Abstract
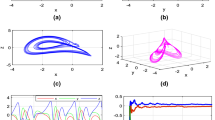
One of the important applications of chaotic oscillators is their employment as sources of entropy for True Random Bit Generators (TRBGs). In this work, we introduce high-speed TRBGs realized on a modular Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) hardware platform using two different switching-type chaotic oscillators. While both oscillators are autonomous, one is 3-D and the other is 4-D. This enables us to investigate and compare the advantages/disadvantages of higher dimensional chaotic oscillators on the throughput, hardware requirements and security of the generated bit-streams. For that purpose, two different implementations are described for each TRBG; a throughput-optimized architecture and a resource-optimized architecture that utilizes fewer FPGA blocks. In both cases, high speed is achieved by concatenating all state-space variables of each chaos generator into one variable. Furthermore, a new postprocessing method that enables the generated bit-streams to pass all NIST 800.22 statistical tests is introduced. Experimental results show that the throughput-optimized TRBG architecture, based on the 4-D system, can exceed 1882 Mbit/s. However, the resource-optimized TRBG architecture, based on the 3-D system, is the best in terms of FPGA resources and overall Figure of Merit.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Abid, Q. Nasir, A.S. Elwakil, Implementation of an encrypted wireless communication system using nested chaotic maps. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 20(12), 4087–4096 (2010)
M.S. Azzaz, C. Tanougast, S. Sadoudi, R. Fellah, A. Dandache, A new auto-switched chaotic system and its FPGA implementation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 18(7), 1792–1804 (2013)
J.M. Bahi, X. Fang, C. Guyeux, L. Larger, FPGA design for pseudorandom number generator based on chaotic iteration used in information hiding application. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 7(6), 2175–2188 (2013)
M.L. Barakat, A.S. Mansingka, A.G. Radwan, K.N. Salama, Hardware stream cipher with controllable chaos generator for colour image encryption. IET Image Process. 8(1), 33–43 (2014)
T. Bonny, S. Henno, Image edge detectors under different noise levels with FPGA implementations. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218126618502092. (in press)
T. Bonny, A.S. Elwakil, FPGA realizations of high speed switching-type chaotic oscillators using compact VHDL codes. J. Nonlinear Dyn. 93(2), 819–833 (2018)
C. Chen, H. Ma, H. Chen, Y. Meng, Q. Ding, FPGA implementation of a UPT chaotic signal generator for image encryption. Pac. Sci. Rev. A Nat. Sci. Eng. 17(3), 97–102 (2015)
S.-L. Chen, T. Hwang, S.-M. Chang, W.-W. Lin, A fast digital chaotic generator for secure communication. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos (2010). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218127410028136
K. Cho, T. Miyano, Design and test of pseudorandom number generator using a star network of Lorenz oscillators. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27(12), 1750184 (2017)
J.-L. Danger, S. Guilley, P. Hoogvorst, High speed true random number generator based on open loop structures in FPGAs. Microelectron. J. 40(11), 1650–1656 (2009)
L. De Micco, H. A. Larrondo, Methodology for FPGA implementation of a chaos-based AWGN generator, in Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) Technologies for High Performance Instrumentation, IGI Global, pp. 43–58 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-5225-0299-9.ch003
Digilent, Inc, (2016). www.zedboard.org
A.S. Elwakil, Integrator-based circuit-independent chaotic oscillator structure. Chaos 14(2), 364–369 (2004)
X. Fang, Q. Wang, C. Guyeux, J.M. Bahi, FPGA acceleration of a pseudorandom number generator based on chaotic iterations. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 19(1), 78–87 (2014)
http://csrc.nist.gov/groups/ST/toolkit/rng/documentation_software.html
Inc, X.: 7 Series FPGAs Overview, vol. 1. Xilinx (2014)
H. Istvan, A. Suciu, O. Cret, FPGA based TRNG using automatic calibration, in IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Computer Communication and Processing, pp. 373–376 (2009)
I. Koyuncu, A.T. Ozcerit, The design and realization of a new high speed FPGA-based chaotic true random number generator. Comput. Electr. Eng. 58(2), 203–214 (2017)
Q. Liu, P. Li, M. Zhang, Y. Sui, H. Yang, A novel image encryption algorithm based on chaos maps with Markov properties. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 20(2), 506–515 (2015)
C.-Y. Li, Y.-H. Chen, T.-Y. Chang, L.-Y. Deng, K. To, Period extension and randomness enhancement using high-throughput reseeding-mixing PRNG. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 20(2), 385–389 (2012)
A.S. Mansingka, M.A. Zidan, M.L. Barakat, A.G. Radwan, K.N. Salama, Fully digital Jerk-based chaotic oscillators for high throughput pseudo-random number generators up to 8.77 Gbits/s. Microelectron. J. 44(9), 744–752 (2013)
M.A. Maleki, A. Ahmadi, S.V. Makki, H. Soleimani, M. Bavandpour, Networked adaptive non-linear oscillators: a digital synthesis and application. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34(2), 483–512 (2015)
S. Ozoguz, A.S. Elwakil, S. Ergun, Cross-coupled chaotic oscillators and application to random bit generation. IEE Circuits Devices Syst. 153(10), 506–510 (2006)
S. Ozoguz, A.S. Elwakil, M.P. Kennedy, Experimental verification of the butterfly attractor in a modified Lorenz system. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 12(7), 1627–1632 (2002)
M. Park, J.C. Rodgers, D.P. Lathrop, True random number generation using CMOS Boolean chaotic. Microelectron. J. 46(12), 1364–1370 (2015)
F. Pareschi, R. Rovatti, G. Setti, On statistical tests for randomness included in the NIST SP800-22 test suite and based on the binomial distribution. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 7(2), 491–505 (2012)
M. Qiu, S. Yu, Y. Wen, J. Lu, J. He, Z. Lin, Design and FPGA implementation of a universal chaotic signal generator based on the Verilog HDL fixed-point algorithm and state machine control. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 27(3), 1750040–1750055 (2017)
V. Rashtchi, M. Nourazar, FPGA implementation of a real-time weak signal detector using a Duffing oscillator. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 34(10), 3101–3119 (2015)
J. Sprott, Chaos and Time-Series Analysis (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2003)
E. Tlelo-Cuautle, A. Quintas-Valles, L. de la Fraga, J. Rangel-Magdaleno, VHDL descriptions for the FPGA implementation of PWL-function-based multi-scroll chaotic oscillators. PLoS ONE 11(12), e0168300 (2016)
E. Tlelo-Cuautle, J.J. Rangel-Magdaleno, A.D. Pano-Azucena, P.J. Obeso-Rodelo, J.C. Nunez-Perez, FPGA realization of multi-scroll chaotic oscillators. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 27(13), 66–80 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonny, T., Al Debsi, R., Majzoub, S. et al. Hardware Optimized FPGA Implementations of High-Speed True Random Bit Generators Based on Switching-Type Chaotic Oscillators. Circuits Syst Signal Process 38, 1342–1359 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0905-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-018-0905-6