Abstract
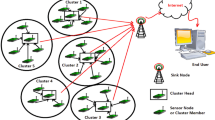
In Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs), the transmission of information through wireless medium is facilitated using nodes which are small and self-organizing and moreover enhances the process. The energy saving and effective utilization of energy are major issues in WSNs. The relationship between the cluster heads and sensor nodes was only considered in previous cluster-based routing protocols by ignoring the cost differences among them. The residual nodes, which are not considered as cluster members, may exist in certain existing clustering protocols. The network lifetime might be reduced by these residual nodes. Clustering is a proven technique for energy optimization. However, most of the clustering algorithms failed to address the routing overhead and the energy consumption rate between the CH nodes and the SINK node. Here, we introduce a new improved energy-efficient intra-cluster routing technique using mobile agents to reduce communication overhead and an optimal positioning strategy of SINK node using PSOGA for energy optimization. A novel framework is proposed in this method, in which an effective clustering mechanism using Intra Mobile Agents (IN-MA) is present. Moreover, on the basis of the network structure, an optimal position is determined for the sink by introducing a Particle Swarm Optimization-Genetic Algorithm (PSO-GA)-based location estimation algorithm. The data are collected from the members and delivered to the CHs using Intra Mobile Agents. The PSO-GA algorithm estimates the optimal position of a sink. Based on the experimental results, the better outcomes are observed using the proposed method when compared to the previous techniques. The parameters like lifetime of a network, consumption of energy, and throughput rate are considered mainly to analyze the efficiency of the proposed energy-efficient strategy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Steen M, Tanenbaum A. Distributed systems principles and paradigms. Network. 2002;2:28.
Enami N, Askari Moghadam R, Haghighat AT. A survey on application of neural networks in energy conservation of wireless sensor networks. In: WiMo 2010, CCIS 84. Heidelberg: Springer; 2010. p. 283–94.
Qi H, Iyengar S, Chakrabarty K. Distributed sensor networks—a review of recent research. J Franklin Inst. 2001;338:655–68.
Zhao F, Shin J, Reich J. Information-driven dynamic sensor collaboration. IEEE Signal Process Mag. 2002;19(2):61–72.
Akyildiz IF, Su W, Subramaniam Y, Cayirci E. A survey on sensor networks. IEEE Commun Mag. 2002;40(8):104–12.
Jiang X, Hong B. ACO based energy-balance routing algorithms for WSNs. In: LNCS-6145. Heidelberg: Springer; 2010. p. 298–305.
Akkaya K, Younis M. A survey on routing protocols for wireless sensor networks. Ad hoc networks. 2005;3(3):325–49.
Goyal D, Tripathy MR. January. Routing protocols in wireless sensor networks: A survey. IEEE; 2012. p. 474–80.
Zhang D, Li G, Zheng K, Ming X, Pan Z-H. An energy-balanced routingmethod based on forward-aware factor for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans Industr Inf. 2014;10(1):766–73. https://doi.org/10.1109/TII.2013.2250910.
Vazirani VV. Approximation algorithms. Berlin: Springer; 2013.
Du H, Xu Y, Zhu B. An incremental version of the k-center problem on boundary of a convex polygon. J Comb Optim. 2015;30(4):1219–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-015-9933-3.
Liang D, Mei L, Willson J, Wang W. A simple greedy approximation algorithm for the minimum connected kcenter problem. J Comb Optim. 2016;31(4):1417–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10878-015-9831-8.
Akkaya K, Younis M. An energy-aware QoS routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. In: Distributed computing systems workshops, 2003. proceedings 23rd international conference on IEEE. 2003. p. 710–5. http://csdl.compu ter.org/comp/proceedings/icdcsw/2003/1921/00/19210710abs.htm.
Xu Y, Qi H, Kuruganti PT. Distributed computing paradigms for collaborative processing in sensor networks. In GLOBECOM'03. IEEE global telecommunications conference (IEEE Cat. No. 03CH37489). IEEE. 2003;6:3531–5.
Xu Y, Qi H. Distributed computing paradigm for collaborative signal and information processing in sensor networks. J Parallel Distrib Comput. 2004;64(8):945–59.
Mohajerani A, Gharavian D. Wirel Netw. 2016;22:2637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-1061-6.
Lohani D, Varma S. Wirel Pers Commun. 2016;89:1165. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3310-0.
Kong L, Pan JS, Snášel V, et al. Telecommun Syst. 2018;67:451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-017-0348-6.
Kaswan A, Singh V, Jana PK. A multi-objective and PSO based energy efficient path design for mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. 2018;46:122–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmcj.2018.02.003 ISSN 1574–1192.
Medina CD, Cortes NC. Routing algorithms for wireless sensor networks using ant colony optimization. In: MICAI 2010, part II, LNAL-6438. Heidelberg: Springer; 2010. p. 337–48.
Cheng D, Xun Y, Zhou T, Li W. An energy aware ant colony routing algorithms for the routing of wireless sensor networks. In: ICICIS 2011, part I, CCIS-134. Heidelberg: Springer; 2011. p. 395–401.
Wang X, Li Q, Xiong N, Pan Y. Ant colony optimization-based location-aware routing for wireless sensor networks. In: Li Y, Huynh DT, Das SK, Du DZ, editors. WASA 2008, vol. 5258. LNCS Heidelberg: Springer; 2008. p. 109–20.
Shih HC, Chu SC, Roddick JF, Hung MH, Pan JS. Power reduction of wireless sensor networks using ant colony optimization. In: 2010 international conference on computational aspects of social networks. IEEE; 2010. p. 464–7.
Camilo T, Carreto C, Silva JS, Boavida F. An energy-efficient ant-based routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. In: Dorigo M, Gambardella LM, Birattari M, Martinoli A, Poli R, Stutzle T, editors. ANTS 2006, vol. 4150. LNCS Heidelberg: Springer; 2006. p. 49–59.
Zhong, Z., Tian, Z., Li, Z. and Xu, P. An ant colony optimization competition routing algorithm for WSN. In 2008 4th International conference on wireless communications, networking and mobile computing, IEEE. 2008;pp 1–4.
Amgoth T, Jana PK. Energy-aware routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Computers & electrical engineering. 2015;41:357–67.
Kassotakis IE, Markaki ME, Vasilakos AV. A hybrid genetic approach for channel reuse in multiple access telecommunication networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun. 2000;18(2):234–43.
Chen M, Gonzalez S, Leung VC. Applications and design issues of mobile agents in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Wirel Commun Magazine (Special Issue on Wireless Sensor Networking). 2007;14(6):20–6.
Qi H, Wang F. Optimal itinerary analysis for mobile agents in ad hoc wireless sensor networks. Proceedings of the IEEE. 2001;18(5):147–53.
Chen M, Kwon T, Yuan Y, Choi Y, Leung VC. Mobile agent-based directed diffusion in wireless sensor networks. EURASIP J Adv Signal Process. 2007;2007(1):219.
Wu Q, Rao NSV, Barhen J, Sitharama Iyengar S, Vaishnavi VK, Qi H, Chakrabarty K. On computing mobile agent routes for data fusion in distributed sensor networks. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. 2004;16(6):740–53.
Chen M, Leung V, Mao S, Kwon T, Li M. Energy-efficient itinerary planning for mobile agents in wireless sensor networks. IEEE; 2009. p. 1–5.
Yu J, Qi Y, Wang G, Gu X. A cluster-based routing protocol for wireless sensor networks with nonuniform node distribution. AEU-Int J Electron Commun. 2012;66(1):54–61.
Bagci H, Yazici A. An energy aware fuzzy approach to unequal clustering in wireless sensor networks. Appl Soft Comput. 2013;13(4):1741–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2012.12.029.
Yu Y, Govindan R, Estrin D. Geographical and energy aware routing: A recursive data dissemination protocol for wireless sensor networks. 2001.
Kaswan A, Nitesh K, Jana PK. A routing load balanced trajectory design for mobile sink in wireless sensor networks. In: 2016 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics (ICACCI). IEEE; 2016. p. 1669–73.
Kaswan A, Nitesh K, Jana PK. Energy efficient path selection for mobile sink and data gathering in wireless sensor networks. AEU-Int J Electron Commun. 2017;73:110–8.
Wang C-F, Shih J-D, Pan B-H, Tin-Yu Wu. A network lifetime enhancement method for sink relocation and its analysis in wireless sensor networks. Sens J IEEE. 2014;14(6):1932–43.
Zhu C, Shuai W, Han G, Shu L, Hongyi W. A tree-cluster-based data-gathering algorithm for industrial wsns with a mobile sink. IEEE Access. 2015;3:381–96.
Jain S, Shah RC, Brunette W, Borriello G, Roy S. Exploiting mobility for energy efficient data collection in wireless sensor networks. Mob Netw Appl. 2006;11(3):327–39.
Palan NG, Barbadekar BV, Patil S. Low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy (LEACH) protocol: A retrospective analysis. In: 2017 International conference on inventive systems and control (ICISC) IEEE; 2017. p. 1–12.
Agarwal K, Agarwal K, Muruganandam K. Low energy adaptive clustering hierarchy (leach) protocol: Simulation and analysis using matlab. In: 2018 International conference on computing, power and communication technologies (GUCON) IEEE; 2018. p. 60–4.
Ghosh S, Kannu AP. Relay placement and spectrum sharing strategies for soft and fractional frequency reuse schemes. In 2015 twenty first National Conference on Communications (NCC), IEEE; 2015. p. 1–6.
Sanyal R, Jaiswal M, Chaudhury KN. On a registration-based approach to sensor network localization. IEEE Trans Signal Process. 2017;65(20):5357–67.
Funding
No financial support from private or government institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the topical collection “Sensor Networks” guest edited by César Benavente-Peces and Nirwan Ansari.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rambabu, C., Prasad, V.V.K.D.V. & Prasad, K.S. A New Version of Energy-Efficient Optimization Protocol Using ICMA-PSOGA Algorithm in Wireless Sensor Network. SN COMPUT. SCI. 3, 353 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-022-01232-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-022-01232-8