Abstract
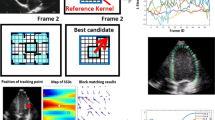
Echocardiographic strain imaging is used to quantify cardiac deformation noninvasively through various techniques including non-rigid image registration. However, non-rigid image registration should be strong enough to deal with the poor spatiotemporal resolution of echocardiographic images. Extracting relevant features and calculating a suitable geometric transformation for the relevant features are the main parts of a registration problem. This paper aims to introduce a suitable geometric transformation for quantifying cardiac deformation based on a modified fuzzy inference system (FIS). The proposed method extracts relevant features of two echocardiographic images to generate proper rules for registration of two echocardiographic images. The modified FIS comprises two FISs in a series structure. We evaluated the performance of the proposed method for echocardiographic motion estimation with both in silico and in vivo databases. Applying the proposed method to the well-known STRAUS database resulted in 0.68 mm tracking error and 0.5 ± 3.78 relative circumferential strain error, which indicate the competitiveness of the proposed method with the state-of-the-art algorithms. In addition, the obtained results from in vivo database, CETUS, expressed the potential of the suggested algorithm for clinical application.









Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Data availability
STRAUS database link: https://team.inria.fr/epione/en/data/straus/. CETUS database link: https://www.creatis.insa-lyon.fr/EvaluationPlatform/CETUS/
Notes
SIFT- Modefied Feature-based Fuzzy Registration.
References
Crosby, J., Amundsen, B.H., Hergum, T., Remme, E.W., Langeland, S., Torp, H.: 3-D speckle tracking for assessment of regional left ventricular function. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 35(3), 458–471 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.09.011
Alessandrini, M., et al.: Detailed evaluation of five 3D speckle tracking algorithms using synthetic echocardiographic recordings. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(8), 1915–1926 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2537848
Chen, X., et al.: 3-D correlation-based speckle tracking. Ultrason. Imaging 27(1), 21–36 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1177/016173460502700102
Somphone, O., et al.: Fast myocardial motion and strain estimation in 3D cardiac ultrasound with Sparse Demons. Proc. Intl. Symp. Biomed. Imaging 1, 1182–1185 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI.2013.6556691
Heyde, B., Alessandrini, M., Hermans, J., Barbosa, D., Claus, P., Dhooge, J.: Anatomical image registration using volume conservation to assess cardiac deformation from 3D ultrasound recordings. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 35(2), 501–511 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2015.2479556
Yu, X., Wang, H., Ma, L.: Ultrasound speckle tracking with deep convolutional neural network. J. Med. Imaging Health Informatics 10(3), 743–749 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1166/jmihi.2020.2927
Hsu, W.Y.: Automatic left ventricle recognition, segmentation and tracking in cardiac ultrasound image sequences, IEEE. Access 7, 140524–140533 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2920957
Shreevastava, S., Tiwari, A.K., Som, T.: Intuitionistic fuzzy neighborhood rough set model for feature selection. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst 7(2), 75–84 (2018). https://doi.org/10.4018/IJFSA.2018040104
Vijayakumar, S., Santhi, V.: Speckle noise reduction in SAR images using fuzzy inference system. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 8(4), 60–83 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4018/IJFSA.2019100104
Chinta, S.S.: Kernelised rough sets based clustering algorithms fused with firefly algorithm for image segmentation. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst 8(4), 25–38 (2019). https://doi.org/10.4018/IJFSA.2019100102
Chung, F.L., Deng, Z., Wang, S.: An adaptive fuzzy-inference-rule-based flexible model for automatic elastic image registration. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 17(5), 995–1010 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2009.2020154
Takagi, T., Sugeno, M.: Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modeling and control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 1, 116–132 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.1985.6313399
Männle, M.: Identifying rule-based TSK fuzzy models, Proc. Eur. Congr. Intell. Tech. Soft Comput. (EUFIT 1999), Aachen, Ger. Elit. Found., pp. 286–299, 1999.
Vafamand, N., Arefi, M.M., Khayatian, A.: Nonlinear system identification based on Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy modeling and unscented Kalman filter. ISA Trans. 74, 34–143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isatra.2018.02.005
Rahimi, M., Davoodi, R., Moradi, M.H.: Deep fuzzy model for non-linear effective connectivity estimation in the intuition of consciousness correlates. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 57, 101732 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101732
Davoodi, R., Moradi, M.H.: Mortality prediction in intensive care units (ICUs) using a deep rule-based fuzzy classifier. J. Biomed. Inform 79, 48–59 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2018.02.008
Hosseini, M.H., Moradi, M.H., Tabassian, M., D’hooge, J.: Non-rigid image registration using a modified fuzzy feature-based inference system for 3D cardiac motion estimation. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 205, 106085 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2021.106085
Hosseini, M.S., Moradi, M.H.: Adaptive fuzzy-SIFT rule-based registration for 3D cardiac motion estimation. Appl. Intell. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10489-021-02430-2
Rister, B., Horowitz, D.L., Rubin, D.L.: Volumetric image registration from invariant keypoints. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 26(10), 4900–4910 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2017.2722689
De Craene, M., et al.: 3D strain assessment in ultrasound (Straus): a synthetic comparison of five tracking methodologies. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 32(9), 1632–1646 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2013.2261823
Bezdek, J.C., Ehrlich, R., Full, W.: FCM: The fuzzy c-means clustering algorithm. Comput. Geosci. 10(2–3), 191–203 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1016/0098-3004(84)90020-7
Alessandrini, M., et al.: A pipeline for the generation of realistic 3d synthetic echocardiographic sequences: methodology and open-access database. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 34(7), 1436–1451 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2015.2396632
Bernard, O. et al.: Challenge on Endocardial Three-dimensional Ultrasound Segmentation (CETUS), in Proceedings MICCAI Challenge on Echocardiographic Three-Dimensional Ultrasound Segmentation (CETUS), pp. 1–8 (2014)
Frisch, D.: point2trimesh - Distance between a point and a triangulated surface in 3D, https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/52882-point2trimesh-distance-between-point-and-triangulated-surface (2021)
Cerqueira, M.D., et al.: Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart. Circulation 105(4), 539–542 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1161/hc0402.102975
Yushkevich, P.A., et al.: User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 31(3), 1116–1128 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.01.015
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their appreciations to Raheleh Davoodi for her kind advices.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hosseini, M.S., Moradi, M.H. A Modified Fuzzy Inference Rule-Based Model for 3D Speckle Tracking. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 25, 1131–1143 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01428-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-022-01428-3