Abstract
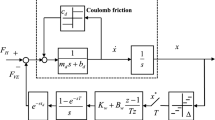
LuGre friction model is a comprehensive model for friction, which can simulate important nonlinear phenomena such as stiction, Stribeck effect, variable break-away force, pre-sliding displacement, and frictional lag. In this paper, an analytical describing function (DF) for this friction model is derived. The theoretical analysis is examined by comparing its result with some existing experimental results. The determined DF can approximate the LuGre friction force with constant viscous damping in a sinusoidal motion. Afterwards, as an application, its effect on the stability of a haptic device (HD) is studied. For this purpose, some simulations in MATLAB software are performed by considering the HD as a one-degree of freedom system with an effective mass that moves with the LuGre friction model, and stability analysis is performed theoretically (using the DF of the LuGre) and compared with the simulation result.















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Boegli, M., De Laet, T., De Schutter, J., Swevers, J.: A smoothed gms friction model suited for gradient-based friction state estimation, in American Control Conference (ACC), 2012, pp. 2627–2632, IEEE (2012)
Cheng, L., Tavakoli, M.: A multilateral impedance-controlled system for haptics-enabled surgical training and cooperation in beating-heart surgery. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 3(3), 314–325 (2019)
Do, T., Tjahjowidodo, T., Lau, M.W.S., Phee, S.J.: A new approach of friction model for tendon-sheath actuated surgical systems: Nonlinear modelling and parameter identification. Mech. Mach. Theory 85, 14–24 (2015)
Dong, R.G., Wu, J.Z., Xu, X.S., Welcome, D.E., Krajnak, K.: A review of hand-arm vibration studies conducted by us niosh since 2000. Vibration 4(2), 482–528 (2021)
Gafvert, M.: Comparisons of two dynamic friction models, in Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE international Conference on Control applications, pp. 386–391, IEEE (1997)
Helmick, D., Messner, W.: Describing function analysis of dahl model friction, in 2009 American control conference, pp. 814–819, IEEE (2009)
Hulin, T., Camarero, R. G., Albu-Schaffer, A.: Optimal control for haptic rendering: Fast energy dissipation and minimum overshoot, in Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on, pp. 4505–4511, IEEE (2013)
Hulin, T., Albu-Schaffer, A., Hirzinger, G.: Passivity and stability boundaries for haptic systems with time delay. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 22(4), 1297–1309 (2014)
Lee, W., Lee, C.-Y., Jeong, Y.H., Min, B.-K.: Distributed component friction model for precision control of a feed drive system. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 20(4), 1966–1974 (2014)
Li, J., Zhou, X., Zhao, H., Shao, M., Li, N., Zhang, S., Du, Y.: Development of a novel parasitic-type piezoelectric actuator. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 22(1), 541–550 (2016)
Lichtsinder, A., Gutman, P.O.: Quasi-analytical describing function for the karnopp friction model. IFAC Proc. Vol. 45(13), 381–386 (2012)
Liu, D.-P.: Parameter identification for lugre friction model using genetic algorithms, in 2006 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, pp. 3419–3422, IEEE (2006)
Liu, Y., Li, J., Zhang, Z., Hu, X., Zhang, W.: Experimental comparison of five friction models on the same test-bed of the micro stick-slip motion system. Mech. Sci. 6(1), 15–28 (2015)
Mashayekhi, A., Boozarjomehry, R.B., Nahvi, A., Meghdari, A., Asgari, P.: Improved passivity criterion in haptic rendering: influence of coulomb and viscous friction. Adv. Robot. 28(10), 695–706 (2014)
Mashayekhi, A., Behbahani, S., Ficuciello, F., Siciliano, B.: Analytical stability criterion in haptic rendering: The role of damping. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 23(2), 596–603 (2018)
Mashayekhi, A., Behbahani, S., Ficuciello, F., Siciliano, B.: Delay-dependent stability analysis in haptic rendering, Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, pp. 1–13 (2019)
Mashayekhi, A., Behbahani, S., Ficuciello, F., Siciliano, B.: Influence of human operator on stability of haptic rendering: a closed-form equation. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 4, 403–415 (2020)
Mashayekhi, A., Nahvi, A., Meghdari, A., Shad, H. M.: A new haptic interaction with a visual tracker: implementation and stability analysis, International Journal of Intelligent Robotics and Applications, pp. 1–12 (2021)
Peng, Y.-C., Carabis, D.S., Wen, J.T.: Collaborative manipulation with multiple dual-arm robots under human guidance. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2(2), 252–266 (2018)
Sharkawy, A.-N., Koustoumpardis, P.N., Aspragathos, N.: A recurrent neural network for variable admittance control in human-robot cooperation: simultaneously and online adjustment of the virtual damping and inertia parameters. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 4(4), 441–464 (2020)
Singh, J., Srinivasan, A.R., Neumann, G., Kucukyilmaz, A.: Haptic-guided teleoperation of a 7-dof collaborative robot arm with an identical twin master. IEEE Trans. Haptics 13(1), 246–252 (2020)
Sun, Y.-H.: Stability of controlled mechanical system with parametric uncertainties in a realistic friction model, PhD Thesis, University of Manitoba (2016)
Vidyasagar, M.: Nonlinear systems analysis. SIAM (2002)
Xia, J., Huang, D., Li, Y., Qin, N.: Iterative learning of human partner’s desired trajectory for proactive human-robot collaboration. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 4, 229–242 (2020)
Zhang, Q., Liu, G.: Precise control of elastic joint robot using an interconnection and damping assignment passivity-based approach. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 21(6), 2728–2736 (2016)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mashayekhi, A., Behbahani, S., Nahvi, A. et al. Analytical describing function of LuGre friction model. Int J Intell Robot Appl 6, 437–448 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-021-00220-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41315-021-00220-0