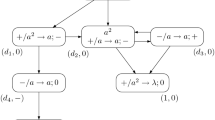
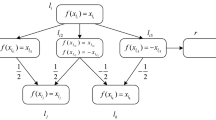
Abstract
Taking neuron-associated polarizations as the firing condition of neuron rules, the concept of polarization is applied to spiking neural P systems (SN P systems), which is adopted to effectively simulate the biological fact that every neuron in the nervous system contains electrical charges. In addition, in biological neural systems, neurons are always connected by multiple synapses. Therefore, a novel computational model referred to as the weighted spiking neural P systems with polarizations and anti-spikes (PAWSN P systems) is obtained by introducing weighted synapses and anti-spikes. The application of anti-spikes further optimizes the computational performance of the systems. We investigate the computational universality of PAWSN P systems. By simulating the register machine, it is verified that PAWSN P systems are able to accomplish the generation and acceptance of numbers, which provides justification for stating that the PAWSN P systems have Turing universality. With further exploration, we apply three types of polarizations and 98 neurons to construct a small universal PAWSN P system, which is capable of computing functions. By comparing several kinds of extended SN P systems, the results show that the PAWSN P systems achieve universality using fewer computational resources.












Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Păun, G. (2000). Computing with membranes. Journal of Computer and System Sciences, 61(1), 108–143. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcss.1999.1693
Jiang, S., Wang, Y., Xu, J., & Xu, F. (2019). The computational power of cell-like p systems with symport/antiport rules and promoters. Fundamenta Informaticae, 164(2–3), 207–225. https://doi.org/10.3233/Fi-2019-1763
Liu, L., Yi, W., Yang, Q., Peng, H., & Wang, J. (2020). Small universal numerical p systems with thresholds for computing functions. Fundamenta Informaticae, 176(1), 43–59. https://doi.org/10.3233/fi-2020-1962
Pan, L., & Song, B. (2020). P systems with rule production and removal. Fundamenta Informaticae, 171(1–4), 313–329. https://doi.org/10.3233/Fi-2020-1885
Liu, L., Yi, W., Yang, Q., Peng, H., & Wang, J. (2019). Numerical p systems with boolean condition. Theoretical Computer Science, 785, 140–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2019.03.021
Jiang, S., Wang, Y., Xu, F., & Deng, J. (2019). Communication p systems with channel states working in flat maximally parallel manner. Fundamenta Informaticae, 168(1), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.3233/Fi-2019-1821
Luo, Y., Zhao, Y., & Chen, C. (2021). Homeostasis tissue-like p systems. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience, 20(1), 126–136. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2020.3025921
Pan, L., Alhazov, A., Su, H., & Song, B. (2020). Local synchronization on asynchronous tissue p systems with symport/antiport rules. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience, 19(2), 315–320. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2020.2973332.Epub2020Feb11
Zhang, Z., Su, Y., & Pan, L. (2018). The computational power of enzymatic numerical p systems working in the sequential mode. Theoretical Computer Science, 724, 3–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2017.12.016
Zeng, X., Pan, L., & Perez-Jimenez, M. J. (2014). Small universal simple spiking neural p systems with weights. Science China-Information Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-013-4848-z
Zhang, X., Luo, B., Fang, X., & Pan, L. (2012). Sequential spiking neural p systems with exhaustive use of rules. Biosystems, 108(1–3), 52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2012.01.007
Orellana-Martín, D., Valencia-Cabrera, L., Riscos-Núñez, A., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2019). A path to computational efficiency through membrane computing. Theoretical Computer Science, 777, 443–453. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2018.12.024
Jiang, S., Wang, Y., & Su, Y. (2019). A uniform solution to sat problem by symport/antiport p systems with channel states and membrane division. Soft Computing, 23(12), 3903–3911. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-018-3254-2
Ye, L., Zheng, J., Guo, P., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2019). Solving the 0–1 knapsack problem by using tissue p system with cell division. IEEE Access, 7, 66055–66067. https://doi.org/10.1109/Access.2019.2917889
Díaz-Pernil, D., Christinal, H. A., & Gutiérrez-Naranjo, M. A. (2018). Solving the 3-col problem by using tissue p systems without environment and proteins on cells. Information Sciences, 430–431, 240–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2017.11.022
Christinal, A. H., Díaz-Pernil, D., & Mathu, T. (2018). A uniform family of tissue p systems with protein on cells solving 3-coloring in linear time. Natural Computing, 17(2), 311–319. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11047-016-9590-1
Buño, K. C., Cabarle, F. G. C., Calabia, M. D., & Adorna, H. N. (2018). Solving the n-queens problem using dp systems with active membranes. Theoretical Computer Science, 736, 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2017.12.013
Guo, P., Zhu, J., Chen, H., & Yang, R. (2018). A linear-time solution for all-sat problem based on p system. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 27(2), 367–373. https://doi.org/10.1049/cje.2018.01.008
Luo, Y., Tan, H., Zhang, Y., & Jiang, Y. (2019). The computational power of timed p systems with active membranes using promoters. Mathematical Structures in Computer Science, 29(5), 663–680. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0960129518000282
Gaol, F. L., & Matsuo, T. (2020). Solving the graph problem on the maximal clique problem on the p-systems with mitochondria enzymes layer. Applied Sciences-Basel. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10010275
Song, B., & Kong, Y. (2019). Solution to pspace-complete problem using p systems with active membranes with time-freeness. Mathematical Problems in Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5793234
Song, B., Zeng, X., & Rodríguez-Patón, A. (2021). Monodirectional tissue p systems with channel states. Information Sciences, 546, 206–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2020.08.030
Song, B., & Zeng, X. (2021). Solving a pspace-complete problem by symport/antiport p systems with promoters and membrane division. Journal of Membrane Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41965-021-00084-0
Dalvand, M., Fathi, A., & Kamran, A. (2021). Flooding region growing: a new parallel image segmentation model based on membrane computing. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 18(1), 37–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-020-00949-0
Gou, X., Liu, Q., Rong, H., Hu, M., Paul, P., Deng, F., Zhang, X., & Yu, Z. (2021). A novel spiking neural p system for image recognition. International Journal of Unconventional Computing, 16(2–3), 121–139.
Yuan, J., Guo, D., Zhang, G., Paul, P., Zhu, M., & Yang, Q. (2019). A resolution-free parallel algorithm for image edge detection within the framework of enzymatic numerical p systems. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24071235
Li, B., Peng, H., Luo, X., Wang, J., Song, X., Pérez-Jiménez, M. J., & Riscos-N’uñez, A. (2021). Medical image fusion method based on coupled neural p systems in nonsubsampled shearlet transform domain. International Journal of Neural Systems. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065720500501
Hao, L., & Liu, J. (2019). Enhanced membrane computing algorithm for sat problems based on the splitting rule. Symmetry-Basel. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym11111412
Zhu, M., Yang, Q., Dong, J., Zhang, G., Gou, X., Rong, H., Paul, P., & Neri, F. (2021). An adaptive optimization spiking neural p system for binary problems. International Journal of Neural Systems. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065720500549
Song, T., Luo, L., He, J., Chen, Z., & Zhang, K. (2014). Solving subset sum problems by time-free spiking neural p systems. Applied Mathematics & Information Sciences, 8(1), 327–332.
Ramachandranpillai, R., & Arock, M. (2021). A solution to dynamic green vehicle routing problems with time windows using spiking neural p systems with modified rules and learning. The Journal of Supercomputing, 77(9), 9689–9720. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-03635-5
RamachandranPillai, R., & Arock, M. (2021). Spiking neural firefly optimization scheme for the capacitated dynamic vehicle routing problem with time windows. Neural Computing and Applications, 33(1), 409–432. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-020-04983-8
Wang, X., Zhang, G., Gou, X., Paul, P., Neri, F., Rong, H., Yang, Q., & Zhang, H. (2021). Multi-behaviors coordination controller design with enzymatic numerical p systems for robots. Integrated Computer-Aided Engineering, 28(2), 119–140. https://doi.org/10.3233/Ica-200627
Xu, J., Huang, Y., & Liu, Y. (2020). Attitude optimization control of unmanned helicopter in coal mine using membrane computing. Mathematical Problems in Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3820896.
Niu, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J., & Xiao, J. (2018). Running cells with decision-making mechanism: Intelligence decision p system for evacuation simulation. International Journal of Computers Communications & Control, 13(5), 865–880.
Sapp, K., Sodt, A. J., & Maibaum, L. (2019). Modeling relaxation timescales of coupled membrane/protein systems. Biophysical Journal, 116(3), 363–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2018.11.1975
Gheorghe, M., Ceterchi, R., Ipate, F., Konur, S., & Lefticaru, R. (2018). Kernel p systems: From modelling to verification and testing. Theoretical Computer Science, 724, 45–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2017.12.010
Liu, W., Wang, T., Zang, T., Huang, Z., Wang, J., Huang, T., et al. (2020). A fault diagnosis method for power transmission networks based on spiking neural p systems with self-updating rules considering biological apoptosis mechanism. Complexity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2462647.
Huang, Z., Wang, T., Liu, W., Valencia-Cabrera, L., Perez-Jimenez, M. J., & Li, P. (2021). A fault analysis method for three-phase induction motors based on spiking neural p systems. Complexity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/2087027.
Aman, B., & Ciobanu, G. (2020). Spiking neural p systems with astrocytes producing calcium. International Journal of Neural Systems. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065720500665
Bîlbîe, F.-D., & Păun, A. (2021). Small snq p systems with multiple types of spikes. Theoretical Computer Science, 862, 14–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2020.10.014
Peng, H., Wang, J., Pérez-Jiménez, M. J., & Riscos-N’uñez, A. (2019). Dynamic threshold neural p systems. Knowledge-Based Systems, 163, 875–884. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2018.10.016
Zeng, X., Zhang, X., Song, T., & Pan, L. (2014). Spiking neural p systems with thresholds. Neural Computation, 26(7), 1340–1361. https://doi.org/10.1162/NECO_a_00605
Song, T., Gong, F., Liu, X., Zhao, Y., & Zhang, X. (2016). Spiking neural p systems with white hole neurons. IEEE Transactions on Nanobioscience, 15(7), 666–673. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnb.2016.2598879
Wu, T., Zhang, L., & Pan, L. (2021). Spiking neural p systems with target indications. Theoretical Computer Science, 862, 250–261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2020.07.016
Wu, T., Lyu, Q., & Pan, L. (2021). Evolution-communication spiking neural p systems. International Journal of Neural Systems. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0129065720500641
Yang, Q., Li, B., Huang, Y., Peng, H., & Wang, J. (2020). Spiking neural p systems with structural plasticity and anti-spikes. Theoretical Computer Science, 801, 143–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2019.08.034
Zhang, X., Wang, B., & Pan, L. (2014). Spiking neural p systems with a generalized use of rules. Neural Computation, 26(12), 2925–2943. https://doi.org/10.1162/NECO_a_00665
Lv, Z., Bao, T., Zhou, N., Peng, H., Huang, X., Riscos-N’uñez, A., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2021). Spiking neural p systems with extended channel rules. International Journal of Neural Systems. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065720500495
Song, X., Valencia-Cabrera, L., Peng, H., Wang, J., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2021). Spiking neural p systems with delay on synapses. International Journal of Neural Systems. https://doi.org/10.1142/s0129065720500422
Garcia, L., Sanchez, G., Vazquez, E., Avalos, G., Anides, E., Nakano, M., Sanchez, G., & Perez, H. (2021). Small universal spiking neural p systems with dendritic/axonal delays and dendritic trunk/feedback. Neural networks : the official journal of the International Neural Network Society, 138, 126–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2021.02.010
Lv, Z., Kou, J., Yi, W., Peng, H., Song, X., & Wang, J. (2020). Sequential coupled neural p systems. International Journal of Unconventional Computing, 15(3), 157–191.
Song, T., Pang, S., Hao, S., Rodriguez-Paton, A., & Zheng, P. (2019). A parallel image skeletonizing method using spiking neural p systems with weights. Neural Processing Letters, 50(2), 1485–1502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-018-9947-9
Zeng, X., Song, T., Zhang, X., & Pan, L. (2012). Performing four basic arithmetic operations with spiking neural p systems. IEEE Transactions on Nanobioscience, 11(4), 366–374. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnb.2012.2211034
Song, T., Zeng, X., Zheng, P., Jiang, M., & Rodriguez-Paton, A. (2018). A parallel workflow pattern modeling using spiking neural p systems with colored spikes. IEEE Transactions on Nanobioscience, 17(4), 474–484. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnb.2018.2873221
Zhang, G., Zhang, X., Rong, H., Paul, P., Zhu, M., Neri, F., & Ong, Y.-S. (2022). A layered spiking neural system for classification problems. International journal of neural systems. https://doi.org/10.1142/s012906572250023x
Rong, H., Yi, K., Zhang, G., Dong, J., Paul, P., & Huang, Z. (2019). Automatic implementation of fuzzy reasoning spiking neural p systems for diagnosing faults in complex power systems. Complexity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2635714.
Wu, T., Paun, A., Zhang, Z., & Pan, L. (2018). Spiking neural p systems with polarizations. IEEE transactions on neural networks and learning systems, 29(8), 3349–3360. https://doi.org/10.1109/tnnls.2017.2726119
Wu, T., Pan, L., & Alhazov, A. (2019). Computation power of asynchronous spiking neural p systems with polarizations. Theoretical Computer Science, 777, 474–489. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2018.10.024
Wu, T., & Pan, L. (2020). The computation power of spiking neural p systems with polarizations adopting sequential mode induced by minimum spike number. Neurocomputing, 401, 392–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.03.095
Yang, Q., Lv, Z., Liu, L., Peng, H., Song, X., & Wang, J. (2019). Spiking neural p systems with multiple channels and polarizations. Biosystems. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystems.2019.104020
Jiang, S., Fan, J., Wang, Y., & Xu, F. (2020). Spiking neural p systems with communication on request and polarizations. International Journal of Unconventional Computing, 15(1–2), 107–126.
Jiang, S., Fan, J., Liu, Y., Wang, Y., & Xu, F. (2020). Spiking neural p systems with polarizations and rules on synapses. Complexity. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8742308.
Wu, T., Zhang, T., & Xu, F. (2020). Simplified and yet turing universal spiking neural p systems with polarizations optimized by anti-spikes. Neurocomputing, 414, 255–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.07.051
Pan, L., Zeng, X., Zhang, X., & Jiang, Y. (2012). Spiking neural p systems with weighted synapses. Neural Processing Letters, 35(1), 13–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-011-9201-1
Wang, J., Hoogeboom, H. J., Pan, L., Păun, G., & Pérez-Jiménez, M. J. (2010). Spiking neural p systems with weights. Neural computation, 22(10), 2615–2646. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco_a_00022
Pan, L., & Paun, G. (2009). Spiking neural p systems with anti-spikes. International Journal of Computers Communications & Control 4(3), 273–282. https://doi.org/10.15837/ijccc.2009.3.2435
Song, T., Jiang, Y., Shi, X., & Zeng, X. (2013). Small universal spiking neural p systems with anti-spikes. Journal of Computational and Theoretical Nanoscience, 10(4), 999–1006. https://doi.org/10.1166/jctn.2013.2799
Korec, I. (1996). Small universal register machines. Theoretical Computer Science, 168(2), 267–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3975(96)00080-1
Cavaliere, M., Ibarra, O. H., Păun, G., Egecioglu, O., Ionescu, M., & Woodworth, S. (2009). Asynchronous spiking neural p systems. Theoretical Computer Science, 410(24), 2352–2364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcs.2009.02.031
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61806114, 61472231, 61876101, 61602282, 61402187, 61502283, 61802234, 61703251), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No.2018M642695, 2019T120607).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhao, Y. Weighted spiking neural P systems with polarizations and anti-spikes. J Membr Comput 4, 269–283 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41965-022-00112-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41965-022-00112-7