Abstract
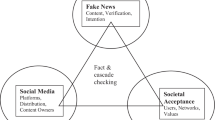
Haze Internet rumors have caused a serious negative impact on people's daily life and social stability in recent years. Therefore, this paper proposes a new approach to identify and assess the Internet rumors by intuitionistic fuzzy linguistic set and Choquet integrals method. First, non-additive measures and Choquet integrals calculating the comprehensive assessments of Internet public opinion are applied to incorporate the interaction between attributes. Then, the attribute weight is determined by the generalized Shapley function. In addition, an example of haze network public opinion risk shows that the approach has good identification and assessment effect. The approach can be used to solve the problems of fuzziness and subjectivity in linguistic assessments, and it can be applied to identify the customer service framework with the linguistic assessments process in emergency management. From the results, it infers that the haze network public opinion risk is directly related to haze incidents, while the role of media and Internet users can only indirectly affect the public opinion dissemination.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fu, H., Chen, J.: Formation, features and controlling strategies of severe haze-fog pollutions in China. Sci Total Environ. 578, 121–138 (2017)
Zhang, Y., et al.: Research on the index system of public opinion on the Internet for abnormal emergency. J. Intell. (in Chinese). 29(11), 71–75 (2010)
Wu, J., Cao, Q.-W.: Same families of geometric aggregation operators with intuitionistic trapezoidal fuzzy numbers. Appl. Math. Model. 37(1–2), 318–327 (2013)
He, H., Patnaik, S.: Research on prediction of internet public opinion based on grey system theory and fuzzy neural network. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 35(1), 325–332 (2018)
Wu, W., et al.: Does the public haze pollution concern expressed on online platforms promoted pollution control? Evidence from Chinese online platforms. J. Clean. Prod. 318, 128477 (2021)
Bao, Q., et al.: Research on Public Environmental Perception of Emotion, Taking Haze as an Example. Int. J. Environ. Res. 18(22), 12115 (2021)
Chen, L., et al.: Agenda-setting on traditional vs social media: An analysis of haze-related content grounded in the extended parallel process model. Internet Res. (2019).
Shan, S., et al.: Analysis of the key influencing factors of haze information dissemination behavior and motivation in WeChat. Inform. Discov. (2017).
Li, C., et al.: Does public concern over haze pollution matter? Evidence from Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region China. Sci Total Environ. 755, 142397 (2021)
Hu, L., Dong, J.: The participators behavior simulation and the government guidance in the progress of web public opinion evolution. Chin. Soft. Sci. (in chinese). 10, 50–61 (2016)
Li, Q., et al.: Spatial characteristics and influencing factors of risk perception of haze in China: The case study of publishing online comments about haze news on Sina. Sci. Total Environ. 785, 147236 (2021)
Ma, X., et al.: Evolution of online public opinion during meteorological disasters. Environ. Hazards 19(4), 375–397 (2020)
Xu, S., et al.: Can public participation in haze governance be guided by government? Evidence from large-scale social media content data mining. J. Clean. Product. 318, 128401 (2021)
Huo, L.A., Ma, C.: The interaction evolution model of mass incidents with delay in a social network. Physica A 484, 440–452 (2017)
Wei, D., Chen, F., Zheng, X.: Internet public opinion chaotic prediction based on chaos theory and the improved radial basis function in neural networks. Acta Physica Sinica. 64(11), 110503 (2015)
Yang, C.C., Dorbin, T.: Ng: analyzing and visualizing web opinion development and social interactions with density-based clustering. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part A 41(6), 1144–1155 (2011)
Huang, W., Wang, Q., Cao, J.: Tracing public opinion propagation and emotional evolution based on public emergencies in social networks. Int. J. Comput. Commun. Control 13(1), 129–142 (2018)
Lingfeng, D., et al.: Continuous content contribution in virtual community: The role of status-standing on motivational mechanisms. Decis. Support Syst. 132, 15 (2020)
Zhang, W., He, H., Cao, B.: Identifying and evaluating the internet opinion leader community based on k-clique clustering. Neural Comput. Appl. 25(3–4), 595–602 (2013)
Wu, X., et al.: Finding of urban rainstorm and waterlogging disasters based on microblogging data and the location-routing problem model of urban emergency logistics. Ann. Oper. Res. 258, 221–258 (2018)
Zhang, Y.-X., Feng, Y.-X., Yang, R.-Q.: Network public opinion propagation model based on the influence of media and interpersonal communication. Int. J. Modern Phys. B 33(32), 1950393 (2020)
Shi, B.: A study of the intrinsic evolution mechanism for network sentiment of public crisis events. J. Intell. (in Chinese). 29(4), 41–45 (2010)
Li, Z., Xing, Y.: Research on the evolution of emergency public opinion topic in the new media environment: a case of “Jiuzhaigou Earthquake” in Sina Micro-blog. Information Science (in Chinese) 35(12), 39–44 (2017)
Yi, C.: Analysis on the Changing mechanism of mass emergency network public opinion. J. Intell. (in Chinese). 30(12), 6–12 (2011)
Du, Y., et al.: Extracting and tracking hot topics of micro-blogs based on improved Latent Dirichlet Allocation. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 87, 103279 (2020)
Liu, J.: Study on evolutionary pathways of microblog public opinion from the perspective of crisis communication. J. Intell. (in Chinese). 31(7), 21–24 (2012)
Mei, Y., et al.: Internet public opinion risk grading under emergency event based on AHPSort II-DEMATEL. Sustainability. 11(16), 4440 (2019)
Wu, X., Li, X.: Effects of mass media exposure and social network site involvement on risk perception of and precautionary behavior toward the haze issue in China. Int. J. Commun. 11, 3975–3997 (2017)
Jia, F., Chen, C.-C.: Emotional characteristics and time series analysis of Internet public opinion participants based on emotional feature words. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 17(1), 172988142090421 (2020)
Xu, Z., Zhao, N.: Information fusion for intuitionistic fuzzy decision making: an overview. Inform. Fusion. 28, 10–23 (2016)
Atanassov, K.T.: Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 20, 87–96 (1986)
Zadeh, L.A.: Fuzzy sets. Inf. Control 8(3), 338–353 (1965)
Sugeno, M.: Theory of fuzzy integral and its applications. Doctoral Thesis Tokyo Institute of Technology (1974).
Wang, Z., Klir, G.J.: Fuzzy measure theory. Verlag US, Springer (1992)
Wei, G.: Some arithmetic aggregation operators with intuitionistic trapezoidal fuzzy numbers and their application to group decision making. J. Comput. 5(3), 345–351 (2010)
Wang, J., Zhong, Z.: Aggregation operators on intuitionistic trapezoidal fuzzy number and its application to multi-criteria decision making problems. Syst. Eng. Theory Pract. 20(2), 321–326 (2009)
Tan, C., Chen, X.: Intuitionistic fuzzy Choquet integral operator for multi-criteria decision making☆. Expert Syst. Appl. 37(1), 149–157 (2010)
Xu, Z.: Choquet integrals of weighted intuitionistic fuzzy information. Inf. Sci. 180(5), 726–736 (2010)
Tan, C.: Generalized intuitionistic fuzzy geometric aggregation operator and its application to multi-criteria group decision making. Soft. Comput. 15(5), 867–876 (2010)
Tan, C.: A multi-criteria interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy group decision making with Choquet integral-based TOPSIS. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(4), 3023–3033 (2011)
Wang, J., Nie, R.: Interdependent multi-criteria intuitionistic fuzzy decision-making approach. Control Decis. 26(9), 1348–1352 (2011)
Wan, S., Dong, J.: Multi-attribute decision making based on triangular intuitionistic fuzzy number choquet integral operator. Chin.J. Manage. Sci. 22(3), 121–129 (2014)
Meng, F., Zhang, Q., Cheng, H.: Approaches to multiple-criteria group decision making based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy Choquet integral with respect to the generalized λ-Shapley index. Knowl.-Based Syst. 37, 237–249 (2013)
Meng, F., Wang, C., Zhang, Y.: Approach to project investment projects based on the generalized-shapley choquet integral. Oper. Res. Manage. Sci. 25(3), 186–194 (2016)
Zhang, L., Meng, F.: An approach to interval-valued hesitant fuzzy multiattribute group decision making based on the generalized shapley-choquet integral. Complexity 2018, 1–19 (2018)
Meng, F., Tang, J.: Interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multiattribute group decision making based on cross entropy measure and choquet integral. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 28(12), 1172–1195 (2013)
Büyüközkan, G., Feyzioğlu, O., Göçer, F.: Selection of sustainable urban transportation alternatives using an integrated intuitionistic fuzzy Choquet integral approach. Transp. Res. Part D 58, 186–207 (2018)
Xu, Z., Yager, R.R.: Some geometric aggregation operators based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Int. J. Gen Syst 35(4), 417–433 (2006)
Chen, S.M., Tan, J.M.: Handling multicriteria fuzzy decision-making problems based on vague set theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 67(2), 163–172 (1994)
Hong, D.H., Choi, C.H.: Multicriteria fuzzy decision-making problems based on vague set theory. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 114(1), 103–113 (2000)
Choquet, G.: Theory of capacities. Ann. Inst. Fourier. 5, 131–295 (1954)
Shapley, L.: A value for n-person games. Princet. Univ. Press 7, 27–34 (1953)
Merigo, J., Gillafuente, A.: The induced generalized OWA operator. Inf. Sci. 179(6), 729–741 (2009)
Huang, X., Liu, L.: The evaluation method and application of unexpected events network public opinion. Inform. Sci. (in Chinese). 36(4), 3–9 (2018)
Xia, L., et al.: Research on evolution of public opinion in the network based on chain of events. Inform Stud. 17, 9235 (2019)
Yager, R.R.: On ordered weighted averaging aggregation operators in multicriteria decisionmaking. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybernet. 18, 183–190 (1988)
Marichal, J.L.: An axiomatic approach of the discrete Choquet integral as a tool to aggregate interacting criteria. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 8(6), 800–807 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by Humanities and social sciences research project of the Ministry of Education (20YJAZH096), and in part by the China Scholarship Council under Grant <202008320538, 202109040034>, Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX21_1035); Meteorological soft science project of China (2022zzxm24).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, B., Zheng, C., Wei, G. et al. Risk Assessment Method on Haze Networks Public Opinion Based on Intuitionistic Fuzzy Choquet Integral. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 24, 2858–2872 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01300-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01300-4