Abstract
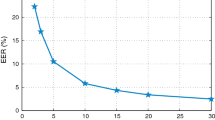
In this work, we explore various noise robust techniques at different stages of a Text-Dependent Speaker Verification (TDSV) system. A speech-specific knowledge-based robust end points detection technique is used for noise compensation at signal level. Feature-level compensation is done by using robust features extracted from Hilbert Spectrum (HS) of the Intrinsic Mode Functions obtained from Modified Empirical Mode Decomposition of speech. We also explored a combined temporal and spectral speech enhancement technique prior to the end points detection for enhancing speech regions embedded in noise. All experimental studies are conducted using two databases, namely the RSR2015 and the IITG database. It is found that the use of robust end points detection improves the performance of the TDSV system compared to the energy-based end points detection in both clean and degraded speech conditions. Use of noise robust HS features augmented with Mel-frequency cepstral coefficients further improves the performance of the system. It is also found that the use of speech enhancement prior to signal and feature-level compensation results in further improvement in performance for the low SNR cases. The final combined system obtained by using three robust methods provides a relative improvement from 6 to 25% in terms of the EER, on the RSR2015 database corrupted with Babble noise of varying strength and by around from 30 to 45% relative improvement on the IITG database.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.D. Alsteris, K.K. Paliwal, Further intelligibility results from human listening tests using the short-time phase spectrum. Speech Commun. 48(6), 727–736 (2006)
Y. Bayya, D.N. Gowda, Spectro-temporal analysis of speech signals using zero-time windowing and group delay function. Speech Commun. 55(6), 782–795 (2013)
H. Beigi, Speaker Recognition: Advancements and Challenges (INTECH Open Access Publisher, London, 2012)
R.K. Bhukya, B.D. Sarma, S.R.M. Prasanna, End point detection using speech-specific knowledge for text-dependent speaker verification. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 37(12), 5507–5539 (2018)
G. Biagetti, P. Crippa, L. Falaschetti, S. Orcioni, C. Turchetti, An investigation on the accuracy of truncated DKLT representation for speaker identification with short sequences of speech frames. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(12), 4235–4249 (2017)
G. Biagetti, P. Crippa, L. Falaschetti, S. Orcioni, C. Turchetti, Speaker identification in noisy conditions using short sequences of speech frames. In: International Conference on Intelligent Decision Technologies (Springer, 2017), pp. 43–52
H. Boril, P. Fousek, P. Pollák, Data-driven design of front-end filter bank for Lombard speech recognition. In: Ninth International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (2006)
A. Bouchikhi, A.O. Boudraa, Multicomponent AM-FM signals analysis based on EMD-B-splines ESA. Signal Process. 92(9), 2214–2228 (2012)
C. Charbuillet, B. Gas, M. Chetouani, J. Zarader, Optimizing feature complementarity by evolution strategy: application to automatic speaker verification. Speech Commun. 51(9), 724–731 (2009)
K.T. Deepak, S.R.M. Prasanna, Foreground speech segmentation and enhancement using glottal closure instants and mel cepstral coefficients. IEEE/ACM Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 24(7), 1205–1219 (2016)
K.T. Deepak, B.D. Sarma, S.R.M. Prasanna, Foreground speech segmentation using zero frequency filtered signal. In: Thirteenth Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (2012)
N. Dehak, P.J. Kenny, R. Dehak, P. Dumouchel, P. Ouellet, Front-end factor analysis for speaker verification. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(4), 788–798 (2011)
S. Dey, S. Barman, R.K. Bhukya, R.K. Das, B.C. Haris, S.R.M. Prasanna, R. Sinha, Speech biometric based attendance system. In: National Conference on Communications (2014)
N. Dhananjaya, B. Yegnanarayana, Voiced/nonvoiced detection based on robustness of voiced epochs. Signal Process. Lett. IEEE 17(3), 273–276 (2010)
G.R. Doddington, M.A. Przybocki, A.F. Martin, D.A. Reynolds, The NIST speaker recognition evaluation—overview, methodology, systems, results, perspective. Speech Commun. 31(2), 225–254 (2000)
Y. Ephraim, D. Malah, Speech enhancement using a minimum mean-square error log-spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 33(2), 443–445 (1985)
P. Flandrin, Some aspects of huangs empirical mode decomposition, from interpretation to applications. In: International Conference of Computational Harmonic Analysis CHA, vol. 4 (2004)
P. Flandrin, P. Gonçalves, G. Rilling, EMD equivalent filter banks, from interpretation to applications, in Hilbert-Huang Transform and Its Applications. Interdisciplinary Mathematical Sciences, ed. by N.E. Huang, S.S.P. Shen (World Scientific Publishing, Singapore, 2005), pp. 57–74
S. Furui, Cepstral analysis technique for automatic speaker verification. IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 29(2), 254–272 (1981)
T. Ganchev, N. Fakotakis, G. Kokkinakis, Comparative evaluation of various MFCC implementations on the speaker verification task. Proc. SPECOM 1, 191–194 (2005)
S. Gazor, W. Zhang, A soft voice activity detector based on a Laplacian–Gaussian model. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Proces. 11(5), 498–505 (2003)
F. Gianfelici, G. Biagetti, P. Crippa, C. Turchetti, Multicomponent AM-FM representations: an asymptotically exact approach. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 15(3), 823–837 (2007)
M. Hébert, Text-dependent speaker recognition, in Springer Handbook of Speech Processing, ed. by J. Benesty, M.M. Sondhi, Y.A. Huang (Springer, 2008), pp. 743–762
R.S. Holambe, M.S. Deshpande, Advances in Non-linear Modeling for Speech Processing (Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin, 2012)
N.E. Huang, Empirical mode decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis (1998), https://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=19990078602
N.E. Huang, S.S. Shen, Hilbert–Huang transform and Its Applications, vol. 5 (World Scientific, Singapore, 2005)
J.C. Junqua, B. Reaves, B. Mak, A study of endpoint detection algorithms in adverse conditions: incidence on a DTW and HMM recognizer. In: Second European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology (1991)
K. Khaldi, A.O. Boudraa, A. Komaty, Speech enhancement using empirical mode decomposition and the Teager–Kaiser energy operator. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 135(1), 451–459 (2014)
A.N. Khan, B. Yegnanarayana, Vowel onset point based variable frame rate analysis for speech recognition. In: Proceedings of 2005 International Conference on Intelligent Sensing and Information Processing, 2005 (IEEE, 2005), pp. 392–394
B.K. Khonglah, R.K. Bhukya, S.R.M. Prasanna, Processing degraded speech for text dependent speaker verification. Int. J. Speech Technol. 20(4), 839–850 (2017)
T. Kinnunen, H. Li, An overview of text-independent speaker recognition: from features to supervectors. Speech Commun. 52(1), 12–40 (2010)
H. Kremer, A. Cohen, T. Vaich, Voice activity detector (VAD) for hmm based speech recognition. In: Proceedings of ICSPAT (1999)
P. Krishnamoorthy, S.R.M. Prasanna, Enhancement of noisy speech by temporal and spectral processing. Speech Commun. 53(2), 154–174 (2011)
A. Larcher, K.A. Lee, B. Ma, H. Li, Text-dependent speaker verification: classifiers, databases and RSR2015. Speech Commun. 60, 56–77 (2014)
K.A. Lee, A. Larcher, H. Thai, B. Ma, H. Li, Joint application of speech and speaker recognition for automation and security in smart home. In: INTERSPEECH (2011), pp. 3317–3318
Q. Li, J. Zheng, A. Tsai, Q. Zhou, Robust endpoint detection and energy normalization for real-time speech and speaker recognition. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 10(3), 146–157 (2002)
D. Mahanta, A. Paul, R.K. Bhukya, R.K. Das, R. Sinha, S.R.M. Prasanna, Warping path and gross spectrum information for speaker verification under degraded condition. In: 22nd National Conference on Communication (NCC) (IEEE, 2016), pp. 1–6
J. Makhoul, Linear prediction: a tutorial review. Proc. IEEE 63(4), 561–580 (1975)
S. Marinov, H.I. Skövde, Text dependent and text independent speaker verification systems. Technology and applications. Overview article (2003)
A. Martin, G. Doddington, T. Kamm, M. Ordowski, M. Przybocki, The DET curve in assessment of detection task performance. Technical report, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Gaithersburg MD (1997)
N. McLaughlin, J. Ming, D. Crookes, Speaker recognition in noisy conditions with limited training data. In: 2011 19th European Signal Processing Conference (IEEE, 2011), pp. 1294–1298
J. Ming, T.J. Hazen, J.R. Glass, D.A. Reynolds, Robust speaker recognition in noisy conditions. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 15(5), 1711–1723 (2007)
K.S.R. Murty, B. Yegnanarayana, M.A. Joseph, Characterization of glottal activity from speech signals. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 16(6), 469–472 (2009)
A. Paul, D. Mahanta, R.K. Das, R.K. Bhukya, S. Prasanna, Presence of speech region detection using vowel-like regions and spectral slope information. In: 2017 14th IEEE India Council International Conference (INDICON) (IEEE, 2017), p. 15
G. Pradhan, S.R.M. Prasanna, Speaker verification by vowel and nonvowel like segmentation. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 21(4), 854–867 (2013)
S.R.M. Prasanna, G. Pradhan, Significance of vowel-like regions for speaker verification under degraded conditions. IEEE Trans. Audio Speech Lang. Process. 19(8), 2552–2565 (2011)
S.R.M. Prasanna, B. Yegnanarayana, Detection of vowel onset point events using excitation information. In: Ninth European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology (2005)
S.R.M. Prasanna, J.M. Zachariah, B. Yegnanarayana, Begin-end detection using vowel onset points. In: Workshop on Spoken Language Processing (2003)
L.R. Rabiner, R.W. Schafer et al., Introduction to digital speech processing. Found. Trends® Signal Process. 1(1–2), 1–194 (2007)
K. Ramesh, S.R.M. Prasanna, R.K. Das, Significance of glottal activity detection and glottal signature for text dependent speaker verification. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing and Communications (SPCOM) (2014), pp. 1–5
B.D. Sarma, S.R.M. Prasanna, P. Sarmah, Consonant-vowel unit recognition using dominant aperiodic and transition region detection. Speech Commun. 92, 77–89 (2017)
R. Sharma, R.K. Bhukya, S.R.M. Prasanna, Analysis of the Hilbert spectrum for text-dependent speaker verification. Speech Commun. 96, 207–224 (2018)
R. Sharma, S.R.M. Prasanna, A better decomposition of speech obtained using modified empirical mode decomposition. Digit. Signal Process. 58, 26–39 (2016)
R. Sharma, S.R.M. Prasanna, R.K. Bhukya, R.K. Das, Analysis of the intrinsic mode functions for speaker information. Speech Commun. 91, 1–16 (2017)
R. Sharma, L. Vignolo, G. Schlotthauer, M.A. Colominas, H.L. Rufiner, S.R.M. Prasanna, Empirical mode decomposition for adaptive AM-FM analysis of speech: a review. Speech Commun. 88, 39–64 (2017)
A. Varga, H.J. Steeneken, Assessment for automatic speech recognition: II. noisex-92: a database and an experiment to study the effect of additive noise on speech recognition systems. Speech Commun. 12(3), 247–251 (1993)
J.D. Wu, Y.J. Tsai, Speaker identification system using empirical mode decomposition and an artificial neural network. Expert Syst. Appl. 38(5), 6112–6117 (2011)
B. Yegnanarayana, S.R.M. Prasanna, J.M. Zachariah, C.S. Gupta, Combining evidence from source, suprasegmental and spectral features for a fixed-text speaker verification system. IEEE Trans. Speech Audio Process. 13(4), 575–582 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhukya, R.K., Prasanna, S.R.M. & Sarma, B.D. Robust Methods for Text-Dependent Speaker Verification. Circuits Syst Signal Process 38, 5253–5288 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01125-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-019-01125-x