Abstract
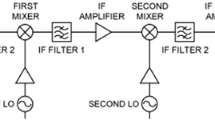
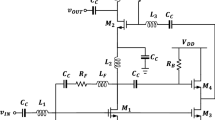
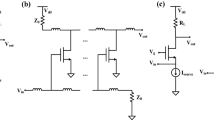
A noise optimization method for millimeter-wave RF wideband applications is reported. Intrinsic noise laws in wideband RF systems are discovered, and a noise flatness methodology based on a network quality factor algorithm is proposed. This algorithm aims to reduce the total noise in an RF system and increase the noise flatness over a full operating band. An RF wideband front end is investigated to verify the noise optimization theory and maintain circuit performance. Using noise flatness methodology and a SiGe heterojunction bipolar transistor process featuring a fT/fmax of 240/280 GHz, the front-end results show good performance and compliance with the proposed method.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Bhatia, S. Hyvonen, E. Rosenbaum, A compact, ESD-protected, SiGe BiCMOS LNA for ultra-wideband applications. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 42, 1121–1130 (2007)
H. Chen, Y. Lin, S. Lu, Analysis and design of a 1.6–28-GHz compact wideband LNA in 90-nm CMOS using a π-match input network. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 58(8), 2092–2104 (2010)
C. Feng, X.P. Yu, Z.H. Lu, W.M. Lim, W.Q. Sui, 3-10 GHz self-biased resistive-feedback LNA with inductive source degeneration. Electron. Lett. 49(6), 409–410 (2013)
B.Q. Guo, J. Chen, H.Y. Jin, A linearized common-gate low-noise amplifier using active cross-coupled feedback technique. Analog Integr. Circ. Signal Process 89(1), 239–248 (2016)
B. Guo, X. Li, A 1.6–9.7 GHz CMOS LNA linearized by post distortion technique. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 23(11), 608–610 (2013)
M. Hayati, S. Cheraghaliei, S. Zarghami, Design of UWB low noise amplifier using noise-canceling and current-reused techniques. Integr. VLSI J. 60, 232–239 (2018)
K. Jing, N. Yu, X. Quan, An S- to Ku-wideband low-noise amplifier using asymmetric π filter and shunt-peaking technique with simultaneous input match and noise flatness. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 61(6), 1509–1516 (2019)
J. Kai, Y. Zhuang, Z. Li, Z. Zhao, L. Nie, A SiGe LC-ladder low noise amplifier with base resistance match, gain and noise flatness for UWB applications. Microelectron. J. 45(6), 648–656 (2014)
A.R.A. Kumar, B.D. Sahoo, A. Dutta, A wideband 2–5 GHz noise canceling subthreshold low noise amplifier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 65(7), 834–838 (2018)
N. Li, W.W. Feng, X.P. Li, A CMOS 3–12-GHz ultrawideband low noise amplifier by dual-resonance network. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 27(4), 383–385 (2017)
Y.S. Lin, C.C. Chen, C.Y. Lee, 7.2 mW CMOS low-noise amplifier with 17.3 dB gain and 7.7 dB NF for 76–77 GHz long-range and 77–81 GHz short-range automotive radars. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process 87(1), 1–9 (2016)
G. Nikandish, A. Medi, A 40-GHz bandwidth tapered distributed LNA. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 65(11), 1614–1618 (2018)
Z. Pan, C. Qin, Z. Ye, Y. Wang, Z. Yu, Wideband inductorless low-power LNAs with gm enhancement and noise-cancellation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 65(1), 26–38 (2018)
J.-Y. Park, J.-Y. Lee, C.-K. Yeo, T.-Y. Yun, Analysis and optimization of a resistive-feedback inverter LNA. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 60(5), 1143–1151 (2018)
P. Qin, Q. Xue, Compact wideband LNA with gain and input matching bandwidth extensions by transformer. IEEE Microwave Wirel. Compon. Lett. 27(7), 657–659 (2017)
C. Wang, 11.81 mW 3.1–10.6 GHz ultra-wideband low-noise amplifier with 2.87 ± 0.19 dB noise figure and 12.52 ± 0.81 dB gain using 0.18 mu m CMOS technology. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 54(6), 1445–1450 (2012)
A. Yarahmadi, A. Jannesari, Two-path inverter-based low noise amplifier for 10-12 GHz applications. Microelectron. J. 50, 76–82 (2016)
H. Yu, Y. Chen, C.C. Boon, C. Li, P.-I. Mak, R.P. Martins, A 0.044-mm2 0.5-To-7-GHz resistor-plus-source-follower-feedback noise-cancelling LNA achieving a flat NF of 3.3 ± 0.45 dB. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 66(1), 71–75 (2019)
X.P. Yu, W.L. Xu, C. Feng, Z.H. Lu, W.M. Lim, K.S. Yeo, A 11.2 mW 48–62 GHz low noise amplifier in 65 nm CMOS technology. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 35(5), 1531–1543 (2016)
S. Zeinolabedinzadeh, A.C. Ulusoy, M.A. Oakley, N.E. Lourenco, J.D. Cressler, A 0.3–15 GHz SiGe LNA with 1 THz gain-bandwidth product. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 27(4), 380–382 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the National Natural Science Foundation (61771388), the Xi’an Science and Technology Program (2019217814GXRC014CG015-GXYD14.3, 201805037YD15CG 21(11)), the XAUT Education Reform Project (252041911, 251031903), and the Scientific Research Project of Shaanxi Education Department (19JC029) for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jing, K., Yu, N., Wang, X. et al. Methodology of Noise Flatness Based on Network Quality Factor in RF Wideband Applications. Circuits Syst Signal Process 39, 4499–4515 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01380-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01380-3