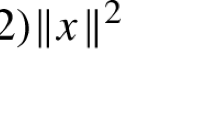Abstract
The goal of simultaneous sparse representation is to capture as much information as possible from a target matrix by a linear combination of several selected columns of another large matrix. This matrix is sometimes called a “dictionary.” Algorithms that address this problem have been used in areas that include, among others, signal processing, computer vision, and machine learning. Finding an optimal solution to the problem is known to be NP-hard. Previously proposed approaches are typically greedy, comparing each target column with all columns in the dictionary. This results in algorithms that are slow when both the target matrix and the dictionary matrix are large. Current fastest nontrivial algorithms have a running time that depends on the product of the numbers of columns of the two matrices. This paper presents an efficient selection algorithm with linear complexity with respect to these parameters. The main idea is to select columns from the dictionary matrix whose span is close to the dominant spectral components of the target matrix. The computational efficiency and the selection accuracy of the proposed algorithm outperform those of the conventional methods. We also derive bounds on the accuracy of the selections computed by our algorithm. These bounds show that our results are typically within a few percentage points from the optimal solutions.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mallat, S.: A Wavelet Tour of Signal Processing. Academic Press, Cambridge (1999)
Miller, A.: Subset Selection in Regression, 2nd edn. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton (2002)
Donoho, D.L.: Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 52(4), 1289–1306 (2006)
Mairal, J., Bach, F., Ponce, J.: Sparse modeling for image and vision processing. Now Found. Trends 8(2–3), 85–283 (2014)
Wright, J., Ma, Y., Mairal, J., Sapiro, G., Huang, T.S., Yan, S.: Sparse representation for computer vision and pattern recognition. Proc. IEEE 98(6), 1031–1044 (2010)
Zhang, Z., Yong, X., Yang, J., Li, X., Zhang, D.: A survey of sparse representation: algorithms and applications. IEEE Access 3, 490–530 (2015)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J.: The Elements of Statistical Learning, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2009)
Malioutov, D., Cetin, M., Willsky, A.S.: A sparse signal reconstruction perspective for source localization with sensor arrays. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 53(8), 3010–3022 (2005)
Tropp, J.A., Gilbert, A.C., Strauss, M.J.: Algorithms for simultaneous sparse approximation. Part I: Greedy pursuit. Signal Process. 86(3), 572–588 (2006)
Chen, J., Huo, X.: Theoretical results of sparse representations of multiple measurement vectors. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 54(12), 4634–4643 (2006)
Belmerhnia, L., Djermoune, E.-H., Carteret, C., Brie, D.: Simultaneous variable selection for the classification of near infrared spectra. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 211, 104268 (2021)
Zhu, X., Hu, R., Lei, C., Thung, K.H., Zheng, W., Wang, C.: Low-rank hypergraph feature selection for multi-output regression. World Wide Web 22, 517–531 (2019)
Guha, T., Ward, R.K.: Learning sparse representations for human action recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(8), 1576–1588 (2011)
Zhang, Q., Liu, Y., Blum, R.S., Han, J., Tao, D.: Sparse representation based multi-sensor image fusion for multi-focus and multi-modality images: a review. Inf. Fusion 40, 57–75 (2018)
Xu, X., Shi, Z.: Multi-objective based spectral unmixing for hyperspectral images. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 124, 54–69 (2017)
Cheng, X., Dong, C., Ren, Y., Cheng, K., Yan, L., Yao, H., Hao, Q.: Reduced data set for multi-target recognition using compressed sensing frame. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 129, 86–91 (2020)
Çivril, A., Magdon-Ismail, M.: Column subset selection via sparse approximation of SVD. Theor. Comput. Sci. 421, 1–14 (2012)
Maung, C., Schweitzer, H.: Improved greedy algorithms for sparse approximation of a matrix in terms of another matrix. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 27(3), 769–780 (2015)
Halko, N., Martinsson, P.G., Tropp, J.A.: Finding structure with randomness: probabilistic algorithms for constructing approximate matrix decompositions. SIAM Rev. 53(2), 217–288 (2011)
Daniel, J.W., Gragg, W.B., Kaufman, L., Stewart, G.W.: Reorthogonalization and stable algorithms for updating the Gram-Schmidt QR factorization. Math. Comput. 30(136), 772–795 (1976)
Wan, G., Schweitzer, H.: A fast algorithm for simultaneous sparse approximation. In: Pacific-Asia Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Springer (2021)
Tropp, J.A.: Greed is good: algorithmic results for sparse approximation. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 50(10), 2231–2242 (2004)
Furnival, G.M., Wilson, R.W.: Regressions by leaps and bounds. Technometrics 16(4), 499–511 (1974)
Zhang, T.: Adaptive forward-backward greedy algorithm for sparse learning with linear models. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 1921–1928 (2009)
Qian, C., Yu, Y., Zhou, Z.: Subset selection by pareto optimization. In: Cortes, C., Lawrence, N.D., Lee, D.D., Sugiyama, M., Garnett, R. (eds.) Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 28, pp. 1774–1782. Curran Associates, Inc., New York (2015)
Bertsimas, D., King, A., Mazumder, R., et al.: Best subset selection via a modern optimization lens. Annal. Stat. 44(2), 813–852 (2016)
Bertsimas, D., Van Parys, B., et al.: Sparse high-dimensional regression: exact scalable algorithms and phase transitions. Annal. Stat. 48(1), 300–323 (2020)
Pati, Y.C., Rezaiifar, R., Krishnaprasad, P.S.: Orthogonal matching pursuit: recursive function approximation with applications to wavelet decomposition. In: The 27th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, vol. 1, pp. 40–44 (1993)
Neff, R., Zakhor, A.: Very low bit-rate video coding based on matching pursuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 7(1), 158–171 (1997)
Hastie, T., Tibshirani, R., Friedman, J.: The Elements of Statistical Learning, section 3.3.1. Springer, 2nd edn (2009)
Moreira Costa, C., Kreber, D., Schmidt, M.: An alternating method for cardinality-constrained optimization: a computational study for the best subset selection and sparse portfolio problems. INFORMS Journal on Computing (2022)
Tibshirani, R.: Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. J. R. Stat. Soc B. 58(1), 267–288 (1996)
Golub, G.H., Van-Loan, C.F.: Matrix Computations, 4th edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore (2013)
Wei, H.L., Billings, S.A.: Feature subset selection and ranking for data dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(1), 162–166 (2007)
Maung, C., Schweitzer, H.: Pass-efficient unsupervised feature selection. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. (NIPS) 26, 1628–1636 (2013)
Arai, H., Maung, C., Schweitzer, H.: Optimal column subset selection by A-Star search. In: Proceedings of the 29th National Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI’15), pp. 1079–1085. AAAI Press (2015)
Arai, H., Maung, C., Xu, K., Schweitzer, H.: Unsupervised feature selection by heuristic search with provable bounds on suboptimality. In: Proceedings of the 30th National Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI’16), pp. 666–672. AAAI Press (2016)
He, B., Shah, S., Maung, C., Arnold, G., Wan, G., Schweitzer, H.: Heuristic search algorithm for dimensionality reduction optimally combining feature selection and feature extraction. In: Proceedings of the 33rd National Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI’19), pp. 2280–2287. California. AAAI Press (2019)
Zaeemzadeh, A., Joneidi, M., Rahnavard, N., Shah, M.: Iterative projection and matching: finding structure-preserving representatives and its application to computer vision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 5414–5423 (2019)
Joneidi, M., Vahidian, S., Esmaeili, A., Wang, W., Rahnavard, N., Lin, B., Shah, M.: Select to better learn: fast and accurate deep learning using data selection from nonlinear manifolds. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7819–7829 (2020)
Belmerhnia, L., Djermoune, E.-H., Brie, D.: Greedy methods for simultaneous sparse approximation. In: 22nd European Signal Processing Conference (2014)
Cotter, S.F., Rao, B.D., Engen, K., Kreutz-Delgado, K.: Sparse solutions to linear inverse problems with multiple measurement vectors. ASP 53(7), 2477–2488 (2005)
Wan, G., Schweitzer, H.: Heuristic search for approximating one matrix in terms of another matrix. In: IJCAI (2021)
Soussen, C., Gribonval, R., Idier, J., Herzet, C.: Joint k-step analysis of orthogonal matching pursuit and orthogonal least squares. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 59(5), 3158–3174 (2013)
Blumensath, T., Davies, M.E.: On the difference between orthonormal matching pursuit and orthogonal least squares. Technical report, University of Edinburgh, March (2007)
Das, A., Kempe, D.: Approximate submodularity and its applications: subset selection, sparse approximation and dictionary selection. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 19(1), 74–107 (2018)
Donoho, D.L., Tsaig, Y., Drori, I., Starck, J.L.: Sparse solutions of undetermined systems of linear equations by stagewise orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 58(2), 1094–1896 (2012)
Marshall, A.W., Olkin, I., Arnold, B.C.: Inequalities: Theory of Majorization and Its Applications, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Çivril, A.: Column subset selection problem is ug-hard. J. Comput. Syst Sci. 80(4), 849–859 (2014)
Natarajan, B.K.: Sparse approximate solutions to linear systems. SIAM J. Comput. 25(2), 227–234 (1995)
Davis, G., Mallat, S., Avellaneda, M.: Constructive approximation. Adapt. Greedy Approx. 13(1), 57–98 (1997)
Amaldi, E., Kann, V.: On the approximability of minimizing nonzero variables or unsatisfied relations in linear systems. Theor. Comput. Sci. 209(1–2), 237–260 (1998)
Koren, Y., Bell, R., Volinsky, C.: Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems. Computer 42(8), 30–37 (2009)
Raza, S., Ding, C.: Progress in context-aware recommender systems—an overview. Comput. Sci. Rev. 31, 84–97 (2019)
Wan, G., Schweitzer, H.: A new robust subspace recovery algorithm (student abstract). In: The 35th National Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI) (2021)
Lerman, G., Maunu, T.: Fast, robust and non-convex subspace recovery. Inf. Inference J. IMA 7(2), 277–336 (2018)
Wan, G., Schweitzer, H.: A lookahead algorithm for robust subspace recovery. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 1379–1384. IEEE (2021)
Gepperth, A., Hammer, B.: Incremental learning algorithms and applications. In: European symposium on artificial neural networks (ESANN) (2016)
West, M., Blanchette, C., Dressman, H., Huang, E., Ishida, S., Spang, R., Zuzan, H., Olson, J.A., Marks, J.R., Nevins, J.R.: Predicting the clinical status of human breast cancer by using gene expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 98(20), 11462–11467 (2001)
Georghiades, A.S., Belhumeur, P.N., Kriegman, D.J.: From few to many: illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 23(6), 643–660 (2001)
Bertin-Mahieux, T., Ellis, D.P.W., Whitman, B., Lamere, P.: The million song dataset. (2011)
Jegou, H., Douze, M., Schmid, C.: Product quantization for nearest neighbor search. IEEE Trans. Pattern Analy. Mach. Intell. 33(1), 117–128 (2010)
Wan, G., Maung, C., Zhang, C., Schweitzer, H.: Fast distance metrics in low-dimensional space for neighbor search problems. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining (ICDM), pp. 1304–1309 (2020)
Huang, Q., Feng, J., Fang, Q., Ng, W.: Two efficient hashing schemes for high-dimensional furthest neighbor search. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 29(12), 2772–2785 (2017)
Xu, Y., Li, Z., Yang, J., Zhang, D.: A survey of dictionary learning algorithms for face recognition. IEEE Access 5, 8502–8514 (2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, G., Schweitzer, H. Spectral pursuit for simultaneous sparse representation with accuracy guarantees. Int J Data Sci Anal 17, 425–441 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41060-023-00480-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41060-023-00480-y