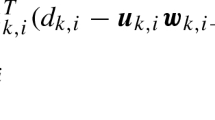Abstract
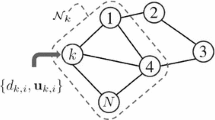
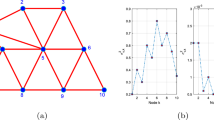
With the development of distributed algorithms, many researchers are committed to the goal of maintaining the long-term stability of the network by reducing the communication cost. However, many algorithms that lessen communication costs often result in a significant decrease in estimation accuracy. In order to reduce the communication cost with less performance degradation, the distributed neighbor-partial diffusion least-mean-square algorithm (NPDLMS) is proposed in this paper. Besides, considering the data redundancy in the network, we offer the distributed data selection NPDLMS algorithm, which further improves the estimation accuracy and reduces the communication cost. In the performance analysis, the stability and the communication cost of the algorithms are given.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Abdolee, B. Champagne, A. H. Sayed, A diffusion LMS strategy for parameter estimation in noisy regressor applications, in: Proceedings of the 20th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), IEEE, pp. 749753 (2012)
R. Arablouei, K. Dogancay, S. Werner, Y. Huang, Adaptive distributed estimation based on recursive least-squares and partial diffusion. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(14), 3510–3522 (2014)
R. Arablouei, S. Werner, Y.F. Huang et al., Distributed least mean-square estimation with partial diffusion. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(2), 472–484 (2014)
A. Bertrand, M. Moonen, Consensus-based distributed total least squares estimation in ad hoc wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(5), 2320–2330 (2011)
A. Bertrand, M. Moonen, Low-complexity distributed total least squares estimation in ad hoc sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(8), 4321–4333 (2012)
A. Bertrand, M. Moonen, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion bias-compensated RLS estimation over adaptive networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(11), 5212–5224 (2011)
D.P. Bertsekas, A new class of incremental gradient methods for least squares problems. SIAM J. Optim. 7(4), 913–926 (1997)
N. Bogdanovic, J. Platachaves, K. Berberidis, Distributed incremental-based LMS for node-specific adaptive parameter estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 62(20), 5382–5397 (2014)
F.S. Cattivelli, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion LMS strategies for distributed estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(3), 1035–1048 (2010)
J. Chen et al., Multi-step-length gradient iterative algorithm for equation-error type models. Syst. Control Lett. 115, 15–21 (2018)
J. Chen et al., Variational Bayesian approach for ARX systems with missing observations and varying time-delays. Automatica 94, 194–204 (2018)
J. Chen, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion adaptation strategies for distributed optimization and learning over networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(8), 4289–4305 (2012)
F. Chen, X. Shao, Broken-motifs diffusion LMS algorithm for reducing communication load. Signal Process. 133, 213–218 (2017)
B. Chen, J. Wang, H. Zhao, N. Zheng, J.C. Principe, Convergence of a fixed-point algorithm under maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 22(10), 1723–1727 (2015)
B. Chen, L. Xing, H. Zhao, N. Zheng, J.C. Principe, Generalized correntropy for robust adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 64(13), 3376–3387 (2016)
F. Chen, X. Li, S. Duan, L. Wang, J. Wu, Diffusion generalized maximum correntropy criterion algorithm for distributed estimation over multitask network. Digit. Signal Process. 81, 16–25 (2018)
F. Chen, T. Shi, S. Duan, L. Wang, J. Wu, Diffusion least logarithmic absolute difference algorithm for distributed estimation. Signal Process. 142, 423–430 (2018)
S. Chouvardas, K. Slavakis, S. Theodoridis, Adaptive robust distributed learning in diffusion sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 59(10), 4692–4707 (2011)
L. Dang et al., Kernel Kalman filtering with conditional embedding and maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 66(11), 4265–4277 (2019)
P.S. Diniz, On data-selective adaptive filtering. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 66(16), 4239–4252 (2018)
J. Hua, C. Li, H. Shen, Distributed learning of predictive structures from multiple tasks over networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(5), 4246–4256 (2017)
S. Huang, C. Li, Distributed sparse total least-squares over networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 63(11), 2986–2998 (2015)
Y. Jiang, S. Yin, Recursive total principle component regression based fault detection and its application to vehicular cyber-physical systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 14(4), 1415–1423 (2017)
Y. Jiang, S. Yin, O. Kaynak, Data-driven monitoring and safety control of industrial cyber-physical systems: basics and beyond. IEEE Access 6, 47374–47384 (2018)
S. Kar, J.M. Moura, Distributed consensus algorithms in sensor networks with imperfect communication: link failures and channel noise. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57(1), 355–369 (2009)
C. Li, P. Shen, Y. Liu, Z. Zhang, Diffusion information theoretic learning for distributed estimation over network. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(16), 4011–4024 (2013)
H. Liang, Y. Zhang, T. Huang, H. Ma, Prescribed performance cooperative control for multiagent systems with input quantization. In: IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics (Early Access), pp. 1–10. IEEE (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TCYB.2019.2893645
H. Liang, Z. Zhang, C.K. Ahn, Event-triggered fault detection and isolation of discrete-time systems based on geometric technique. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Br. 67(2), 335–339 (2019)
Y. Liu, C. Li, Z. Zhang, Diffusion sparse least-mean squares over networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(8), 4480–4485 (2012)
C.G. Lopes, A.H. Sayed, Incremental adaptive strategies over distributed networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 55(8), 4064–4077 (2007)
G. Mateos, I.D. Schizas, G.B. Giannakis, Distributed recursive least-squares for consensus-based in-network adaptive estimation. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 57(11), 4583–4588 (2009)
A. Nedic, D.P. Bertsekas, Incremental subgradient methods for nondifferentiable optimization. SIAM J. Optim. 12(1), 109–138 (2001)
M.G. Rabbat, R.D. Nowak, Quantized incremental algorithms for distributed optimization. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 23(4), 798–808 (2005)
I.D. Schizas, A. Ribeiro, G.B. Giannakis, Consensus in ad hoc wsns with noisy links<apart i: distributed estimation of deterministic signals. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(1), 350–364 (2008)
S.S. Stankovic, M.S. Stankovic, D.M. Stipanovic, Decentralized parameter estimation by consensus based stochastic approximation. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 56(3), 531–543 (2011)
N. Takahashi, I. Yamada, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion least-mean squares with adaptive combiners: formulation and performance analysis. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 58(9), 4795–4810 (2010)
V. Vadidpour, A. Rastegarnia, A. Khalili, S. Sanei, Partial-diffusion least mean-square estimation over networks under noisy information exchange. arXiv:1511.09044
S. Wang, C. Li, Distributed robust optimization in networked system. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 47(8), 2321–2333 (2017)
Z. Wang, Y. Wang, Z. Ji, A novel two-stage estimation algorithm for nonlinear Hammerstein–Wiener systems from noisy input and output data. J. Frankl. Inst. 354(4), 1937–1944 (2017)
Z. Wang, Z. Tang, J.H. Park, A novel two-stage ellipsoid filtering-based system modeling algorithm for a Hammerstein nonlinear model with an unknown noise term. Nonlinear Dyn. 98, 1–7 (2019)
H. Zhang et al., A new delay-compensation scheme for networked control systems in controller area networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 65(9), 7239–7247 (2018)
H. Zhang, J. Wang, Active steering actuator fault detection for an automatically-steered electric ground vehicle. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 66(5), 3685–3702 (2016)
X. Zhao, S.-Y. Tu, A.H. Sayed, Diffusion adaptation over networks under imperfect information exchange and non-stationary data. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(7), 3460–3475 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported in part by National Key R&D Program of China (Nos. 2018YFB1306600, 2018YFB1306604), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2020B034).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, F., Deng, S., Hua, Y. et al. Communication-Reducing Algorithm of Distributed Least Mean Square Algorithm with Neighbor-Partial Diffusion. Circuits Syst Signal Process 39, 4416–4435 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01374-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01374-1