Abstract
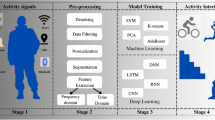
Pattern lock, an effective and convenient authentication mechanism, has been widely used in smart devices to resist malicious attacks. However, increasing in smart devices’ quantity and variety can contribute to the possibility of credential compromise, which can impair security of traditional pattern unlocking. The basic intuition of our proposed system is to utilize users’ behaviors when inputting pattern passwords as additional information, thus users’ devices remain safe even though the pattern passwords on any other devices are disclosed to attacker. First, the mobile crowd sensing is adopted for users to collect their behavior information unconsciously. Moreover, considering the interaction authentication among heterogeneous devices, we normalize sensor readings to reduce its diversity impacts. In case of multi-modal, we adopt domain adaption to transfer authentication model from single designated posture to all scenarios, thus enable the security in more realistic and complex applications. In addition, we also reduce the amount of required samples to improve users’ experience. Based on 28,800 samples collected from 40 participants on five devices, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our system.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andriotis, P., Oikonomou, G., Mylonas, A., et al.: A study on usability and security features of the Android pattern lock screen. Inf. Comput. Secur. 24, 53–72 (2016)
Andriotis, P., Oikonomou, G., Mylonas, A., et al.: A study on usability and security features of the Android pattern lock screen. Inf. Comput. Secur. 24(1), 53–72 (2016)
Binbeshr, F., Kiah, M., Por, Y.L., Zaidan, A.A.: A systematic review of pin-entry methods resistant to shoulder-surfing attacks. Comput. Secur. 101, 1–14 (2020)
Feng, T., Yang, J., Yan, Z., et al.: TIPS: context-aware implicit user identification using touch screen in uncontrolled environments. In: Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems & Applications, pp. 1–6. ACM (2014)
Gui-song, Y.A.N.G., Han-qing, L.I., Xing-yu, H.E.: Incentive mechanism based on user collaboration pair for mobile crowd sensing. J. Chin. Comput. Syst. 43(7), 1401–1405 (2022)
Gurary, J., Ye, Z., Alnahash, N., et al.: Implicit authentication for mobile devices using typing behavior. International Conference on Human Aspects of Information Security, pp.25–36. Springer (2016)
Inoue, M., Ogawa, T.: TapOnce: a novel authentication method on smartphones. Int. J. Pervasive Comput. Commun. 14, 33–48 (2018)
Khan, H., Hengartner, U.: Towards application-centric implicit authentication on smartphones[C]. In: Proceedings of the 15th Workshop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications, pp. 1–6. ACM (2014)
Massoli, F.V., Carrara, F., Amato, G., Falchi, F.: Detection of face recognition adversarial attacks. Comput Vis Image Underst 202, 1–11 (2021)
Schölkopf, B., Platt, J., Hofmann, T.: Correcting sample selection bias by unlabeled data. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19: Proceedings of the 2006 Conference, pp. 601–608. MIT Press (2007)
Shi, D., Tao, D.: Sensor fusion based implicit authentication for smartphones. In: 14th China Conference on Internet of Things (Wireless Sensor Network), pp. 157–168 (2020)
Shi, D., Tao, D., Wang, J.T., et al.: Fine-grained and context-aware behavioral biometrics for pattern lock on smartphones. Proc ACM Interact Mobile Wearable Ubiquitous Technol 33, 1–30 (2021)
Shin, H., Sim, S., Kwon, H., et al.: A new smart smudge attack using CNN. Int. J. Inf. Secur. 21, 1–12 (2021)
Vhaduri, S., Poellabauer, C.: Summary: multi-modal biometric-based implicit authentication of wearable device users. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forens. Secur. 14, 3116–3125 (2019)
Xue, M., He, C., Wang, J., et al.: LOPA: a linear offset based poisoning attack method against adaptive fingerprint authentication system. Comput. Secur. 99, 1–13 (2020)
Yao, M.Y., Tao, D.: Implicit authentication mechanism of pattern unlock based on over-sampling and one-class classification for smartphones. Comput. Sci., pp. 19–24 (2020)
Ye, G., Tang, Z., Fang, D., Chen, X., Wolff, W., Aviv, A.J., Wang, Z.: A video-based attack for android pattern lock. ACM Trans. Priv. Secur. (TOPS) 21(4), 1–31 (2018)
Zafar, M. R., Shah, M.A.: Fingerprint authentication and security risks in smart devices. In: International Conference on Automation Computing, pp. 1-6. IEEE (2016)
Zhang, Y., Hu, W., Xu, W., et al.: Continuous authentication using eye movement response of implicit visual stimuli. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 1(4), 1–22 (2018)
Zheng, N., Bai, K., Huang, H., Wang, H.: You are how you touch: user verification on smartphones via tapping behaviors. In: 2014 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Network Protocols, pp. 221–232 (2014)
Zhou, M., Wang, Q., Yang, J., et al.: PatternListener: cracking android pattern lock using acoustic signals. p 1775–1787 (2018)
Zhou, J., Fan, J., Wang, J.: Task scheduling for mobile edge computing enabled crowd sensing applications. Int. J. Sens. Netw. 35(2), 88–98 (2021)
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant numbers 61872027) and the Open Research Fund of the State Key Laboratory of Integrated Services Networks (Grant numbers ISN21-16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose. We ensure that there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, Z., Yao, M. & Tao, D. Implicit authentication with sensor normalization and multi-modal domain adaption based on mobile crowd sensing. CCF Trans. Pervasive Comp. Interact. 4, 370–380 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42486-022-00117-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42486-022-00117-2