Abstract
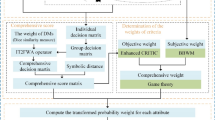
In the context of the increasingly competitive post-epidemic social marketing era, the sustainable development of supply chain finance is also facing the impact of more complex risk factors. However, the issue concerning how to scientifically and reasonably select the appropriate applicant company for financing cooperation on the basis of risk evaluation remains unresolved. For the smooth operation of banks’ sustainable supply chain finance (SSCF) business, this paper aims to develop a novel multi-attribute group decision-making (MAGDM) method considering the robustness and comprehensiveness among risk attributes and decision-makers (DMs). First, based on the idea that quantitative assessment values and qualitative linguistic sets can more accurately express uncertain risk information and importance degree of indicators, a novel concept is proposed that combines the probabilistic linguistic term set (PLTS) with the plithogenic set to evaluate the risk attributes of each alternative. Additionally, risk decision matrices evaluated by DMs are integrated and transformed through the operation of PLTS scoring function aggregation operators and the plithogenic contradiction degree. For deriving the integrated weight information of attributes, the objective attribute weights are determined on the basis of the subjective weights by adjusting coefficients. Then, the ranking order of alternatives is generated by applying the VIKOR method and constructing a MAGDM model with plithogenic PLTSs. Finally, the solving of a practical example concerning the selection of financing objects for SSCF oriented by risk evaluation verifies the effectiveness of the proposed model, where five risk indicators are developed, and the superiority of our studies is demonstrated by comparing with the existing TOPSIS and ELECTRE methods.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Moretto, A., Caniato, F.: Can Supply Chain Finance help mitigate the financial disruption brought by Covid-19. J. Purch. Supply Manag. 27, 100713 (2021)
Gupta, N., Soni, G.: A decision-making framework for sustainable supply chain finance in post-COVID era. Int. J. Glob. Bus. Compet. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42943-021-00028-6
Tseng, M.L., Lim, M.K., Wu, K.J.: Improving the benefits and costs on sustainable supply chain finance under uncertainty. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 218, 308–321 (2019)
Haimes, Y.Y.: On the complex definition of risk: a systems-based approach. Risk. Anal. 29, 1647–1654 (2019)
Tseng, M.L., Bui, T.D., Lim, M.K., Tsai, F.M., Tan, R.R.: Comparing world regional sustainable supply chain finance using big data analytics: a bibliometric analysis. Ind. Manag. Data. Syst. 121, 657–770 (2021)
Su, Y., Zhao, M., Wei, C., Chen, X.: PT-TODIM method for probabilistic linguistic MAGDM and application to industrial control system security supplier selection. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-021-01125-7
Yue, Z.: A method for group decision-making based on determining weights of decision makers using TOPSIS. Appl. Math. Model. 35, 1926–1936 (2011)
Wan, S.P., Jin, Z., Dong, J.Y.: Pythagorean fuzzy mathematical programming method for multi-attribute group decision making with Pythagorean fuzzy truth degrees. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 55, 437–466 (2018)
Zadeh, L.A.: A fuzzy-set-theoretic interpretation of linguistic hedges. J. Cybern. 2, 4–34 (1972)
Turksen, I.B.: Interval valued fuzzy sets based on normal forms. Fuzzy. Set. Syst. 20, 191–210 (1986)
Takeuti, G., Titani, S.: Intuitionistic fuzzy logic and intuitionistic fuzzy set theory. J. Symb. Log. 49, 851–866 (1984)
Smarandache, F.: A unifying field in logics: neutrosophic logic. In: Philosophy, pp. 1–141. American Research Press (1999)
Smarandache, F.: Plithogenic set, an extension of crisp, fuzzy, intuitionistic fuzzy, and neutrosophic sets-revisited. Infinite Study 21, 153–166 (2018)
Abdel-Basset, M., El-Hoseny, M., Gamal, A., Smarandache, F.: A novel model for evaluation Hospital medical care systems based on plithogenic sets. Artif. Intell. Med. 100, 1–8 (2019)
Sankari, H., Abobala, M.: n-Refined neutrosophic modules. Infinite Study 36, 1–11 (2020)
Abdel-Basset, M., Mohamed, R., Smarandache, F., Elhoseny, M.: A new decision-making model based on plithogenic set for supplier selection. Cmc-Comput. Mater. Continua 66, 2751–2769 (2021)
Wu, Z., Xu, J.: Possibility distribution-based approach for MAGDM with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. IEEE. T. Cybern. 46, 694–705 (2015)
Xu, Z., Wang, H.: On the syntax and semantics of virtual linguistic terms for information fusion in decision making. Inform. Fusion. 34, 43–48 (2017)
Zadeh, L.A.: The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inform. Sci. 8, 199–249 (1975)
Herrera, F., Martínez, L.: A 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic representation model for computing with words. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. 8, 746–752 (2000)
Ye, J.M., Xu, Z., Gou, X.J.: Virtual linguistic trust degree-based evidential reasoning approach and its application to emergency response assessment of railway station. Inform. Sci. 513, 341–359 (2020)
Wei, G., Lu, M., Alsaadi, F.E., Hayat, T., Alsaedi, A.: Pythagorean 2-tuple linguistic aggregation operators in multiple attribute decision making. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 33, 1129–1142 (2017)
Rodriguez, R.M., Martinez, L., Herrera, F.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy. Syst. 20, 109–119 (2011)
Torra, V.: Hesitant fuzzy sets. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 25, 529–539 (2010)
Pang, Q., Wang, H., Xu, Z.: Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Inform. Sci. 369, 128–143 (2016)
Zhang, Y., Xu, Z., Wang, H., Liao, H.: Consistency-based risk assessment with probabilistic linguistic preference relation. Appl. Soft. Comput. 49, 817–833 (2016)
Gou, X., Xu, Z.: Novel basic operational laws for linguistic terms, hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets and probabilistic linguistic term sets. Inform. Sci. 372, 407–427 (2016)
Zhang, X.L., Xing, X.M.: Probabilistic linguistic VIKOR method to evaluate green supply chain initiatives. Sustainability Basel 9, 1231 (2017)
Zhai, Y., Xu, Z., Liao, H.: Probabilistic linguistic vector-term set and its application in group decision making with multi-granular linguistic information. Appl. Soft. Comput. 49, 801–816 (2016)
Wu, X., Liao, H., Xu, Z., Hafezalkotob, A., Herrera, F.: Probabilistic linguistic MULTIMOORA: a multicriteria decision making method based on the probabilistic linguistic expectation function and the improved Borda rule. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 26, 3688–3702 (2018)
Wei, G., Wei, C., Wu, J., Guo, Y.: Probabilistic linguistic multiple attribute group decision making for location planning of electric vehicle charging stations based on the generalized Dice similarity measures. Artif. Intell. Rev. 54, 4137–4167 (2021)
Zhang, X., Gou, X., Xu, Z., Liao, H.: A projection method for multiple attribute group decision making with probabilistic linguistic term sets. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cyb. 10, 2515–2528 (2019)
Lu, J., Wei, C., Wu, J., Wei, G.: TOPSIS method for probabilistic linguistic MAGDM with entropy weight and its application to supplier selection of new agricultural machinery products. Entropy-Switz. 21, 953 (2019)
Zhang, Z., Wu, C.: A novel method for single-valued neutrosophic multi-criteria decision making with incomplete weight information. Neutrosophic Sets Syst. 4, 35–49 (2014)
Gou, X., Xu, Z., Liao, H.: Multiple criteria decision making based on Bonferroni means with hesitant fuzzy linguistic information. Soft. Comput. 21, 6515–6529 (2017)
Chang, T.W., Lo, H.W., Chen, K.Y., Liou, J.J.: A novel FMEA model based on rough BWM and rough TOPSIS-AL for risk assessment. Mathematics Basel 7, 874–894 (2019)
Davoudabadi, R., Mousavi, S.M., Mohagheghi, V.: A new last aggregation method of multi-attributes group decision making based on concepts of TODIM, WASPAS and TOPSIS under interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy uncertainty. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 62, 1371–1391 (2020)
Pang, J., Guan, X., Liang, J., Wang, B., Song, P.: Multi-attribute group decision-making method based on multi-granulation weights and three-way decisions. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 117, 122–147 (2020)
Shyur, H.-J.: COTS evaluation using modified TOPSIS and ANP. Appl. Math. Comput. 177, 251–259 (2005)
Qin, J.D., Liu, X.W., Pedrycz, W.: An extended VIKOR method based on prospect theory for multiple attribute decision making under interval type-2 fuzzy environment. Knowl.-Based. Syst. 86, 116–130 (2015)
Gul, M., Celik, E., Aydin, N., Gumus, A.T., Guneri, A.F.: A state of the art literature review of vikor and its fuzzy extensions on applications. Appl. Soft. Comput. 46, 60–89 (2016)
Peng, X.D., Dai, J.G.: Approaches to single-valued neutrosophic MADM based on MABAC, TOPSIS and new similarity measure with score function. Neural. Comput. Appl. 29, 939–954 (2018)
Opricovic, S., Tzeng, G.H.: Extended VIKOR method in comparison with outranking methods. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 178, 514–529 (2017)
Tavana, M., Di Caprio, D., Santos-Arteaga, F.J.: An extended stochastic VIKOR model with decision maker’s attitude towards risk. Inf. Sci. 432, 301–318 (2018)
Chatterjee, K., Samarjit, K.: Unified Granular-number-based AHP-VIKOR multi-criteria decision framework. Granul. Comput. 2, 199–221 (2017)
Zhou, W., Yin, W.Y., Peng, X.Q., Liu, F.M., Yang, F.: Comprehensive evaluation of land reclamation and utilisation schemes based on a modified VIKOR method for surface mines. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 32, 93–108 (2018)
Lin, M., Chen, Z., Xu, Z., Gou, X., Herrera, F.: Score function based on concentration degree for probabilistic linguistic term sets: an application to TOPSIS and VIKOR. Inform. Sci. 551, 270–290 (2021)
Li, Y., Liu, Y.S.: Extended VIKOR-QUALIFLEX method based on trapezoidal fuzzy two-dimensional linguistic information for multiple attribute decision-making with unknown attribute weight. Mathematics-Basel. 9, 37–63 (2020)
Abdel-Basset, M., Mohamed, R., Elhoseny, M., Chang, V.: Evaluation framework for smart disaster response systems in uncertainty environment. Mech. Syst. Signal. Pr. 145, 1–18 (2020)
Gou, X., Xu, Z., Liao, H., Herrera, F.: Probabilistic double hierarchy linguistic term set and its use in designing an improved VIKOR method: the application in smart healthcare. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 72, 2611–2630 (2021)
Liu, P., You, X.: Probabilistic linguistic TODIM approach for multiple attribute decision-making. Granul. Comput. 2, 333–342 (2017)
Wei, G., Wei, C., Wu, J., Wang, H.: Supplier selection of medical consumption products with a probabilistic linguistic MABAC method. Int. J. Env. Res. Pub. He. 16, 5082 (2019)
Opricovic, S., Tzeng, G.H.: Compromise solution by MCDM methods: a comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 156, 445–455 (2014)
Lei, F., Wei, G., Gao, H., Wu, J., Wei, C.: TOPSIS method for developing supplier selection with probabilistic linguistic information. Int. J. Fuzzy. Syst. 22, 749–759 (2020)
Xu, Z.: Deviation measures of linguistic preference relations in group decision making. Omega 33, 249–254 (2005)
Wang, Z.P., Peng, Z.W., Wang, H.C.: Research on probabilistic linguistic multi-attribute group decision making method based on improved possibility degree and distance measure. J. Math. Pract. Theory 11, 10–20 (2021)
Shen, L.L., Pang, X.D., Zhang, Q., Qian, G.: TODIM method based on probabilistic language term set and its application. J. Stat. Decis. 18, 80–83 (2019)
Chen, Z.S., Chin, K.S., Li, Y.L., Yang, Y.: Proportional hesitant fuzzy linguistic term set for multiple criteria group decision making. Inform. Sci. 357, 61–87 (2016)
Abdel-Basset, M., Mohamed, R.: A novel plithogenic TOPSIS- CRITIC model for sustainable supply chain risk management. J. Clean. Prod. 247, 119586 (2020)
Mao, X.B., Wu, M., Dong, J.Y., Wan, S.P., Jin, Z.: A new method for probabilistic linguistic multi-attribute group decision making: application to the selection of financial technologies. Appl. Soft. Comput. 77, 155–175 (2019)
Liao, H.C., Jiang, L.S., Lev, B., Fujita, H.: Novel operations of PLTSs based on the disparity degrees of linguistic terms and their use in designing the probabilistic linguistic ELECTRE III method. Appl. Soft. Comput. 80, 450–464 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant No. 3132019353.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YL was responsible for the analysis and preparation of the manuscript; ZW and MF contributed to the structure and main idea of the article, the revision of the full text; and PW performed the data processing and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Lin, Y., Fu, M. et al. VIKOR Method for Plithogenic Probabilistic Linguistic MAGDM and Application to Sustainable Supply Chain Financial Risk Evaluation. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 25, 780–793 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01401-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01401-0