Abstract
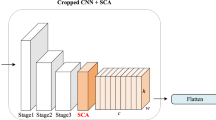
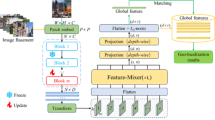
Visual place recognition (VPR) is a crucial task in robotics and autonomous systems, enabling robots to localize themselves in complex and dynamic environments. Due to significant differences in appearance that arise from changes in environmental factors like season, weather, and lighting (day or night), VPR is particularly challenging in outdoor settings. This paper presents a novel method to address this challenge called MS-MixVPR, which is proposed based on an existing work, MixVPR. The proposed MS-MixVPR extracts global features from different layers of pre-trained CNN backbones using MixVPR’s Feature Mixer blocks. These visual cues are combined further to create a compact, holistic representation that is highly robust to changes in environmental conditions. We evaluate the proposed MS-MixVPR on four challenging real-world benchmark datasets, including Nordland, SPEDTest, MSLS, and Pittsburgh30k. The experimental results show that our MS-MixVPR outperforms several current state-of-the-art methods while maintaining low computational time. Consequently, our approach is suitable for real-world applications that are often resource-constrained.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lowry S, Sünderhauf N, Newman P, Leonard JJ, Cox D, Corke P, Milford MJ. Visual place recognition: a survey. IEEE Trans Robot. 2016;32(1):1–19. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2015.2496823.
Masone C, Caputo B. A survey on deep visual place recognition. IEEE Access. 2021;9:19516–47. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3054937.
Garg S, Fischer T, Milford M. Where is your place, visual place recognition? In: Proceedings of the thirtieth international joint conference on artificial intelligence. International joint conferences on artificial intelligence organization; 2021. https://doi.org/10.24963/ijcai.2021/603 .
Dusmanu M, Rocco I, Pajdla T, Pollefeys M, Sivic J, Torii A, Sattler T. D2-Net: a trainable CNN for joint detection and description of local features. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition; 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00828.
Noh H, Araujo A, Sim J, Weyand T, Han B. Large-scale image retrieval with attentive deep local features. In: Proceedings of 2017 IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp. 3476–3485; 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.374.
Garg S, Babu V, M, Dharmasiri T, Hausler S, Suenderhauf N, Kumar S, Drummond T, Milford M. Look no deeper: recognizing places from opposing viewpoints under varying scene appearance using single-view depth estimation. In: 2019 international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), pp. 4916–4923; 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2019.8794178.
Revaud J, Weinzaepfel P, Souza CR, Humenberger M. R2D2: repeatable and reliable detector and descriptor. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), pp. 12414–12424; 2019. https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3454287.3455400.
Hausler S, Garg S, Xu M, Milford M, Fischer T. Patch-NetVLAD: multi-scale fusion of locally-global descriptors for place recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 14141–14152; 2021. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR46437.2021.01392.
Jégou H, Douze M, Schmid C, Pérez P. Aggregating local descriptors into a compact image representation. In: 2010 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3304–3311; 2010. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2010.5540039.
Sattler T, Maddern W, Toft C, Torii A, Hammarstrand L, Stenborg E, Safari D, Okutomi M, Pollefeys M, Sivic J, Kahl F, Pajdla T. Benchmarking 6DOF outdoor visual localization in changing conditions. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 8601–8610; 2018. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2018.00897.
Arandjelović R, Gronat P, Torii A, Pajdla T, Sivic J. NetVLAD: CNN architecture for weakly supervised place recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2018;40(6):1437–51. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2711011.
Cao B, Araujo A, Sim J. Unifying deep local and global features for image search. In: Vedaldi A, Bischof H, Brox T, Frahm J-M, editors. Computer vision—ECCV 2020, pp. 726–743. Springer, Cham; 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58565-5_43.
Torii A, Arandjelović R, Sivic J, Okutomi M, Pajdla T. 24/7 place recognition by view synthesis. In: 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 1808–1817; 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298790.
Chen Z, Jacobson A, Sünderhauf N, Upcroft B, Liu L, Shen C, Reid I, Milford M. Deep learning features at scale for visual place recognition. In: Proceedings of 2017 ieee international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA), pp. 3223–3230; 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRA.2017.7989366.
Jégou H, Perronnin F, Douze M, Sánchez J, Pérez P, Schmid C. Aggregating local image descriptors into compact codes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2012;34(9):1704–16. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2011.235.
Lowe DG. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vis. 2004;60(2):91–110. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94.
Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L. Speeded-up robust features (SURF). Comput Vis Image Understand. 2008;110(3):346–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cviu.2007.09.014.
Sivic Z. Video Google: a text retrieval approach to object matching in videos. In: Proceedings ninth IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp. 1470–14772; 2003. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2003.1238663.
Galvez-López D, Tardos JD. Bags of binary words for fast place recognition in image sequences. IEEE Trans Robot. 2012;28(5):1188–97. https://doi.org/10.1109/TRO.2012.2197158.
Perronnin F, Dance C. Fisher kernels on visual vocabularies for image categorization. In: Proceedings of 2007 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 1–8; 2007. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2007.383266.
Perronnin F, Liu Y, Sánchez J, Poirier H. Large-scale image retrieval with compressed Fisher vectors. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3384–3391; 2010. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2010.5540009.
Arandjelovic R, Zisserman A. All about VLAD. In: Proceedings of 2013 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CPVR), pp. 1578–1585; 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.207.
Radenović F, Tolias G, Chum O. Fine-tuning CNN image retrieval with no human annotation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2019;41(7):1655–68. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2018.2846566.
Zhu S, Yang L, Chen C, Shah M, Shen X, Wang H. \(R^{2}\) former: unified retrieval and reranking transformer for place recognition. In: Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 19370–19380; 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52729.2023.01856.
Zhang H, Chen X, Jing H, Zheng Y, Wu Y, Jin C. ETR: an efficient transformer for re-ranking in visual place recognition. In: 2023 IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV), pp. 5654–5663; 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00562.
Wang R, Shen Y, Zuo W, Zhou S, Zheng N. TransVPR: transformer-based place recognition with multi-level attention aggregation. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 13638–13647; 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01328.
Tolstikhin I, Houlsby N, Kolesnikov A, Beyer L, Zhai X, Unterthiner T, Yung J, Steiner A, Keysers D, Uszkoreit J, Lucic M, Dosovitskiy A. MLP-mixer: an all-MLP architecture for vision; 2021. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2105.01601.
Touvron H, Bojanowski P, Caron M, Cord M, El-Nouby A, Grave E, Izacard G, Joulin A, Synnaeve G, Verbeek J, Jegou H. ResMLP: feedforward networks for image classification with data-efficient training. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2023;45(04):5314–21. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3206148.
Ali-Bey A, Chaib-Draa B, Giguére P. MixVPR: feature mixing for visual place recognition. In: Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV), pp. 2997–3006; 2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/WACV56688.2023.00301.
Zhang H, Dong Z, Li B, He S. Multi-scale MLP-mixer for image classification. Knowl-Based Syst. 2022;258:109792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.knosys.2022.109792.
Kim HJ, Dunn E, Frahm J-M. Learned contextual feature reweighting for image geo-localization. In: Proceedings of 2017 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 3251–3260; 2017. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.346.
Liu L, Li H, Dai Y. Stochastic attraction-repulsion embedding for large scale image localization. In: Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp. 2570–2579; 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2019.00266.
Yu J, Zhu C, Zhang J, Huang Q, Tao D. Spatial pyramid-enhanced NetVLAD with weighted triplet loss for place recognition. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst. 2020;31(2):661–74. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2908982.
Zhang J, Cao Y, Wu Q. Vector of locally and adaptively aggregated descriptors for image feature representation. Pattern Recogn. 2021;116:107952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2021.107952.
Berton G, Masone C, Caputo B. Rethinking visual geo-localization for large-scale applications. In: Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 4868–4878; 2022. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.00483.
Ali-bey A, Chaib-draa B, Giguère P. GSV-cities: toward appropriate supervised visual place recognition. Neurocomputing. 2022;513:194–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2022.09.127.
Sarlin P-E, DeTone D, Malisiewicz T, Rabinovich A. SuperGlue: learning feature matching with graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 4937–4946; 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00499.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. In: Fleet D, Pajdla T, Schiele B, Tuytelaars T, editors. Computer vision—ECCV 2014, pp. 346–361. Springer, Cham; 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10578-9_23.
Nakayama Y, Lu H, Li Y, Kim H. Wide residual networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of 18th international conference on control, automation and systems (ICCAS), pp. 1476–1480; 2018. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8571971.
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A. Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of 2015 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 1–9; 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2015.7298594.
Radenović F, Tolias G, Chum O. CNN image retrieval learns from BoW: unsupervised fine-tuning with hard examples. In: Leibe B, Matas J, Sebe N, Welling M, editors. Computer vision—ECCV 2016, pp. 3–20. Springer, Cham; 2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46448-0_1.
Tolias G, Sicre R, Jégou H. Particular object retrieval with integral max-pooling of CNN activations. In: Bengio Y, LeCun Y, editors. Proceedings of 4th international conference on learning representations (ICLR); 2016. http://arxiv.org/abs/1511.05879.
Gong Y, Wang L, Guo R, Lazebnik S. Multi-scale orderless pooling of deep convolutional activation features. In: Fleet D, Pajdla T, Schiele B, Tuytelaars T, editors. Computer vision—ECCV 2014, pp. 392–407. Springer, Cham; 2014. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-10584-0_26.
Mao J, Hu X, He X, Zhang L, Wu L, Milford MJ. Learning to fuse multiscale features for visual place recognition. IEEE Access. 2019;7:5723–35. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2889030.
Sünderhauf N, Shirazi S, Dayoub F, Upcroft B, Milford M. On the performance of ConvNet features for place recognition. In: Proceedings of 2015 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), pp. 4297–4304; 2015. https://doi.org/10.1109/IROS.2015.7353986.
Chen Z, Liu L, Sa I, Ge Z, Chli M. Learning context flexible attention model for long-term visual place recognition. IEEE Robot Autom Lett. 2018;3(4):4015–22. https://doi.org/10.1109/LRA.2018.2859916.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In: Proceedings of 2016 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 770–778; 2016. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2016.90.
Wang X, Han X, Huang W, Dong D, Scott MR. Multi-similarity loss with general pair weighting for deep metric learning. In: Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 5017–5025; 2019. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2019.00516.
Skrede S. Nordlandsbanen: minute by minute, season by season; 2013. https://nrkbeta.no/2013/01/15/nordlandsbanen-minute-by-minute-season-by-season/.
Warburg F, Hauberg S, López-Antequera M, Gargallo P, Kuang Y, Civera J. Mapillary street-level sequences: a dataset for lifelong place recognition. In: Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), pp. 2623–2632; 2020. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR42600.2020.00270.
Torii A, Sivic J, Pajdla T, Okutomi M. Visual place recognition with repetitive structures. In: Proceedings of 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 883–890; 2013. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2013.119.
Zaffar M, Garg S, Milford M, Kooij J, Flynn D, McDonald-Maier K, Ehsan S. VPR-bench: an open-source visual place recognition evaluation framework with quantifiable viewpoint and appearance change. Int J Comput Vis. 2021;129:2136–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-021-01469-5.
Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition; 2015. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1409.1556.
Funding
Not applicable
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Methodology, M.-D Quach, D.-M Vo, and H.-A Pham; Coding and Validation, M.-D Quach and D.-M Vo; Writing—original draft preparation, M.-D Quach and D.-M Vo; Writing—review and editing, H.-A Pham.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no Conflict of interest.
Research involving human and /or animals
Not applicable.
Informed consent
All authors agreed with the content and that all gave explicit consent to submit and publish the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Quach, MD., Vo, DM. & Pham, HA. MS-MixVPR: Multi-scale Feature Mixing Approach for Long-Term Place Recognition. SN COMPUT. SCI. 5, 656 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-03011-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-03011-z