Abstract
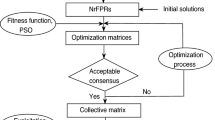
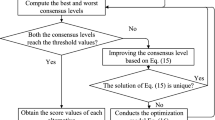
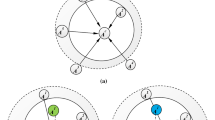
In group decision-making (GDM) problems, the elicitation of preferences from decision makers (DMs) and consensus reaching process are two critical issues to be resolved. Many kinds of preference relations have been proposed in the recent two decades. In this paper, we propose a novel pairwise comparison structure called fuzzy-uncertainty-based distributed preference relation (FUDPR), which could not only indicate the intensity of preferred, non-preferred, indifferent and uncertain information of one alternative against another simultaneously, but also has the ability to represent local ignorance expressed by DMs. The FUDPR introduces the set of consecutive evaluation grades into the distributed preference relation (DPR) where only discrete single evaluation grades and global ignorance can be modeled in the preference relation. The missing values in FUDPR are estimated by the defined score function. Two kinds of consensus reaching process (CRP) are then proposed, namely soft and hard consensus mechanism, respectively, which are suitable for different decision-making situations. Both of them consider the individual dissimilarity, trust relations and self-confidence in the designed feedback mechanism. Comparative analysis is performed between the proposed method and other state-of-the-art pairwise comparison GDM models. An illustrative example of life cycle sustainability assessment (LCSA) is proposed to demonstrate the rationality and effectiveness of the proposed method in supporting real-world GDM problems.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Beg, I., Syed, A.: An interactive fuzzy judgment aggregation model for consensus with partially undecided judges. J. Fuzzy Math. 26(4), 809–815 (2016)
Chen, T.Y.: Multiple criteria decision analysis using a likelihood-based outranking method based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Inf. Sci. 286, 188–208 (2014)
Chiclana, F., Herrera, F., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Integrating multiplicative preference relations in a multipurpose decision making model based on fuzzy preference relations. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 122(2), 277–291 (2001)
Cao, M.S., Wu, J., Chiclana, F., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A bidirectional feedback mechanism for balancing group consensus and individual harmony in group decision making. Inform. Fusion 76, 133–144 (2021)
Deng, Y.: Uncertainty measure in evidence theory. Sci. China Inform. Sci. 63(11), 210201 (2020)
Deng, Y.: Information volume of mass function. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 15(6), 3983 (2020)
Dong, Y., Wu, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, G.: Multi-granular unbalanced linguistic distribution assessments with interval symbolic proportions. Knowl. Based Syst. 82, 139–151 (2015)
Dong, Y.C., Zha, Q.B., Zhang, H.J., Herrera, F.: Consensus reaching and strategic manipulation in group decision making with trust relationships. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 51(10), 6304–6318 (2021)
Fu, C., Chang, W.J., Xue, M., Yang, S.L.: Multiple criteria group decision making with belief distributions and distributed preference relations. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 273(2), 623–633 (2019)
Fu, C., Xu, D.L., Yang, S.L.: Distributed preference relations for multiple attribute decision analysis. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 67(3), 457–473 (2016)
Gao, J., Yao, Y.L., Zhu, V.C.Y., Sun, L.Y., Lin, L.: Service-oriented manufacturing: a new product pattern and manufacturing paradigm. J. Intell. Manuf. 22(3), 435–436 (2011)
Herrera-Viedma, E., Martinez, L., Mata, F., Chiclana, F.: A consensus support system model for group decision-making problems with multigranular linguistic preference relations. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 13(5), 644–658 (2005)
Liang, Q., Liao, X.W., Liu, J.P.: A social ties-based approach for group decision-making problems with incomplete additive preference relations. Knowl. Based Syst. 119, 68–86 (2017)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J.: Distance and similarity measures for hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and their application in multi-criteria decision making. Inf. Sci. 271, 125–142 (2014)
Liao, H.C., Xu, Z.S., Zeng, X.J., Xu, D.L.: An enhanced consensus reaching process in group decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations. Inf. Sci. 329, 274–286 (2016)
Liu, X., Xu, Y.J., Montes, R., Herrera, F.: Social network group decision making: Managing self-confidence-based consensus model with the dynamic importance degree of experts and trust-based feedback mechanism. Inf. Sci. 505, 215–232 (2019)
Liu, Y.J., Liang, C.Y., Chiclana, F., Wu, J.: A trust induced recommendation mechanism for reaching consensus in group decision making. Knowl. Based Syst. 119, 221–231 (2017)
Miao, R., Cao, J.T., Zhang, K., Chen, B.X., Jiang, Z.B., Wang, L.Y.: Value-added path of service-oriented manufacturing based on structural equation model: the case of electric car rental for instance. Int. J. Prod. Res. 52(18), 5502–5513 (2014)
Miller, M.: Judgment aggregation and subjective decision making. Econ. Philos. 24, 205–231 (2008)
Onat, N.C., Kucukvar, M., Tatari, O.: Towards life cycle sustainability assessment of alternative passenger vehicles. Sustainability 6(12), 9305–9342 (2014)
Sun, Q., Wu, J., Chiclana, F., Fujita, H., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A dynamic feedback mechanism with attitudinal consensus threshold for minimum adjustment cost in group decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2021.3057705
Szmidt, E., Kacprzyk, J.: A consensus-reaching process under intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 18(7), 837–852 (2003)
Wang, S.Y., Chang, S.L., Wang, R.C.: Assessment of supplier performance based on product-development strategy by applying multi-granularity linguistic term sets. Omega 37(1), 215–226 (2009)
Wang, S., Wu, J., Chiclana, F., Sun, Q., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Two stage feedback mechanism with different power structures for consensus in large-scale group decision-making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2022.3144536
Wu, J., Wang, S., Chiclana, F., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Twofold personalized feedback mechanism for social network consensus by uninorm interval trust propagation. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2021.3076420
Wu, J., Sun, Q., Fujita, H., Chiclana, F.: An attitudinal consensus degree to control the feedback mechanism in group decision making with different adjustment cost. Knowl. Based Syst. 164, 265–273 (2019)
Wu, J., Zhao, Z.W., Sun, Q., Fujita, H.: A maximum self-esteem degree based feedback mechanism for group consensus reaching with the distributed linguistic trust propagation in social network. Inf. Fusion 67, 80–93 (2021)
Wu, Z.B., Xu, J.P.: Managing consistency and consensus in group decision making with hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations. Omega 65, 28–40 (2016)
Xiao, F.: CaFtR: A fuzzy complex event processing method. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-40021-01118-40816
Xiao, F.: CEQD: a complex mass function to predict interference effects. IEEE Trans. Cybern. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2020.3040770
Xu, D.L., Yang, J.B., Wang, Y.M.: The evidential reasoning approach for multi-attribute decision analysis under interval uncertainty. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 174(3), 1914–1943 (2006)
Xu, Z.S., Yager, R.R.: Intuitionistic and interval-valued intutionistic fuzzy preference relations and their measures of similarity for the evaluation of agreement within a group. Fuzzy Optim. Decis. Making 8(2), 123–139 (2009)
Xue, W.T., Xu, Z.S., Wang, H., Ren, Z.L.: Hazard assessment of landslide dams using the evidential reasoning algorithm with multi-scale hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Appl. Soft Comput. 79, 74–86 (2019)
Yang, J.B., Xu, D.L.: On the evidential reasoning algorithm for multiple attribute decision analysis under uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part A 32(3), 289–304 (2002)
Zhang, G.Q., Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F.: Consistency and consensus measures for linguistic preference relations based on distribution assessments. Inf. Fusion 17, 46–55 (2014)
Zhang, Q., Fan, Z.P., Pan, D.H.: A ranking approach for interval numbers in uncertain multiple attribute decision making problems. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 19(5), 129–133 (1999)
Zhang, Y.X., Xu, Z.S., Wang, H., Liao, H.C.: Consistency-based risk assessment with probabilistic linguistic preference relation. Appl. Soft Comput. 49, 817–833 (2016)
Zhang, Z.M., Pedrycz, W.: Goal programming approaches to managing consistency and consensus for intuitionistic multiplicative preference relations in group decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26(6), 3261–3275 (2018)
Zhou, M., Chen, Y.W., Liu, X.B., Cheng, B.Y., Yang, J.B.: Weight assignment method for multiple attribute decision making with dissimilarity and conflict of belief distributions. Comput. Ind. Eng. 147, 106648 (2020)
Zhou, M., Liu, X.B., Chen, Y.W., Qian, X.F., Yang, J.B., Wu, J.: Assignment of attribute weights with belief distributions for MADM under uncertainties. Knowl. Based Syst. 189, 105110 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Grant Nos. 72071056, 72101077, 71571166 and 71971135, NSFC-Zhejiang Joint Fund for the Integration of Industrialization and Informatization under the Grant No. U1709215, Innovative Research Groups of the National Natural Science Foundation of China under the Grant No. 71521001.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, 72071056, Mi Zhou, 72101077, Zhi-Ping Zhou, 71571166, Jian Wu, 71971135, Jian Wu, NSFC-Zhejiang Joint Fund for the Integration of Industrialization and Informatization, U1709215, Innovative Research Group Project of the National Natural Science Foundation of China, 71521001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendices
Appendix
Proof of Theorem 2
Given a FUDPR such that \({r}_{ij}^{t}=\left\{\left({H}_{mn},{\beta }_{ij}^{t}\left({H}_{mn}\right)\right). m,n=\mathrm{1,2},\ldots ,N;m\le n\right\}\). The following two situations may occur.
(1) When \(m<n\), \({\beta }_{ij}^{t}\left({H}_{mn}\right)\) signifies the belief degree of local ignorance, so it can be assigned to any grade between \({H}_{m}\) and \({H}_{n}\). Suppose that it’s assigned to \({H}_{\xi }(m\le \xi \le n,\xi \in \{\mathrm{1,2},\ldots ,N\})\), the score of \({H}_{mn}\) will satisfy the following condition:
Then
(2) When \(m=n\), we have
Then
Combining the above two situations, the following conclusions can be drawn:
Proof of Theorem 3
According to Definition 5, it can be concluded that
From Property 2, we have
And Remark 1 indicates that
As for \({H}_{mn}\), when \(m=n\), \({H}_{mn}\) represents a single grade \({H}_{m}\) or \({H}_{n}\), so it can be inferred that
Then we can conclude that
For any \({\beta }_{ij}^{t}({H}_{mn}) \cdot s({H}_{m})\) in \({r}_{ij}^{t}\), there’s always \(-{\beta }_{ji}^{t}({H}_{\left(N-n+1\right)\left(N-m+1\right)})\cdot s\left({H}_{N-m+1}\right)\) in \({r}_{ji}^{t}\) that corresponds to it, so we have
Then
So the following conclusion can be drawn:
Thus, we have
Similarly, we can prove that \({{s}_{ij}^{t}}^{-}+{{s}_{ji}^{t}}^{+}=0\).
Proof of Property 4
Given the preference relations of \({DM}_{t}\) and \({DM}_{{t}^{^{\prime}}}\) such that \({r}_{i(i+1)}^{t}=\left\{{H}_{11},1\right\}\) and \({r}_{i(i+1)}^{{t}^{^{\prime}}}=\left\{{H}_{NN},1\right\}\) respectively. The distributed dissimilarity between the two DMs is:
According to Definition 9, we have:
Similarly, when \({r}_{i(i+1)}^{t}=\left\{{H}_{NN},1\right\}\) and \({r}_{i(i+1)}^{{t}^{^{\prime}}}=\left\{{H}_{11},1\right\}\), we also have \({AD}_{i(i+1)}^{t{t}^{^{\prime}}}=1\).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, M., Li, JL., Chen, YW. et al. Consensus Reaching Process for Group Decision Making with Distributed Preference Relations Under Fuzzy Uncertainty. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 24, 2363–2381 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01280-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01280-5