Abstract
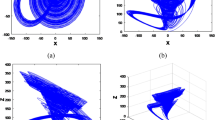
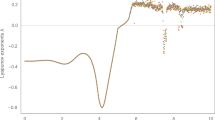
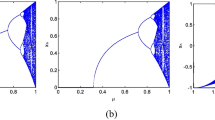
In this work, we demonstrate the possibility of performing two-dimensional rotation on a chaotic system. This enables the rotation of its attractor in space without changing its chaotic dynamics. In particular, the rotated system preserves the same eigenvalues at all equilibrium points and its largest Lyapunov exponent remains unchanged. Two chaotic systems, one of which is the classical Lorenz system, are used to illustrate and validate the rotation operation using numerical simulations and further experimentally using a digital FPGA platform.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.T. Alligood, T.D. Sauer, J.A. Yorke, Chaos: An Introduction to Dynamical Systems (Springer, Berlin, 1996)
M.L. Barakat, A.S. Mansingka, A.G. Radwan, K.N. Salama, Generalized hardware post-processing technique for chaos-based pseudorandom number generators. ETRI J. 35(3), 448–458 (2013)
T. Bonny, A.S. Elwakil, FPGA realizations of high speed switching-type chaotic oscillators using compact VHDL codes. Nonlinear Dyn. 93(2), 819–833 (2018)
V.H. Carbajal-Gomez, E. Tlelo-Cuautle, J.M. Muñoz-Pacheco, L.G. de la Fraga, C. Sanchez-Lopez, F.V. Fernandez-Fernandez, Optimization and CMOS design of chaotic oscillators robust to PVT variations: INVITED. Integration (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vlsi.2018.10.010
V. Carbajal-Gomez, E. Tlelo-Cuautle, C. Sanchez-Lopez, F. Fernandez-Fernandez, PVT-robust CMOS programmable chaotic oscillator: synchronization of two 7-scroll attractors. Electronics 7(10), 252 (2018a)
A.S. Elwakil, M.P. Kennedy, Construction of classes of circuit-independent chaotic oscillators using passive-only nonlinear devices. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I 48(3), 289–307 (2001)
A.S. Elwakil, S. Özoguz, A system and circuit for generating “multi-butterflies”. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 18(03), 841–844 (2008)
A.S. Elwakil, S. Ozoguz, M.P. Kennedy, Creation of a complex butterfly attractor using a novel Lorenz-type system. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst.-I: Fundam. Theory Appl. 49(4), 527–530 (2002)
D.A. Hsieh, Chaos and nonlinear dynamics: application to financial markets. J. Finance 46(5), 1839–1877 (1991)
http://fpgasoftware.intel.com/?edition=lite (Release date: September) (2018)
S.M. Ismail, L.A. Said, A.A. Rezk, A.G. Radwan, A.H. Madian, M.F. Abu-Elyazeed, A.M. Soliman, Generalized fractional logistic map encryption system based on FPGA. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 80, 114–126 (2017)
G. Kaddoum, Wireless chaos-based communication systems: a comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 4, 2621–2648 (2016)
L. Kocarev, S. Lian, Chaos-Based Cryptography: Theory, Algorithms and Applications, vol. 354 (Springer, Berlin, 2011)
F. Lau, C.K. Tse, Chaos-Based Digital Communication Systems (Springer, Berlin, 2003)
E.N. Lorenz, Deterministic nonperiodic flow. J. Atmos. Sci. 20(2), 130–141 (1963)
I. Pan, S. Das, Evolving chaos: identifying new attractors of the generalised lorenz family. Appl. Math. Model. 57, 391–405 (2018)
A. Pano-Azucena, E. Tlelo-Cuautle, G. Rodriguez-Gomez, L. de la Fraga, FPGA-based implementation of chaotic oscillators by applying the numerical method based on trigonometric polynomials. AIP Adv. 8(7), 075217 (2018)
A. Radwan, A. Soliman, A. El-Sedeek, MOS realization of the modified lorenz chaotic system. Chaos Solitons Fract. 21(3), 553–561 (2004)
A.G. Radwan, S.H. AbdElHaleem, S.K. Abd-El-Hafiz, Symmetric encryption algorithms using chaotic and non-chaotic generators: a review. J. Adv. Res. 7(2), 193–208 (2016)
E. Schöll, Nonlinear Spatio-temporal Dynamics and Chaos in Semiconductors, vol. 10 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2001)
D. Shah, R. Charasiys, V. Vyawahare, K. Pichhode, M. Patil, FPGA implementation of fractional-order chaotic systems. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 78, 245–257 (2017)
S.H. Strogatz, Nonlinear Dynamics and Chaos with Applications to Physics, Biology, Chemistry, and Engineering (Westview Press, Boulder, 2014)
M.F. Tolba, A.M. AbdelAty, N.S. Soliman, L.A. Said, A.H. Madian, A.T. Azar, A.G. Radwan, FPGA implementation of two fractional order chaotic systems. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 78, 162–172 (2017)
H. Wang, H.F. Liang, Z.H. Miao, A new color image encryption scheme based on chaos synchronization of time-delay Lorenz system. Adv. Manuf. 4(4), 348–354 (2016)
G.C. Wu, D. Baleanu, Z.X. Lin, Image encryption technique based on fractional chaotic time series. J. Vib. Control 22(8), 2092–2099 (2016)
S. Yu, J. Lü, W.K. Tang, G. Chen, A general multiscroll Lorenz system family and its realization via digital signal processors. Chaos: an interdisciplinary. J. Nonlinear Sci. 16(3), 033126 (2006)
M.A. Zidan, A.G. Radwan, K.N. Salama, Controllable V-shape multiscroll butterfly attractor: system and circuit implementation. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 22(06), 1250143 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sayed, W.S., Radwan, A.G., Elnawawy, M. et al. Two-Dimensional Rotation of Chaotic Attractors: Demonstrative Examples and FPGA Realization. Circuits Syst Signal Process 38, 4890–4903 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01096-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01096-z