Abstract
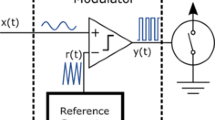
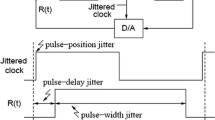
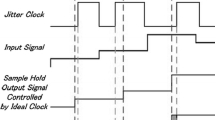
A practical digital clock noise mitigation technique based on pulse removal is presented. Clock frequency is increased to generate an excess pulse, which is removed in order to match the number of pulses in an average time frame. The location of the excess pulse is selected as the same time point or randomly selected in every time frame. Mathematical analyses are presented for both methods. The circuit is implemented using a state machine on a FPGA. Measurement results indicate more than 40 dB improvement on the digital noise level within a band of interest.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Backenius, M. Vesterbacka, R. Hagglund, A strategy for reducing clock noise in mixed-signal circuits, in The 2002 45th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, MWSCAS, vol. 1 (2002), pp. 29–32. doi:10.1109/MWSCAS.2002.1187145
G.R. Black, C.P. Binzel, Method and apparatus for avoiding spurious signal receiver desensitizing. US Patent 6898420 (2005)
H.M. Chen, M.H. Wu, B. Liau, L. Chang, C.F. Wu, The study of substrate noise and noise-rejection-efficiency of guard-ring in monolithic integrated circuits, in IEEE International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, vol. 1, (2000), pp. 123–128. doi:10.1109/ISEMC.2000.875549
O. Eliezer, B. Staszewski, S. Bhatara, I. Bashir, P. Balsara, Active mitigation of induced phase distortion in a gsm soc, in Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, RFIC 2008. (IEEE, New York, 2008), pp. 17–20. doi:10.1109/RFIC.2008.4561376
O. Eliezer, R. Staszewski, I. Bashir, S. Bhatara, P. Balsara, A phase domain approach for mitigation of self-interference in wireless transceivers. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 44(5), 1436–1453 (2009). doi:10.1109/JSSC.2009.2014941
C.G. Lin, B. Kelleci, H. Kiper, Y. Deng, Receiver dynamically switching to pseudo differential mode for soc spur reduction. US Patent 8023919 (2011)
Y. Matsumoto, K. Fujii, A. Sugiura, An analytical method for determining the optimal modulating waveform for dithered clock generation. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 47(3), 577–584 (2005). doi:10.1109/TEMC.2005.852221
Y. Moon, D.K. Jeong, G. Kim, Spread spectrum phase modulation for suppression of electromagnetic interference in parallel data channels. US Patent 6600771 (2003)
A.V. Oppenheim, A.S. Willsky, S.H. Nawab, Signals and Systems (Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, 1997)
B. Razavi, Design of Analog CMOS Integrated Circuits, 1st edn. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 2000)
H.E. Rowe, Signals and Noise in Communication Systems (Nostrand, New York, 1965)
D. Su, M. Loinaz, S. Masui, B. Wooley, Experimental results and modeling techniques for substrate noise in mixed-signal integrated circuits. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 28(4), 420–430 (1993). doi:10.1109/4.210024
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kelleci, B. Pulse Suppression Technique for Mitigating Digital Clock Noise. Circuits Syst Signal Process 33, 1325–1336 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-013-9697-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-013-9697-x