Abstract
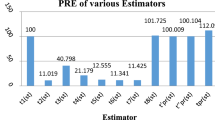
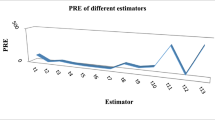
In this article, we consider the memory type product estimator to estimate the population mean of the study variable in stratified random sampling. The suggested estimators’ bias and mean square error (MSE) expressions for the first order of approximation are derived. The proposed estimator is compared with the competing estimators under consideration and the efficiencies’ conditions are obtained. Further, we obtain the optimum allocation of samples in different strata along with MSEs. To achieve the solution of the problem, we frame our problem as AINLPP and solve through genetic programming technique. To show the efficiency of the estimator, we conduct simulation study. An empirical analysis based on real-life data is also offered to support the findings of the simulation study. The most efficient estimator is recommended for different practical applications. The suggested estimator is proven to be the best among the competing estimators.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Materials
Not applicable.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Robson DS. Applications of multivariate polykays to the theory of unbiased ratio type estimation. J Am Stat Assoc. 1957;59:511–22.
Bandopadhyaya S. Improved ratio and product estimators. Sankhy a Ser C. 1980;42(1–2):262–75.
Agrawal MC, Jain N. A new predictive product estimator. Biometrika. 1991;76(4):822–3.
Khoshnevisan M, Singh R, Chauhan P, Sawan N, Smarandache F. A general family of estimators for estimating population mean using known value of some population parameter(s). Far East J Theor Stat. 2007;22:181–91.
Koyuncu N, Kadilar C. Ratio and product estimators in stratified random sampling. J Stat Plann Inference. 2009;139:2552–8.
Searls TJ. Utilization of known coefficient of kurtosis in the estimation procedure of variance. J Am Stat Assoc. 1991;59:1225–6.
Singh HP, Vishwakarma GK. A general procedure for estimating population mean in successive sampling. Commun Stat. 2009;38(2):293–308.
Noor–Ul–Amin M, Asghar SUD, Sanaullah A, Shehzad MA. Redescending M–estimator for robust regression. J Reliabil Stat Stud. 2018;2(2):69–80.
Noor–Ul–Amin M. Memory type estimators of population mean using exponentially weighted moving averages for time scaled surveys. Commun Stat. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/03610926.2019.1670850.
Raza A, Noor–Ul–Amin M, Hanif M. Regression–in–ratio estimators in the presence of outliers based on redescendingm–estimator. J Reliabil Stat Stud. 2019;2(12):01–10.
Aslam I, Noor–Ul–Amin M, Yasmeen U, Hanif M. Memory type ratio and product estimators in stratified sampling. J Reliabil Stat Stud. 2020;13(1):1–20.
Mradula, Yadav SK, Varshney R, Dube M. Efficient estimation of population mean under stratified random sampling with linear cost function. Commun Stat. 2021;50(12):4364–87.
Varshney R, Pal A, Yadav SK, Singh L. Optimal strategy for improved estimation of population mean under stratified sampling design using genetic programming. Int J Agric Stat Sci. 2022;18(2):799–804.
Raghav YS, Varshney R, Modibbo UM, Ahmadini AAH, Ali I. Estimation and optimization for system availability under preventive maintenance. IEEE Access. 2022;10:94337–53.
Acknowledgements
The authors are very much thankful to the editor in chief Prof. Umapada Pal, Section Editor Prof. Swagatam Das and learned referee for their critical reviews, which improved the manuscript.
Funding
No funding received to carry this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SKY planned the study, AP performed the study, and RV prepared the manuscript. GKV wrote the methodological details to finalize the manuscript. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict and competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yadav, S.K., Vishwakarma, G.K., Varshney, R. et al. Improved Memory Type Product Estimator for Population Mean in Stratified Random Sampling Under Linear Cost Function. SN COMPUT. SCI. 4, 235 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-01673-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-01673-9