Abstract
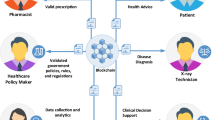
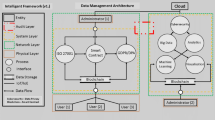
Security is essential for all facts, information sharing around the internet and maintaining personalized information. In recent days, the healthcare industry needs privacy-preserving to keep personalized data from others containing sensitive information. Due to increasing security breaches, fundamental sharing problems with personalized details shared on the internet lead to security problems. To resolve this problem, we propose a Secure Blockchain-based Healthcare-sensitive data prediction using a Pragmatic quasi identifier in a decentralized cloud environment. Pragmatic quasi-sensitivity Identification (PQSI) based Privacy-preserving for securing personalized records Using Hyper Recurrent feature classification for improved cloud security. Initially, the sensitivity fitness value of the feature is estimated through Intensive feature success rate (IFSR) and clustered by marginal subset features. By marginalizing the sensitivity threshold frequency rate, the components are extracted by pragmatic quasi-sensitive identifier and classified using Hyper recurrent Neural classification (HRNC) to find the sensitive and non-sensitive records based on frequency fitness weight to split and store perception as individually in the private cloud. Further, to improve the security level Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) based master node authentication technique is used in the blockchain concept. Peer end Block chain principle is applied to secure the sensitive data. To ensure the sensitive records are sanitized into data blocks to assure in a blockchain environment. This proposed system produces higher prediction accuracy than other methods and achieves higher sensitivity and specificity rate performance.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ram Mohan Rao P, Murali Krishna S, Siva Kumar AP. Privacy preservation techniques in big data analytics: a survey. J Big Data. 2018;5(33):1–12.
Liu X, Wang Z, Jin C, Li F, Li G. A blockchain-based medical data sharing and protection scheme. IEEE Access. 2019;7:118943–53.
Cha S, Baek S, Kim S. Blockchain-based sensitive data management by using key escrow encryption system from the perspective of supply chain. IEEE Access. 2020;8:154269–80.
Hua Y, Li Z, Wang B, Li J. A method for solving quasi-identifiers of single structured relational data. IEEE Access. 2021;9:166293–302.
Sei Y, Okumura H, Takenouchi T, Ohsuga A. Anonymization of sensitive quasi-identifiers for l-diversity and t-closeness. IEEE Trans Depend Secure Comput. 2019;16(4):580–93.
Jayapradha J, Prakash M, Alotaibi Y, Khalaf OI, Alghamdi SA. Heap bucketization anonymity—an efficient privacy-preserving data publishing model for multiple sensitive attributes. IEEE Access. 2022;10:28773–91.
Wu X, et al. Adaptive diffusion of sensitive information in online social networks. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. 2021;33(8):3020–34.
Sun Y, Sun Y, Dai H. Two-stage cost-sensitive learning for data streams with concept drift and class imbalance. IEEE Access. 2020;8:191942–55.
Yao L, Chen Z, Wang X, Liu D, Wu G. Sensitive label privacy preservation with anatomization for data publishing. IEEE Trans Depend Secure Comput. 2021;18(2):904–17.
Zhang R, Xue R, Liu L. Security and privacy for healthcare blockchains. IEEE Trans Serv Comput. 2022;15(6):3668–86.
Su Q, Zhang R, Xue R, Li P. Revocable attribute-based signature for blockchain-based healthcare system. IEEE Access. 2020;8:127884–96.
Itoo S, Khan A, Kumar V, Alkhayyat A, Ahmad M, Srinivas J. CKMIB: construction of key agreement protocol for cloud medical infrastructure using blockchain. IEEE Access. 2022;10:67787–801.
Ghayvat H, et al. CP-BDHCA: blockchain-based confidentiality-privacy preserving big data scheme for healthcare clouds and applications. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2022;26(5):1937–48.
Egala BS, Pradhan AK, Badarla V, Mohanty SP. Fortified-chain: a blockchain-based framework for security and privacy-assured internet of medical things with effective access control. IEEE Internet of Things J. 2021;8(14):11717–31.
Liu Q, Liu Y, Luo M, He D, Wang H, Choo K-KR. The security of blockchain-based medical systems: research challenges and opportunities. IEEE Syst J. 2022;16(4):5741–52.
Ali S, et al. Towards pattern-based change verification framework for cloud-enabled healthcare component-based. IEEE Access. 2020;8:148007–20.
Guo R, Shi H, Zheng D, Jing C, Zhuang C, Wang Z. Flexible and efficient blockchain-based ABE scheme with multi-authority for medical on demand in telemedicine system. IEEE Access. 2019;7:88012–25.
Son S, Lee J, Kim M, Yu S, Das AK, Park Y. Design of secure authentication protocol for cloud-assisted telecare medical information system using blockchain. IEEE Access. 2020;8:192177–91.
Nguyen DC, Pathirana PN, Ding M, Seneviratne A. Block chain for secure EHRs sharing of mobile cloud based E-health systems. IEEE Access. 2019;7:66792–806.
Younis M, Lalouani W, Lasla N, Emokpae L, Abdallah M. Blockchain-enabled and data-driven smart healthcare solution for secure and privacy-preserving data access. IEEE Syst J. 2022;16(3):3746–57.
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the topical collection “Advances in Computational Approaches for Image Processing, Wireless Networks, Cloud Applications and Network Security” guest edited by P. Raviraj, Maode Ma and Roopashree H R.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Punithavathi, S., Jeyalaksshmi, S. Secure Block Chain-Based Healthcare Sensitive Data Prediction Using Pragmatic Quasi-Identifiers in a Decentralized Cloud Environment. SN COMPUT. SCI. 5, 41 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-02333-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-02333-8