Abstract
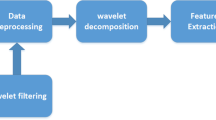
The thriving development of big data has provided powerful techniques for pedestrian counting and monitoring in public places, which has attracted great attention. Current pedestrian counting solutions based on computer vision and sensors have privacy leakage issues and cost issues. As a wireless technique, millimeter wave has diverse application scenarios because of its advantages of safety, cheapness and stability. In this paper, we propose a novel system to realize pedestrian counting leveraging millimeter wave. Based on the point cloud data collected by radar, we design an efficient denoising algorithm based on the point cloud distribution and transform the problem into a multi-classification task, and then extract features from pedestrian trajectories to form a series of density maps describing pedestrians’ movement information. We also propose a classifier model mmCountNet to accurately predict the pedestrian and build a data set containing 2000 samples for model training. The experiment results show that the accuracy of the proposed system is 95.92% in the Single-Crowd testing, and 91.35% in the Multi-Crowds testing, which basically achieves the purpose of pedestrian counting.

























Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
In our work, we designed and collected a dataset containing 2000 samples with a total time of 6.7 h for training the model. If readers need more details about the dataset, they can contact corresponding author through email.
References
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 886–893 (2005)
Dollár, P., Tu, Z., Perona, S. P.: Belongie: integral channel features. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, pp. 1–11 (2009)
Feng, Y., Zhang, K., Wang, C., Xie, L., Ning, J., Chen, S.: mmeavesdropper: signal augmentation-based directional eavesdropping with mmwave radar. In: IEEE INFOCOM 2023-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications, pp. 1–10 (2023)
Filipic, J., Biagini, M., Mas, I., Pose, C.D., Giribet, J.I., Parisi, D.R.: People counting using visible and infrared images. Neurocomputing 450, 25–32 (2021)
Hafeezallah, A., Al-Dhamari, A., Abu-Bakar, S.A.R.: U-asd net: supervised crowd counting based on semantic segmentation and adaptive scenario discovery. IEEE Access. 9, 127444–127459 (2021)
Kianoush, S., Savazzi, S., Rampa, V., Nicoli, M.: People counting by dense WiFi MIMO networks: channel features and machine learning algorithms. Sensors. 19(16), 3450 (2019)
Kong, H., Chen, Z., Yue, W., Ni, K.: Improved YOLOv4 for pedestrian detection and counting in UAV images. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 6106853 (2022)
Lee, S.P., Kini, N.P., Peng, W.H., Ma, C.W., Hwang, J.N.: Hupr: A benchmark for human pose estimation using millimeter wave radar. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 5715–5724 (2023)
Lesani, A., Nateghinia, E., Miranda-Moreno, L.F.: Development and evaluation of a real-time pedestrian counting system for high-volume conditions based on 2d lidar. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 114, 20–35 (2020)
Li, H., Liu, S. R.and Wang, Jiang, W., Lu, C.X.: Pedestrian liveness detection based on mmWave radar and camera fusion. In: 19th Annual IEEE International Conference on Sensing, Communication, and Networking (SECON), pp. 262–270 (2022)
Li, J., He, Q., Zhang, C., Wang, H.: An indoor people counting model based on global attention. Comp. Eng. Sci./Jisuanji Gongcheng yu Kexue. 44(3), 471–478 (2022)
Liu, H., Wang, Y., Zhou, A., He, H., Wang, W., Wang, K., Pan, P., Lu, Y., Liu, L., Ma, H.: Real-time arm gesture recognition in smart home scenarios via millimeter wave sensing. Proc. ACM Inter. Mob. Weara. Ubiquitous Technol. 4(4), 1–28 (2020)
Liu, L., Jiang, J., Jia, W., Amirgholipour, S., Wang, Y., Zeibots, M., He, X.: Denet: a universal network for counting crowd with varying densities and scales. IEEE Trans. Multimedia 23, 1060–1068 (2020)
Lv, M., Zhang, W., Zhang, C., Liu, X.: A pedestrian sensing warning system with edge compute module on millimeter wave radar. In: International Conference on Transportation and Development, pp. 261–270 (2022)
Meng, Z., Fu, S., Yan, J., Liang, H., Zhou, A., Zhu, S., Ma, H., Liu, J.: Gait recognition for co-existing multiple people using millimeter wave sensing. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 849–856 (2020)
Pham, C.T., Luong, V.S., Nguyen, D.K., Vu, H.H.T., Le, M.: Convolutional neural network for people counting using UWB impulse radar. J. Instrum. 16(08), 08031 (2021)
Sandaruwan, R., Alagiyawanna, I., Sandeepa, S., Dias, S., Dias, D.: Device-free pedestrian count estimation using wi-fi channel state information. In: 2021 IEEE International Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), pp. 2610–2616 (2021)
Shahzad, A.R., Jalal, A.: A smart surveillance system for pedestrian tracking and counting using template matching. In 2021 International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Industry (ICRAI), pp. 1-6 (2021)
Shang, H., Sun, L., Qin, W.: Pedestrian detection at night based on the fusion of infrared camera and millimeter-wave radar. Chin. J. Sens. Actuat. 34(9), 1137–1145 (2020)
Shen, J., Xiong, X., Xue, Z., Bian, Y.: A convolutional neural-network-based pedestrian counting model for various crowded scenes. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 34(10), 897–914 (2019)
Wang, H., Zhang, D., Ma, J., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., Wu, D., Gu, T., Xie, B.: Human respiration detection with commodity WiFi devices: Do user location and body orientation matter? In: Proceedings of the 2016 ACM international joint conference on pervasive and ubiquitous computing, pp. 25–36 (2016)
Xiao, J., Ding, L., Shu, X., Zhang, W.: A computer vision-based pedestrian traffic counting method. Inform. Technol. 39(8), 22–25 (2015)
Yan, B., Wang, P., Du, L., Chen, X., Fang, Z., Wu, Y.: mmgesture: Semi-supervised gesture recognition system using mmwave radar. Expert Syst. Appl. 213, 119042 (2023)
Yang, Y., Xu, H., Chen, Q., Cao, J., Wang, Y.: Multi-vib: precise multi-point vibration monitoring using mmwave radar. Proc. ACM Inter. Mob. Wearab. Ubiquitous Technol. 6(4), 1–26 (2023)
Yao, Y., Zhang, X., Liang, X.Y., Zhang, S.F., Zhao, J.: A real-time pedestrian counting system based on rgb-d. In: 2020 12th international conference on advanced computational intelligence (ICACI), pp. 110-117 (2020)
Yu, Y., Qin, X., Hussain, S., Hou, W., Weis, T.: Pedestrian counting based on piezoelectric vibration sensor. Appl. Sci. 12(4), 1920 (2022)
Zeng, Y., Wu, D., Xiong, J., Yi, E., Gao, R., Zhang, D.: Farsense: Pushing the range limit of wifi-based respiration sensing with csi ratio of two antennas. Proc. ACM Inter. Mob. Wearab. Ubiquitous Technol. 3(3), 1–26 (2019)
Zeng, Y., Wu, D., Xiong, J., Liu, J., Liu, Z., Zhang, D.: Multisense: enabling multi-person respiration sensing with commodity wifi. Proc. ACM Inter. Mob. Wearab. Ubiquitous Technol. 4(3), 1–29 (2020)
Zeng, S., Wan, H., Shi, S., Wang, W.: msilent: towards general corpus silent speech recognition using cots mmwave radar. Proc. ACM Inter. Mob. Wearab. Ubiquitous Technol. 7(1), 1–28 (2023)
Zhang, Z., Wang, X., Huang, D., Fang, X., Zhou, M., Zhang, Y.: Mrpt: millimeter-wave radar-based pedestrian trajectory tracking for autonomous urban driving. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 71, 1–17 (2021)
Zhao, P., Lu, C.X., Wang, J., Chen, C., Wang, W., Trigoni, N., Markham, A.: Human tracking and identification through a millimeter wave radar. Ad Hoc Netw. 116, 102475 (2021)
Zhou, W., Pan, Y., Lei, J., Ye, L., Yu, L.: Defnet: dual-branch enhanced feature fusion network for rgb-t crowd counting. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 23(12), 24540–24549 (2022)
Zhu, J., Cao, J., Yang, Y., Ren, W., Han, H.: mmDrive: Fine-grained fatigue driving detection using mmWave radar. ACM Trans. Internet Things 4(4), 1–30 (2023)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported in part by National Key R &D Program of China under Grant No. 2022YFB3303900; National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 62372224, 62272216, 61832008; The Key R &D Program of Jiangsu Province under Grant BE2020001–3. This work is partially supported by Collaborative Innovation Center of Novel Software Technology and Industrialization under Grant Nos. 62272216. This work is partially supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities No. 2023300175(020214380100). Chuyu Wang is the corresponding author.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Wang, C., Xie, L. et al. Research on pedestrian counting based on millimeter wave. CCF Trans. Pervasive Comp. Interact. 6, 82–100 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42486-023-00145-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42486-023-00145-6