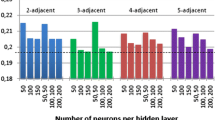
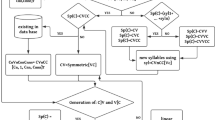
Abstract
The purpose of this paper is to address speech processing phase of the synthesizer to produce artificial speech from the phonetic sequences generated at the linguistic processing level. This research work is part of the realization of a text-to-speech synthesizer based on concatenation rules for standard Arabic language. In this paper, we will detail the different steps we followed to generate the synthetic voice. These steps consist in selecting the prerecorded acoustic units to be concatenated, stored in an acoustic database by using the selection rules. Then these acoustic units undergo specific processing at the concatenation points according to the nature of sounds to be concatenated (voiced, unvoiced) to generate a synthetic speech signal as natural and intelligible as possible. This innovative method that we have developed specifically for the Arabic language acts directly on the acoustic units at the concatenation points (less signal processing on the selected acoustic units, less execution time) and reconstitute at the same time the synthetic voice using concatenation rules based on the overlap-add (OLA) method with a specific processing at the concatenation points.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Abdelmalek, R., Mnasri, Z. High quality Arabic text-to-speech synthesis using unit selection. In Proceedings of the 13th international multi-conference on systems, signals & devices. 2016. pp. 1–5
Al-ghamdi, M., Elshafei, M., Al-muhtaseb, H. Arabic Text-to-speech: speech units. Supported by King Abdulaziz City for science and technology project number AT-18-12. 2002
Al-ghamdi, M., Al-hamid, A., Adasouki, M. Arabic data base of the sounds: Sentences. Supported by King Abdulaziz City for science and technology. 2004
Alsharif B, Tahboub R, Arafeh L. Arabic text to speech synthesis using Quran-based natural language processing module. J Theor Appl Inf Technol. 2016;83(1):148–55.
Birkholz, P., Drechsel, S., Stone, S. Perceptual optimization of an enhanced geometric vocal fold model for articulatory speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the interspeech. 2019. pp. 3765–3769
Birkholz P, Drechsel S. Effects of the piriform fossae, transvelar acoustic coupling, and laryngeal wall vibration on the naturalness of articulatory speech synthesis. Speech Commun. 2021;132:96–105.
Chabchoub A, Cherif A. High quality Arabic concatenative speech synthesis. Signal Image Process: Int J. 2011;2(4):27–36.
Chabchoub A, Alahmadi S, Barkouti W. Di-Diphone Arabic speech synthesis concatenation. Int J Comput Technol. 2012;3(2):218–22.
Charoenrattana, K., Seresangtakul, P. Pali speech synthesis using HMM. In Proceedings of the 13th international conference on knowledge and smart technology. 2021. pp. 165–169
Corral, A., Leturia, I., Séguier, A. et al. Neural text-to-speech synthesis for an under-resourced language in a diglossic environment: the case of Gascon Occitan. In Proceedings of the 1st Joint workshop on spoken language technologies for under-resourced languages (SLTU) and collaboration and computing for under-resourced languages (CCURL). 2020. pp. 53–60
D’Souza AV, Ravi DJ. An approach for formant synthesis of Kannada. J Signal Process. 2022;8(2):31–8.
Gujarathi, P., Patil, S.R. Review on unit selection-based concatenation approach in text to speech synthesis system. In: Gunjan, V.K. et al. (Eds) Cybernetics, cognition and machine learning applications. Algorithms for intelligent systems. 2021. pp. 191–202).
Hamad, M., Hussain, M. Arabic text-to-speech synthesizer. In Proceedings of the IEEE student conference on research and development. 2011. pp 409–414
Illa, A., Nair, A., Ghosh, P.K. The impact of cross language on acoustic-to-articulatory inversion and its influence on articulatory speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing. 2022. pp. 8267–8271
Imedjdouben F, Houacine A. Automatic phonetization of Arabic text. In: Amine A, Otmane A, Bellatreche L, editors. Modeling approaches and algorithms for advanced computer applications. Studies computational intelligence, vol. 488. Springer, Cham; 2013. p. 85–94.
Imedjdouben F, Houacine A. Development of an automatic phonetization system for Arabic text-to-speech synthesis. Int J Speech Technol. 2014;17(4):417–26.
Jaiswal, R.K., Dubey, R.K. Concatenative text-to-speech synthesis system for communication recognition. In Proceedings of the 5th international conference on electronics, communication and aerospace technology. 2021. pp. 867–872).
Kadhi, A.E., Gherri, F., Amiri, H. Building diphone database for Arabic text to speech synthesis system. In Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on control, engineering & information technology. 2015. pp. 1–5.
Koffi E, Petzold M. A tutorial on formant-based speech synthesis for the documentation of critically endangered languages. Linguist Portf. 2022;11:26–55.
Kumari R, Dev A, Kumar A. An efficient adaptive artificial neural network based text to speech synthesizer for Hindi language. Multimed Tools Appl. 2021;80:24669–95.
Li, N., Liu, S., Liu, Y. et al. Neural speech synthesis with transformer network. In Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence. 2019; 33 (01), pp. 6706–6713.
Lukose, S., Upadhya, S.S. Text to speech synthesizer-formant synthesis. In Proceedings of the international conference on nascent technologies in engineering. 2017. pp. 1–4.
Manoharan, J.S. A novel text-to-speech synthesis system using syllable-based HMM for Tamil language. In: Shakya, S., et al. (Eds) Proceedings of second international conference on sustainable expert systems. lecture notes in networks and systems. 2022; 351, pp. 305–314.
Sefara, T.J., Mokgonyane, T.B., Manamela, M.J. et al. HMM-based speech synthesis system incorporated with language identification for low-resourced languages. In Proceedings of the international conference on advances in big data, computing and data communication systems. 2019. pp. 1–6.
Vainer, J., Dušek, O. Speedyspeech: efficient neural speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the interspeech. 2020. pp. 3575–3579.
Wu, P., Watanabe, S., Goldstein, L. et al. Deep speech synthesis from articulatory representations. In Proceedings of the Interspeech. 2022. pp. 779–783.
Zhou X, Ling ZH, Dai LR. UnitNet: a sequence-to-sequence acoustic model for concatenative speech synthesis. IEEE/ACM Trans Audio, Speech Lang Process. 2021;29:2643–55.
Zine, O., Meziane, A. Novel approach for quality enhancement of arabic text to speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the international conference on advanced technologies for signal and image processing. 2017. pp. 1–6.
Zine, O., Meziane, A., Boudchiche, M. Towards a high-quality lemma-based text to speech system for the Arabic language. In: Lachkar, A., et al. (Eds) Arabic language processing: from theory to practice. 6th international conference, ICALP. Communications in computer and information science. 2018; 782, 53–66.
Funding
Not Applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not Applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.”
Research Involving Human and /or Animals
Not applicable.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Imedjdouben, F. Speech Processing for Arabic Speech Synthesis Based on Concatenation Rules. SN COMPUT. SCI. 5, 316 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-02649-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-02649-z