Abstract
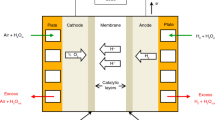
The value of parametric coefficients in proton exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFC) are not specified by the manufacturer thus it becomes necessary to extract those values as they affect the system performance. The losses in the FC systems highly depend on these parameters which result in reduced output voltage. To minimise the losses occurring in PEMFC, improving output voltage, obtaining a better V–I curve, and improving the performance of PEMFC system extraction of parameters are a must. A static semi-empirical PEMFC model is developed in MATLAB to estimate the value of parametric coefficients. Chaotic Embedded Particle Swarm Optimization (CEPSO) algorithm is used to estimate the optimal values of seven parametric coefficients of PEMFC. The voltage-based objective function is proposed to minimise the sum of squared error (SSE) which is obtained due to the difference in simulated values and experimental data collected at N points. The algorithm coding is done in MATLAB. A Ballard Mark V PEMFC stack is numerically simulated to depict the effectiveness of the parameter determination process. The V–I curve of the PEMFC model obtained using optimised values is verified with the simulated model curve. The minimum SSE of 0.690 was obtained in 63 iterations using CEPSO that showed a higher convergence. The proposed technique was verified for different operating conditions. The V–I curve obtained in both cases is closely matched. The performance of the proposed algorithm is compared with DKPSO, grasshopper optimization algorithm, chaotic Mayfly optimization algorithm and harmony global search algorithm. The proposed technique outperformed other mentioned techniques and proved its superiority over others in obtaining minimum error and a better V–I curve.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mitra U, Arya A, Gupta S, Gupta AK. A brief overview on fuel cell electric vehicles. In: International conference on emerging trends in engineering and medical sciences (ICETEMS), Nagpur, India 2022. pp. 124–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICETEMS56252.2022.10093428.
Akinyele D, Olabode E, Amole A. Review of fuel cell technologies and applications for sustainable microgrid systems. Inventions. 2020;5(3):42 (31–35).
Lai J, Ellis MW. Fuel cell power systems and applications. Proc IEEE. 2017;105(11):2166–90. https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2017.2723561.
Mitra U, Arya A, Dwivedi R, Gupta S, Paliwal P, Tomar S. Modelling proton exchange membrane fuel cell for power generation using multi-stage power conversion system. In: IEEE international students' conference on electrical, electronics and computer science (SCEECS), Bhopal, India, 2023. pp. 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/SCEECS57921.2023.10063048.
Mitra U, Arya A, Gupta S. A comprehensive and comparative review on parameter estimation methods for modelling proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Fuel. 2023;335:127080. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2022.127080. (ISSN 0016-2361).
Yu X, Starke MR, Tolbert LM, Ozpineci B. Fuel cell power conditioning for electric power applications: a summary. IET Electr Power Appl. 2007;1(5):643–56.
Ye M, Wang X, Xu Y. Parameter identification for proton exchange membrane fuel cell model using particle swarm optimization. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2009;34:981–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.11.026.
Salim R, Nabag M, Noura H, Fardoun AA. The parameter identification of the Nexa 1.2 kW PEMFC’s model using particle swarm optimization. Renew Energy. 2015;82:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2014.10.012z.
Isa ZM, Rahim NA. PEM fuel cell model parameters optimization using modified particle swarm optimization algorithm. In: IEEE conference on clean energy and technology (CEAT) 2013. pp. 442–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/CEAT.2013.6775672.
Askarzadeh A, Rezazadeh A. Optimization of PEMFC model parameters with a modified particle swarm optimization. Int J Energy Res. 2011;35:1258–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.1787.
Özdemir MT. Optimal parameter estimation of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells model with chaos embedded particle swarm optimization. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2021;46(30):16465–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.12.203.
Li X, Yan Q, Yu D. Parameter optimization for a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell model. Appl Mech Mater. 2010. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.37-38.834.
Sedighizadeh M, Kashani MF. A tribe particle swarm optimization for parameter identification of proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Int J Eng Trans A. 2015;28:16–25. https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.ije.2015.28.01a.03.
Li Q, Chen W, Wang Y, Liu S, Jia J. Parameter identification for PEM fuel-cell mechanism model based on effective informed adaptive particle swarm optimization. IEEE Trans Ind Electron. 2011;58(6):2410–9. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2010.2060456.
Abdullah A, Rezk H, Hadad A, Hassan M, Mohamed A. Optimal parameter estimation of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. Intell Autom Soft Comput. 2021;29:619–31. https://doi.org/10.32604/iasc.2021.018289.
Kumar P, Sathishkumar K, Natarajan R. A comprehensive review on parameter estimation techniques for proton exchange membrane fuel cell modelling. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2018;93:121-144.1325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.05.017.
Mitzel J, Gülzow A, Kabza A, Hunger J, Araya SS, Piela P, Alecha I, Tsotridis G. Identification of critical parameters for PEMFC stack performance characterization and control strategies for reliable and comparable stack benchmarking. Int J Hydrog Energy. 2016;41(46):21415–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.08.065.
Alatas B, Akin E, Bedri-Ozer A. Chaos embedded particle swarm optimization algorithms. Chaos Solitons Fractals. 2009;40(4):1715–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chaos.2007.09.063. (ISSN 0960 0779).
El-Fergany AA. Electrical characterisation of proton exchange membrane fuel cells stack using grasshopper optimiser. IET Renew Power Gener. 2017;12(1):9–17.
Shaheen MA, Hasanien HM, El Moursi MS, El-Fergany AA. Precise modelling of PEM fuel cell using improved chaotic MayFly optimization algorithm. Int J Energy Res. 2021;45:18754–69. https://doi.org/10.1002/er.6987.
Fahim SR, Hasanien HM, Turky RA, Alkuhayli A, Al-ShammaÁ AA, Noman AM, Tostado-Veliz M, Jurado F. Parameter identification of proton exchange membrane fuel cell based on hunger games search algorithm. Energies. 2021;5022:1–21.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the topical collection “Research Trends in Computational Intelligence” guest edited by Anshul Verma, Pradeepika Verma, Vivek Kumar Singh and S. Karthikeyan.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mitra, U., Arya, A., Gupta, S. et al. Parameter Estimation of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Model Using Chaotic Embedded Particle Swarm Optimization Technique. SN COMPUT. SCI. 4, 473 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-01957-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-01957-0