Abstract
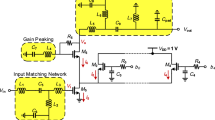
This paper demonstrates the design and implementation of a 5-GHz frequency synthesizer using 55-nm complementary metal-oxide semiconductor technology. The proposed synthesizer achieves an ultra-low 0.35-ps jitter with a high-resolution adaptive frequency calibration scheme that automatically chooses frequency-tuning curves and improves calibration accuracy. The proposed synthesizer employs a high-Q LC voltage-controlled oscillator, constant bandwidth, low, and even \(K_{\mathrm{VCO}}\) technique using thermometer-weighted capacitor calibration, a low-power divider, and a charge-pump (CP) circuit to achieve low jitter. The oscillator comprises a modified digitally controlled capacitor and varactor array, which extend the tuning range and minimize the phase noise. A matched differential CP is adopted to reduce reference spurs and phase-noise performance. The proposed frequency synthesizer achieves an output frequency of 4.4–5.6 GHz with a chip area of \(0.33\hbox { mm}^{2}\). The power consumption is 20 mW from a 1.2-V supply at 5 GHz, and the reference spur is −67.99 dBc. The measured root mean-square random jitter and phase noise are 0.35 ps and −110.04 dBc/Hz at 1 MHz, respectively.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Aktas, M. Ismail, CMOS PLL calibration techniques. IEEE Circuits Devices Mag. 20(5), 6–11 (2004). doi:10.1109/MCD.2004.1343243
S. Broussev, T. Lehtonen, N. Tchamov, A wideband low phase-noise LC-VCO with programmable \(K_{{ VCO}}\). IEEE Microwave Wirel. Compon. Lett. 17(4), 274–276 (2007). doi:10.1109/LMWC.2007.892966
D. Cai, H. Fu, J. Ren, W. Li, N. Li, H. Yu, K. Yeo, A dividerless PLL with low power and low reference spur by aperture-phase detector and phase-to-analog converter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I, Regul. Pap. 60(1), 37–50 (2013). doi:10.1109/TCSI.2012.2215751
Z. Cao, Y. Li, S. Yan, A 0.4ps-rms-jitter 1–3GHz ring-oscillator PLL using phase-noise pre-amplification. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 43(9), 2079–2089 (2008). doi:10.1109/JSSC.2008.2001873
X. Gao, E. Klumperink, G. Socci, M. Bohsali, B. Nauta, Spur reduction techniques for phase-locked loops exploiting a sub-sampling phase detector. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 45(9), 1809–1821 (2010). doi:10.1109/JSSC.2010.2053094
X. Gao, E. Klumperink, P. Geraedts, B. Nauta, Jitter analysis and a benchmarking figure-of-merit for phase-locked loops. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II, Express Br. 56(2), 117–121 (2009). doi:10.1109/TCSII.2008.2010189
D. Huang, W. Li, J. Zhou, N. Li, J. Chen, A frequency synthesizer with optimally coupled QVCO and harmonic-rejection SSBmixer for multi-standard wireless receiver. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 46(6), 1307–1320 (2011). doi:10.1109/JSSC.2011.2124970
T. Jang, X. Nan, F. Liu, J. Shin, H. Ryu, J. Kim, T. Kim, J. Park, H. Park, A \(0.026 \text{mm}^{2}\) 5.3mW 32-to-2000 MHz digital fractional-N phase locked-loop using a phase-interpolating phase-to-digital converter. in IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), pp. 254–255 (2013)
J. Kim, J. Shin, S. Kim, H. Shin, A wide-band CMOS LC VCO with linearized coarse tuning characteristics. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-II, Express Br. 55(5), 399–403 (2008). doi:10.1109/TCSII.2007.914896
M. Kondou, A. Matsuda, H. Yamazaki, O. Kobayashi, A \(0.3\text{ mm }^{2}\) 90-to-770 MHz fractional-N synthesizer for a digital TV tuner. in IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) Digest of Technical Papers, vol 248, (2010)
J . Lee, K. Kim, J. Lee, T. Jang, S. Cho, A 480-MHz to 1-GHz sub-picosecond clock generator with a fast and accurate automatic frequency calibration in 0.13-\(\mu \text{ m }\) CMOS. in IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, pp. 67–70 (2007)
C. Lee, L. Kabalican, Y. Ge et al., A 2.7GHz to 7GHz fractional-N LC-PLL utilizing multi-metal layer SoC technology in 28nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 50(4), 1–9 (2015). doi:10.1109/JSSC.2014.2371136
M. Li, S. Zhang, S. Wang, R. Zhou, A fully-integrated CMOS UWB transceiver for ultra-low-power short-range application. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 39, 783–790 (2011)
T. Lin, Y. Lai, An agile VCO frequency calibration technique for a 10-GHz CMOS PLL. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 42(2), 340–349 (2007). doi:10.1109/JSSC.2006.889360
J. Liu, S. Jeon, T. Jang, D. Kim, J. Kim, J. Park, H. Park, A 0.8V, sub-mW, varactor-tuning ring-oscillator-based clock generator in 32 nm CMOS. in IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, pp. 337–340 (2011)
L. Lu, J. Chen, Y. Lu, H. Min, Z. Tang, An 18-mW 1.175-2-GHz frequency synthesizer with constant bandwidth for DVB-tuners. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 57(4), 928–937 (2009). doi:10.1109/TMTT.2009.2014449
S. Min, T. Copani, S. Kiaei et al., A 90-nm CMOS 5-GHz ring-oscillator PLL with delay-discriminator-based active phase-noise cancellation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 48(5), 1151–1160 (2013). doi:10.1109/JSSC.2013.2252515
Y. Moon, Y. Roh, C. Jeong, C. Yoo, A 4.39-5.26 GHz LC-tank CMOS voltage-controlled oscillator with small VCO-gain variation. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 19(8), 524–526 (2009). doi:10.1109/LMWC.2009.2024846
Y. Pan, Y. Huang, Z. Hong, A 3–5GHz low-phase noise fractional-N frequency synthesizer with AFC for GSM/PCS/DCS/WCDMA transceivers. IEEE Int. Symp. Radio-Freq. Integr. Technol. (RFIT) 30(2), 53–56 (2011)
J. Shin, H. Shin, A 1.9-3.8GHz fractional-N PLL frequency synthesizer with fast auto-calibration of loop bandwidth and VCO frequency. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 47(3), 665–675 (2012). doi:10.1109/JSSC.2011.2179733
J. Shu, Z. Li, A fast AFC loop with low power consumption, low phase noise LC VCO. in International Conference on Multimedia Technology (ICMT), pp. 1580–1587 (2013)
K. Sogo, A. Toya, T. Kikkawa, A ring-VCO-based sub-sampling PLL CMOS circuit with -119dBc/Hz phase noise and 0.73ps. in Proceedings of European Solid-State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC), pp. 253–256 (2012)
M. Sugawara, S. Choi, D. Wood, Ultra-high-definition television (Rec. ITU-R BT.2020): a generational leap in the evolution of television [standards in a nutshell]. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 31(3), 170–174 (2014)
Y. Sun, J. Qiao, X. Yu, W. Rhee, B. Park, Z. Wang, A continuously tunable hybrid LC-VCO PLL with mixed-mode dual-path control and Bi-level \(\Delta -\Sigma \) modulated coarse tuning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I, Regul. Pap. 58(9), 2149–2158 (2011). doi:10.1109/TCSI.2011.2114735
T. Wu, P. Hanumolu, K. Mayaram, U. Moon, Method for a constant loop bandwidth in LC_VCO PLL frequency synthesizers. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 44(2), 427–435 (2009). doi:10.1109/JSSC.2008.2010792
Z. Xu, Q. Gu, Y. Wu, H. Jian, M. Chang, A 70–78-GHz integrated CMOS frequency synthesizer for \(W\)-band satellite communications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 59(12), 3206–3218 (2011). doi:10.1109/TMTT.2011.2168972
Y. You, D. Huang, J. Chen, S. Chakraborty, A 12GHz 67% tuning range 0.37ps \({\mathit{RJ}_{{}rms}}\) PLL with LC-VCO temperature compensation scheme in 0.13um CMOS. in IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuit Symposium (RFIC), pp. 101–104. (2014) doi:10.1109/RFIC.2014.6851669
B. Zhao, Y. Lian, H. Yang, A low-power fast-settling bond-wire frequency synthesizer with a dynamic-bandwidth scheme. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I, Regul. Pap. 60(5), 1188–1199 (2013). doi:10.1109/TCSI.2013.2249177
J. Zhou, W. Li, D. Huang et al., A 0.4-6GHz frequency synthesizer using dual-mode VCO for software-defined radio. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 61(2), 848–859 (2013). doi:10.1109/TMTT.2012.2233493
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61474134).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, Y., Zhao, L. & Zhang, F. Design of 0.35-ps RMS Jitter 4.4–5.6-GHz Frequency Synthesizer with Adaptive Frequency Calibration Using 55-nm CMOS Technology. Circuits Syst Signal Process 37, 1479–1504 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0645-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-017-0645-z