Abstract
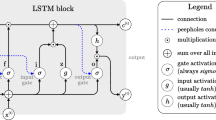
Recently, artificial intelligence-based machine translation has been much improved over traditional methods. A machine translator is very useful for translating text or speech from one language to another. Machine translators have replaced the word mechanism in one language for words in another with verbatim translations. However, a good translation should be employed as both a sentence and a word that has a completed meaning in accordance with the context of the relevant sentence. In this paper, we studied English–Vietnamese translation using deep learning methods including recurrent neural network, long short-term memory, gated recurrent units, attention, and transformer. The deep learning-based machine translators were compared based on the test accuracy of the result translation. It was found that the best deep learning-based machine translator model was the Attention mechanism, and the Transformer yielded the second rank.















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Tsai C, Lai C, Chao H, Vasilakos AV. Big data analytics: a survey. J Big Data. 2015;2(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-015-0030-3.
Ghavami P. Big data analytics methods: analytics techniques in data mining, deep learning and natural language processing. De Gruyter. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1515/9781547401567.
Vu HHP, Tran VT, Nguyen VN, Dang HV, Do PT. Neural machine translation between Vietnamese and English: an empiracal study. J Comput Sci Cybern. 2019;35(2):147–66.
Gong J, Xu K, Ma Z, Lu ZJ, Zhang QC. A deep learning method for recovering missing signals in transcriptome-wide RNA structure profiles from probing experiments. Nat Mach Intell. 2021;3(11):995–1006.
Minh TN, Meesad P. A study of predicting the sincerity of a question asked using machine learning. In: 5th international conference on natural language processing and information retrieval (NLPIR). 2021. p. 129–134.
Tuan NM. Machine learning performance on predicting banking term deposit. In: 24th international conference on enterprise information systems, vol 1. 2022. p. 267–272.
Tapsai C, Meesad P. Natural language interface to database for data retrieval and processing. Appl Sci Eng Prog. 2020;14:435–46.
Xiang S, Tang J, Yang L, Guo Y, Zhao Z, Zhang W. Deep learning-enabled real-time personal handwriting electronic skin with dynamic thermoregulating ability. Npj Flex Electron. 2022;6(1):59.
Luo Z, Zhang J, Fei J, Ke S. Deep learning modeling m6a deposition reveals the importance of downstream cis-element sequences. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):2720.
Maliyaem M, Tuan NM, Lockhart D, Muenthong S. A study of using machine learning in predicting covid-19 cases. NCloud Computing and Data Science. 2022. p. 54–61.
Minh TN, Meesad P, Ha HCN. English–Vietnamese machine translation using deep learning. Recent Adv Inf Commun Technol. 2021;2021(251):99–107.
Chotirat S, Meesad P. Natural language processing with “more than words—BERT’’. Recent Adv Inf Commun Technol. 2021;2021(251):108–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-79757-7_11.
Calin O. Deep learning architectures: a mathematical approach. Berlin: Springer; 2020.
Xu S, Li J, Liu K, Wu L. A parallel gru recurrent network model and its application to multi-channel time-varying signal classification. IEEE Access. 2019;7:118739–48. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2936516.
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Kaiser L, Polosukhin I. Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st international conference on neural information processing systems. 2017.
Aggarwal A, Chauhan A, Kumar D, Mittal M, Verma S, Devlin J. Classification of fake news by fine-tuning deep bidirectional transformers based language model. European Alliance for Innovation (EAI). 2020.
Krishnan S, Magalingam P, Ibrahim R. Hybrid deep learning model using recurrent neural network and gated recurrent unit for heart disease prediction. Int J Electr Comput Eng. 2021;11(6):5467.
Adamopoulou E, Moussiades L. An overview of chatbot technology. In: IFIP international conference on artificial intelligence applications and innovations, vol 584. 2020. p. 373–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-49186-4_31.
Lu Z, Chen Y. User evaluation sentiment analysis model based on machine learning. In: 2nd international conference on consumer electronics and computer engineering (ICCECE). 2022. p. 461–464.
Meesad Phayung. Thai fake news detection based on information retrieval, natural language processing and machine learning. SN Comput Sci. 2021;2(6):425.
Chotirat S, Meesad P. Part-of-speech tagging enhancement to natural language processing for thai wh-question classification with deep learning. Heliyon. 2021;7(10):08216.
Dutta N, Kaliannan P, Shanmugam P. Application of machine learning for inter turn fault detection in pumping system. Sci Rep. 2022;12:12960.
Popel M, Tomkova M, Tomek J, Kaiser Ł, Uszkoreit J, Bojar O, Žabokrtský Z,. Transforming machine translation: a deep learning system reaches news translation quality comparable to human professionals. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4381.
Javidi H, Mariam A, Khademi G, Zabor EC, Zhao R, Radivoyevitch T, Rotroff DM. Identification of robust deep neural network models of longitudinal clinical measurements. Npj Digit Med. 2022;5:106.
Renaud N, Geng C, Georgievska S, Ambrosetti F, Ridder L, Marzella DF, Réau MF, Bonvin AMJJ, Xue LC. Deeprank: a deep learning framework for data mining 3d protein–protein interfaces. Nat Commun. 2021;12:7068.
Chen W, Zhichen Y, Simon F. How to build a chatbot : chatbot framework and its capabilities. In: 10th international conference on machine learning and computing. 2018. p. 369–373.
Plunza RA, Zhoua Y, Vintimillab MIC, Mckeownc K, Yud T, Uguccionia L, Sutto MP. Twitter sentiment in New York city parks as measure of well-being. Sci Direct. 2019;189:235–46.
Ngoc PV, Ngoc CVT, Ngoc TVT, Nguyen DD, Doan DKL. A valence-totaling model for Vietnamese sentiment classification. Evol Syst. 2019;10(3):453–99.
Amaar A, Aljedaani W, Rustam F, Ullah S, Rupapara V, Ludi S. Detection of fake job postings by utilizing machine learning and natural language processing approaches. Neural Process Lett. 2022;54(3):2219–47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors hereby state that there is no conflict of Interest for this article.
Ethical Approval
Our article is published with the consent of the authors without any dispute and conflict of interest between the authors.
Informed Consent
The images and experimental data are with the permission of the parties involved, there is no dispute or conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the topical collection “Advanced Machine Learning Approaches in Cognitive Computing” guest edited by Kuntpong Woraratpanya and Phayung Meesad.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tuan, N.M., Meesad, P. & Nguyen, H.H.C. English–Vietnamese Machine Translation Using Deep Learning for Chatbot Applications. SN COMPUT. SCI. 5, 5 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-02339-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-023-02339-2