hesitant fuzzy best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method and its applications. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 34, 1953–1967 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/int.22131
Guo, S., Zhao, H.: Fuzzy best-worst multi-criteria decision-making method and its applications. Knowledge-Based Syst. 121, 23–31 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2017.01.010
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, P., Hendalianpour, A., Fakhrabadi, M. et al. Integrating IVFRN-BWM and Goal Programming to Allocate the Order Quantity Considering Discount for Green Supplier. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 24, 989–1011 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01181-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01181-z