Abstract
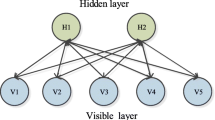
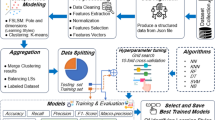
E-learning environments represent digital platforms designed to facilitate online learning experiences. Recognizing the diverse learning preferences of individuals, the need for identifying and integrating multi-layered learning styles within these environments is paramount. Existing approaches often face limitations in accurately capturing and accommodating these intricate learning styles. To address these challenges, this study proposes a novel approach. Firstly, the integration of word embedding-based feature extraction transforms textual data into continuous vector representations, enhancing feature robustness and meaningfulness. Secondly, leveraging deep belief networks (DBNs) allows for the automatic learning of hierarchical data representations, improving model performance by capturing complex patterns. Thirdly, the DBN-based model accommodates multi-layered learning styles, including visual, auditory, kinaesthetic, and read/write preferences, offering personalized recommendations to learners. Lastly, the proposed approach is scalable and generalizable, capable of handling large datasets and diverse educational contexts, thus enhancing the efficacy of e-learning platforms. This innovative approach demonstrates promising advancements in learning style identification within e-learning environments, providing personalized guidance to learners and improving the overall effectiveness of online education. The proposed Deep Belief Network (DBN) model exhibits a significant average increase in accuracy compared to other methods implemented in Python. With an accuracy of 99.5%, the DBN model surpasses the accuracy of the K-Nearest Neighbours (KNN) and Random Forest (RF) models by 25.4 and 3.3%, respectively. This substantial improvement underscores the superiority of the proposed DBN model in learning style identification.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The corresponding author can provide the dataset generated and analyzed during this study upon reasonable request.
References
Burbules NC, Fan G, Repp P. Five trends of education and technology in a sustainable future. Geogr Sustain. 2020;1(2):93–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geosus.2020.05.001.
Chen X, Zou D, Xie H, Cheng G, Liu C. Two decades of artificial intelligence in education: contributors, collaborations, research topics, challenges, and future directions. Educ Technol Soc. 2022;25(1):28–47.
Alam A. Platform utilising blockchain technology for eLearning and online education for open sharing of academic proficiency and progress records. In: Asokan R, Ruiz DP, Baig ZA, Piramuthu S, editors. Smart data intelligence. Singapore: Springer Nature; 2022. pp. 307–320. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-3311-0_26.
Liu Z-Y, Lomovtseva N, Korobeynikova E. Online learning platforms: reconstructing modern higher education. Int J Emerg Technol Learn. 2020;15(13):4–21.
El-Sabagh HA. Adaptive e-learning environment based on learning styles and its impact on development students’ engagement. Int J Educ Technol High Educ. 2021;18(1):53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s41239-021-00289-4.
Alqahtani AY, Rajkhan AA. E-learning critical success factors during the COVID-19 pandemic: a comprehensive analysis of E-learning managerial perspectives. Educ Sci. 2020;10(9):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci10090216.
Rasheed F, Wahid A. Learning style detection in E-learning systems using machine learning techniques. Expert Syst Appl. 2021;174:114774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.114774.
Amarneh BM, Alshurideh MT, Al Kurdi BH, Obeidat Z. The Impact of COVID-19 on E-learning: advantages and challenges. In: Hassanien AE, Haqiq A, Tonellato PJ, Bellatreche L, Goundar S, Azar AT, Sabir E, Bouzidi D, editors. Proceedings of the international conference on artificial intelligence and computer vision (AICV2021). Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2021. pp. 75–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-76346-6_8.
Liu M, Yu D. Towards intelligent E-learning systems. Educ Inf Technol. 2023;28(7):7845–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11479-6.
Logan RM, Johnson CE, Worsham JW. Development of an e-learning module to facilitate student learning and outcomes. Teach Learn Nurs. 2021;16(2):139–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.teln.2020.10.007.
Wu EH-K, Lin C-H, Ou Y-Y, Liu C-Z, Wang W-K, Chao C-Y. Advantages and constraints of a hybrid model K-12 E-Learning assistant chatbot. IEEE Access. 2020;8:77788–801. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2988252.
Gomede E, Miranda de Barros R, de Souza Mendes L. Use of deep multi-target prediction to identify learning styles. Appl Sci. 2020;10(5):1756. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10051756.
Al Abdullatif A, Gameil A. The effect of digital technology integration on students’ academic performance through project-based learning in an e-learning environment. Int J Emerg Technol Learn. 2021;16:189. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v16i11.19421.
Barari N, RezaeiZadeh M, Khorasani A, Alami F. Designing and validating educational standards for E-teaching in virtual learning environments (VLEs), based on revised Bloom’s taxonomy. Interact Learn Environ. 2022;30(9):1640–52. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2020.1739078.
Sáiz-Manzanares MC, et al. Teaching and learning styles on moodle: an analysis of the effectiveness of using STEM and non-STEM qualifications from a gender perspective. Sustainability. 2021;13(3):1166. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031166.
Fazazi HE, Elgarej M, Qbadou M, Mansouri K. Design of an adaptive e-learning system based on multi-agent approach and reinforcement learning. Eng Technol Appl Sci Res. 2021;11(1):6637–44. https://doi.org/10.48084/etasr.3905.
Hibbi F-Z, Abdoun O, Haimoudi EK. Integrating an intelligent tutoring system into an adaptive e-learning process. In: Dos Santos S, Maslouhi M, Okoudjou KA, editors. Recent Advances in Mathematics and Technology: Proceedings of the first international conference on technology, engineering, and mathematics, Kenitra, Morocco, March 26–27, 2018. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2020. pp. 141–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-35202-8_8.
“Learning Style (VAK).” Accessed 19 Feb 2024. [Online]. https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/zeyadkhalid/learning-style-vak
Benabbes K, Housni K, Zellou A, Brahim H, El Mezouary A. Context and learning style aware recommender system for improving the e-learning environment. Int J Emerg Technol Learn. 2023;18(09):180–202. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijet.v18i09.38361.
Fong S, Dey N, Joshi A, editors. ICT analysis and applications: proceedings of ICT4SD 2020, volume 2, vol. 154. Singapore: Springer Singapore; 2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-8354-4.
Zhang H, et al. A learning style classification approach based on deep belief network for large-scale online education. J Cloud Comp. 2020;9(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13677-020-00165-y.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledged the SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Vadapalani campus as well as Kattankulathur campus, Chennai, Tamilnadu, India for supporting the research work by providing the facilities.
Funding
No funding received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
This research work was made possible by the collaboration and contributions of all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ramesh, M., Jayashree, R. Adaptive E-Learning Environments: A Methodological Approach to Identifying and Integrating Multi-layered Learning Styles. SN COMPUT. SCI. 5, 772 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-03114-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42979-024-03114-7