Abstract
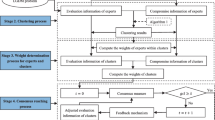
The remote sensing satellite observation process involves multiple stakeholders and significant costs, so selecting an appropriate observation scheme and reaching an agreement on the chosen scheme among the evaluators/stakeholders is essential. From this perspective, the observation scheme selection problem can be viewed as a large-scale group decision-making (LSGDM) problem, challenging due to its complex group composition and the high consensus level required. Accordingly, this paper investigates an adaptive bi-directional consensus model that incorporates the evolution of social influence to address the LSGDM problem. Firstly, the dual-attribute affinity propagation algorithm is employed to divide the large-group into manageable subgroups. Secondly, the social influence evolution model is established, where evaluators’ social influences are determined by considering their opinion similarity and trust level, and subgroups’ social influences are updated by measuring their decision risk. Thirdly, the bi-directional feedback mechanism is designed to adaptively generate adjustment strategies corresponding to different scenarios based on the evolution model. Finally, an observation scheme selection case is analyzed using the proposal to demonstrate its practicality. During the process of remote sensing satellite observation, the selection of an appropriate observation scheme can optimize the utilization of existing satellite resources and ensure the quality of satellite observation services, thereby better meeting the demands of diverse application areas such as environmental monitoring, disaster management, and urban planning.















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed in this study may be provided by the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Cheng, X.T., Zhang, K., Wu, T., Xu, Z.S., Gou, X.J.: An opinions-updating model for large-scale group decision-making driven by autonomous learning. Inf. Sci. 662(1), 120238 (2024)
Feng, S.H., Xin, Y.J., Xiong, S.H., Chen, Z.S., Deveci, M., Garcia-Zamora, D., Pedrycz, W.: Safety perception evaluation of civil aviation based on Weibo posts in China: an enhanced large-scale group decision-making framework. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-023-01510-4
Liao, H.C., Wu, Z., Tang, M., Wan, Z.J.: An interactive consensus reaching model with updated weights of clusters in large-scale group decision making. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 107, 104532 (2022)
Yu, S.M., Du, Z.J., Xu, X.H.: Hierarchical punishment-driven consensus model for probabilistic linguistic large-group decision making with application to global supplier selection. Group Decis. Negot. 30, 1343–1372 (2021)
Tang, M., Liao, H.C., Xu, J.P., Streimikiene, D., Zheng, X.S.: Adaptive consensus reaching process with hybrid strategies for large-scale group decision making. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 282(3), 957–971 (2020)
Xiao, J., Wang, X.L., Zhang, H.J.: Managing personalized individual semantics and consensus in linguistic distribution large-scale group decision making. Inf. Fusion 53, 20–34 (2020)
Li, Y.H., Kou, G., Li, G.X., Peng, Y.: Consensus reaching process in large-scale group decision making based on bounded confidence and social network. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 303(2), 790–802 (2022)
Wang, Y.J., Yan, B., Xia, W., Hu, X.X., Ma, H.W., Jin, P.: Personalization-driven consensus reaching model for emergency mission scheduling schemes selection in large-group emergency decision-making with linguistic distribution preference relationship. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 24, 3308–3326 (2022)
Zhang, Y.J.J., Chen, X., Pedrycz, W., Dong, Y.C.: Consensus reaching based on social influence evolution in group decision making. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 53(7), 4134–4147 (2023)
Wu, J., Gong, H., Liu, F., Liu, Y.: Risk assessment of open-pit slope based on large-scale group decision-making method considering non-cooperative behavior. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 25, 245–263 (2023)
Tu, Y., Xie, Y.T., Shi, H.W., Li, Z.M.: Incorporating interaction and transaction behaviors into a bi-level consensus model fusing with maximum return and minimum cost. J. Oper. Res Soc. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1080/01605682.2024.2308560
Wan, S.P., Rao, T., Dong, J.Y.: Time-series based multi-criteria large-scale group decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy information and application to multi-period battery supplier selection. Expert Syst. Appl. 232, 120749 (2023)
Liu, P.D., Li, Y.Y., Wang, P.: Social trust-driven consensus reaching model for multi-attribute group decision making: exploring social trust network completeness. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 31(9), 3040–3054 (2023)
Shen, Y.F., Ma, X.L., Xu, Z.S., Herrere-Viedma, E., Maresova, P., Zhan, J.M.: Opinion evolution and dynamic trust-driven consensus model in large-scale group decision-making under incomplete information. Inf. Sci. 657, 119925 (2024)
Chen, X., Liang, H.M., Zhang, Y.J.J., Wu, Y.Z.: Consensus manipulation in social network group decision making with value-based opinion evolution. Inf. Sci. 647, 119441 (2023)
Dong, Q.X., Sheng, Q., Martinez, L., Zhang, Z.: An adaptive group decision making framework: individual and local world opinion based opinion dynamics. Inf. Fusion 78, 218–231 (2022)
Liang, D.C., Liu, F.S., Xu, Z.S.: A group-based FMEA approach with dynamic heterogeneous social network consensus reaching model for uncertain reliability assessment. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 74(1), 33–47 (2022)
Zhang, G.Q., Dong, Y.C., Xu, Y.F.: Consistency and consensus measures for linguistic preference relations based on distribution assessments. Inf. Fusion 17, 46–55 (2014)
Wasserman, S., Faust, K.: Social Network Analysis: Methods and Applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1994)
Liu, B.S., Jiao, S.X., Shen, Y.H., Chen, Y., Wu, G.B., Chen, S.: A dynamic hybrid trust network-based dual-path feedback consensus model for multi-attribute group decision-making in intuitionistic fuzzy environment. Inf. Fusion 80, 266–281 (2022)
Liu, X., Xu, Y., Montes, R., Herrera, F.: Social network group decision making: managing self-confidence-based consensus model with the dynamic importance degree of experts and trust-based feedback mechanism. Inf. Sci. 505, 215–232 (2019)
Zhao, M., Kou, D., Li, L., Lin, M.W.: An incomplete probabilistic linguistic multi-attribute group decision making method based on a three-dimensional trust network. Appl. Intell. 53, 5029–5047 (2023)
Wu, J., Zhao, Z.W., Sun, Q., Fujita, H.: A maximum self-esteem degree based feedback mechanism for group consensus reaching with the distributed linguistic trust propagation in social network. Inf. Fusion 67, 80–93 (2021)
Wu, J., Dai, L.F., Chiclana, F., Fujita, H., Herrera-Viedma, E.: A minimum adjustment cost feedback mechanism based consensus model for group decision making under social network with distributed linguistic trust. Inf. Fusion 41, 232–242 (2018)
Wang, Y.J., Yan, B., Hu, X.X., Xia, W., Ma, H.W., Jin, P.: A two-stage personalized feedback mechanism considering dynamic interactive behavior under social network in large-group emergency task scheduling schemes selection. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 14, 587–607 (2023)
Chen, X., Ding, Z.G., Dong, Y.C., Liang, H.M.: Managing consensus with minimum adjustments in group decision making with opinions evolution. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 51(4), 2299–2311 (2021)
Li, S.L., Rodríguez, R.M., Wei, C.P.: Two-stage consensus model based on opinion dynamics and evolution of social power in large-scale group decision making. Appl. Soft Comput. 111, 107615 (2021)
Hegselmann, R., Krause, U.: Opinion dynamics and bounded confidence, models, analysis and simulation. J. Artif. Soc. Soc. Simul. 5(3), 1–33 (2002)
Frey, B.J., Dueck, D.: Clustering by passing messages between data points. Science 315, 972–976 (2007)
Liu, B.S., Zhou, Q., Ding, R.X., Palomares, I., Herrera, F.: Large-scale group decision making model based on social network analysis: trust relationship-based conflict detection and elimination. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 275, 737–754 (2019)
Sun, X.L., Zhu, J.J.: Large-scale group classification decision making method and its application with trust-interest dual factors in social network. Appl. Soft Comput. 133, 109890 (2023)
Wu, T., Zhang, K., Liu, X.W., Cao, C.Y.: A two-stage social trust network partition model for large-scale group decision-making problems. Knowl.-Based Syst. 163, 632–643 (2019)
Yu, S.M., Du, Z.J., Zhang, X.Y., Luo, H.Y., Lin, X.D.: Trust Cop-Kmeans clustering analysis and minimum-cost consensus model considering voluntary trust loss in social network large-scale decision-making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30(7), 2634–2648 (2022)
Lu, Y.L., Xu, Y.J., Huang, J., Wei, J., Herrera-Viedma, E.: Social network clustering and consensus-based distrust behaviors management for large-scale group decision-making with incomplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations. Appl. Soft Comput. 117, 108373 (2022)
Liu, P.D., Li, Y.Y., Wang, P.: Opinion dynamics and minimum adjustment-driven consensus model for multi-criteria large-scale group decision making under a novel social trust propagation mechanism. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 30(1), 307–321 (2023)
Palomares, I., Martinez, L., Herrera, F.: A consensus model to detect and manage noncooperative behaviors in large-scale group decision making. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 22(3), 516–530 (2014)
Lu, Y.L., Xu, Y.J., Herrera-Viedma, E., Han, Y.F.: Consensus of large-scale group decision making in social network: the minimum cost model based on robust optimization. Inf. Sci. 547, 910–930 (2021)
Qin, J.D., Li, M.X., Liang, Y.Y.: Minimum cost consensus model for CRP-driven preference optimization analysis in large-scale group decision making using Louvain algorithm. Inf. Fusion 80, 121–136 (2022)
Yang, H., Xu, G.L., Wang, F., Zhang, Y.F.: A clustering-based method for large-scale group decision making in the hesitant fuzzy set environment. Comput. Ind. Eng. 183, 109526 (2023)
Wan, S.P., Yan, J., Dong, Y.C.: Personalized individual semantics based consensus reaching process for large-scale group decision making with probabilistic linguistic preference relations and application to COVID-19 surveillance. Expert Syst. Appl. 191, 116328 (2022)
Li, L., Qiu, L., Liu, X., Xu, Y.J., Herrera-Viedma, E.: An improved HK model-driven consensus reaching for group decision making under interval-valued fuzzy preference relations with self-confidence. Comput. Ind. Eng. 171, 108438 (2022)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 72071064, 72188101, 72271074).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Substantially contributed to conception or design: Yanjun Wang, Xiaoxuan Hu, Bing Yan, Wei Xia. Contributed to acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: Yanjun Wang, Xiaoxuan Hu, Bing Yan. Drafted the manuscript for important content: Yanjun Wang, Xiaoxuan Hu, Wei Xia. Critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual content: Yanjun Wang, Wei Xia. Gave final approval: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained for all data used in this study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Hu, X., Yan, B. et al. Adaptive Bi-directional Consensus Reaching Model with Social Influence Evolution for Large-Scale Group Decision-Making with an Application to Observation Scheme Selection. Int. J. Fuzzy Syst. 26, 2337–2358 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-024-01738-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40815-024-01738-8