Abstract
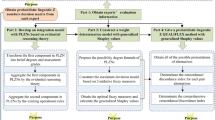
In recent years, evidential reasoning (ER) has provided an effective means to deal with uncertain information depicted by probabilistic linguistic terms sets (PLTSs) during fusion. However, it is worth noting that due to the differences in decision makers’ preferences and understanding of linguistic terms, there is a significant difference between the level of ER and the term in PLTSs, which hinders further development of ER in PLTSs. To fill this gap, this study modifies the existing ER algorithm with linguistic correlation and introduces it to multiple attribute group decision-making (MAGDM) problems within PLTSs. First, the correlations between different linguistic terms are defined based on the expressive preferences of decision-makers. Second, the correlation between different linguistic terms is integrated into the original ER to reduce the contradiction caused by expressive preferences. Moreover, linguistic correlation is also involved in the calculation of reliability to adjust the distance measure, which can reduce the unreliability caused by the preferences expressed by decision-makers. Then, nonlinear programming models are conducted to drive expert reliability. Thereafter, the modified ER algorithm is employed to integrate expert opinions into a comprehensive evaluation of alternatives. Finally, an illustrative example of an industry evaluation problem is conducted to verify the robustness and validity of the proposed method.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, T., He, S.-S., Wang, J.-Q., et al.: Novel operations for linguistic neutrosophic sets on the basis of Archimedean copulas and co-copulas and their application in multi-criteria decision-making problems. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 37, 2887–2912 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-190041
Li, Y.-Y., Wang, J.-Q., Wang, T.-L.: A linguistic neutrosophic multi-criteria group decision-making approach with edas method. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44(3), 2737–2749 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3487-5
Ren, P., Xu, Z., Wang, X., et al.: Group decision making with hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference relations based on modified extent measurement. Expert Syst. Appl. 171, 114235 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2020.114235
Rodríguez, R.M., Labella, Á., Sesma-Sara, M., et al.: A cohesion-driven consensus reaching process for large scale group decision making under a hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets environment. Comput. Ind. Eng. 155, 107158 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107158
Wang, X.K., Zhang, H.Y., Wang, J.Q., et al.: Extended TODIM-PROMETHEE II method with hesitant probabilistic information for solving potential risk evaluation problems of water resource carrying capacity. Expert Syst. 38(4), e12681 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12681
Nie, R.-X., Wang, J.-Q.: Prospect theory-based consistency recovery strategies with multiplicative probabilistic linguistic preference relations in managing group decision making. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04053-9
Luo, S.-Z., Zhang, H.-Y., Wang, J.-Q., et al.: Group decision-making approach for evaluating the sustainability of constructed wetlands with probabilistic linguistic preference relations. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 70(12), 2039–2055 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2018.1510806
Jiang, L., Liao, H.: A nondominated selection procedure with partially consistent non-reciprocal probabilistic linguistic preference relations and its application in social donation channel selection under the COVID-19 outbreaks. Inf. Sci. 564, 416–429 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2021.02.044
Wang, X.-K., Wang, S.-H., Zhang, H.-Y., et al.: The recommendation method for hotel selection under traveller preference characteristics: a cloud-based multi-criteria group decision support model. Group Decis. Negot. 30(6), 1433–1469 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10726-021-09735-0
Wang, X., Wang, J., Zhang, H.: Distance-based multicriteria group decision-making approach with probabilistic linguistic term sets. Expert Syst. 36(2), e12352 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1111/exsy.12352
Chen, S.-X., Wang, J.-Q., Wang, T.-L.: Cloud-based ERP system selection based on extended probabilistic linguistic MULTIMOORA method and Choquet integral operator. Comput. Appl. Math. 38(2), 88 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-019-0839-z
Gao, H., Ju, Y., Zeng, X.-J., et al.: Satisfaction-driven consensus model for social network MCGDM with incomplete information under probabilistic linguistic trust. Comput. Ind. Eng. 154, 107099 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2021.107099
Tian, Z.-P., Nie, R.-X., Wang, J.-Q.: Consistency and consensus improvement models driven by a personalized normalization method with probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Inf. Fusion 69, 156–176 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2020.12.005
Xu, Z., He, Y., Wang, X.: An overview of probabilistic-based expressions for qualitative decision-making: techniques, comparisons and developments. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 10, 1513–1528 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13042-018-0830-9
He, S.-S., Wang, Y.-T., Wang, J.-Q., et al.: A novel risk assessment model based on failure mode and effect analysis and probabilistic linguistic ELECTRE II method. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.3233/JIFS-191398
Gao, J., Guo, F., Li, X., et al.: Risk assessment of offshore photovoltaic projects under probabilistic linguistic environment. Renew. Energy 163, 172–187 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2020.08.110
Peng, H.-G., Zhang, H.-Y., Wang, J.-Q.: Cloud decision support model for selecting hotels on TripAdvisor.com with probabilistic linguistic information. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 68, 124–138 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2017.10.001
Liu, P., Teng, F.: Probabilistic linguistic TODIM method for selecting products through online product reviews. Inf. Sci. 485, 441–455 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.02.022
Xiao, F., Wang, J.-Q.: Multistage decision support framework for sites selection of solar power plants with probabilistic linguistic information. J. Clean. Prod. 230, 1396–1409 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.05.138
Peng, H.-G., Wang, J.-Q., Zhang, H.-Y.: Multi-criteria outranking method based on probability distribution with probabilistic linguistic information. Comput. Ind. Eng. 141, 106318 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cie.2020.106318
Song, C., Wang, X.-K., Cheng, P.-F., et al.: SACPC: a framework based on probabilistic linguistic terms for short text sentiment analysis. Knowl. Based Syst. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105572
Pang, Q., Wang, H., Xu, Z.: Probabilistic linguistic term sets in multi-attribute group decision making. Inf. Sci. 369, 128–143 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2016.06.021
Gao, J., Xu, Z., Liang, Z., et al.: Expected consistency-based emergency decision making with incomplete probabilistic linguistic preference relations. Knowl. Based Syst. 176, 15–28 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2019.03.020
Wang, P., Liu, P., Chiclana, F.: Multi-stage consistency optimization algorithm for decision making with incomplete probabilistic linguistic preference relation. Inf. Sci. 556, 361–388 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.10.004
Jian-Bo, Y., Singh, M.G.: An evidential reasoning approach for multiple-attribute decision making with uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 24(1), 1–18 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1109/21.259681
Yang, J.-B.: Rule and utility based evidential reasoning approach for multiattribute decision analysis under uncertainties. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 131(1), 31–61 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0377-2217(99)00441-5
Yang, J.-B., Xu, D.-L.: On the evidential reasoning algorithm for multiple attribute decision analysis under uncertainty. IEEE T. Syst. Man Cybern. A 32(3), 289–304 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMCA.2002.802746
Zhou, H., Wang, J.-Q., Zhang, H.-Y., et al.: Linguistic hesitant fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making method based on evidential reasoning. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 47(2), 314–327 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/00207721.2015.1042089
Liu, P., Zhang, X.: Approach to multi-attributes decision making with intuitionistic linguistic information based on dempster-shafer evidence theory. IEEE Access 6, 52969–52981 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2869844
Zheng, H., Deng, Y.: Evaluation method based on fuzzy relations between Dempster–Shafer belief structure. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 33(7), 1343–1363 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/int.21956
Zhou, J., Han, C., Sun, L., et al.: Linguistic multi-criteria group decision-making method combining cloud model and evidence theory. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. E102.D(4), 845–855 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1587/transinf.2018EDP7288
Li, P., Wei, C.: An emergency decision-making method based on D–S evidence theory for probabilistic linguistic term sets. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 37, 101178 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdrr.2019.101178
Tian, Z.-P., Nie, R.-X., Wang, J.-Q.: Probabilistic linguistic multi-criteria decision-making based on evidential reasoning and combined ranking methods considering decision-makers’ psychological preferences. J. Oper. Res. Soc. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2019.1632752
Fang, R., Liao, H., Yang, J.-B., et al.: Generalised probabilistic linguistic evidential reasoning approach for multi-criteria decision-making under uncertainty. J. Oper. Res. Soc. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2019.1654415
Yang, J.-B., Xu, D.-L.: Evidential reasoning rule for evidence combination. Artif. Intell. 205, 1–29 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artint.2013.09.003
Fu, C., Yang, J.-B., Yang, S.-L.: A group evidential reasoning approach based on expert reliability. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 246(3), 886–893 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2015.05.042
Ma, Z., Zhu, J., Chen, Y.: A probabilistic linguistic group decision-making method from a reliability perspective based on evidential reasoning. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2018.2815716
Fu, C., Xue, M., Chang, W., et al.: An evidential reasoning approach based on risk attitude and criterion reliability. Knowl. Based Syst. 199, 105947 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2020.105947
Zhai, Y., Xu, Z., Liao, H.: Probabilistic linguistic vector-term set and its application in group decision making with multi-granular linguistic information. Appl. Soft Comput. 49, 801–816 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2016.08.044
Zhai, Y., Xu, Z.: Managing individual evaluator’s personalized semantic environment of linguistic term with improved vector expression in multi-granularity linguistic group decision making. Appl. Soft Comput. 92, 106334 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106334
Zadeh, L.A.: The concept of a linguistic variable and its application to approximate reasoning—I. Inf. Sci. 8(3), 199–249 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-0255(75)90036-5
Rodriguez, R.M., Martinez, L., Herrera, F.: Hesitant fuzzy linguistic term sets for decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 20(1), 109–119 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TFUZZ.2011.2170076
Zhang, G., Dong, Y., Xu, Y.: Consistency and consensus measures for linguistic preference relations based on distribution assessments. Inf. Fusion 17, 46–55 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inffus.2012.01.006
Dempster, A.P.: Upper and lower probabilities induced by a multivalued mapping. Ann. Math. Stat. 38(2), 325–339 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1214/aoms/1177698950
Shafer, G.: A Mathematical Theory of Evidence. Princeton University Press, Princeton (1976)
Zhang, L.: Approaches to multiple attribute group decision making under intuitionistic fuzzy settings: application of Dempster–Shafer theory of evidence. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 44(4), 3719–3732 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3657-5
Mondéjar-Guerra, V.M., Muñoz-Salinas, R., Marín-Jiménez, M.J., et al.: Keypoint descriptor fusion with Dempster–Shafer theory. Int. J. Approx. Reason. 60, 57–70 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijar.2015.03.001
Nakahara, Y.: User oriented ranking criteria and its application to fuzzy mathematical programming problems. Fuzzy Sets Syst. 94(3), 275–286 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-0114(96)00262-X
Ölçer, A.İ, Odabaşi, A.Y.: A new fuzzy multiple attributive group decision making methodology and its application to propulsion/manoeuvring system selection problem. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 166(1), 93–114 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2004.02.010
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Province (Nos. 2018GXNSFBA281004, AD19245134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XK., Deng, Mh., Hou, W.h. et al. Probabilistic Linguistic Group Decision-Making Based on Evidential Reasoning Considering Correlations Between Linguistic Terms. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 25, 3001–3015 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-023-01550-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-023-01550-w