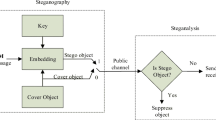
Abstract
In recent years, researchers have considered quantum steganography and its various methods with the development and progress of research in computation theory and quantum signals processing. The destructive use of quantum steganography methods to establish illegal covert communications is rising, so it is essential to introduce ways to detect hidden data in a quantum medium. Accordingly, this paper presents a frequency-based universal audio steganalysis approach to detecting quantum steganography. First, based on the quantum Fourier transform, the characteristic of the quantum spectrum centroid (QSC) was computed, and its circuit network was implemented to extract feature vectors. The proposed method classifies quantum audio signals using a quantum machine learning approach called a quantum ensemble of quantum classifiers. This approach was implemented within the framework of the Deutsch–Jozsa algorithm, which uses the superposition property to create an ensemble of classifiers evaluated in parallel, significantly increasing the computational speed. The accuracy weight of the classifiers is adjusted based on the classifiers' performance in training data classification; finally, the measurement of the first n qubits of the Deutsch–Jozsa algorithm predicts whether the quantum audio signals belong to the stego or clean class. The idea stems from the classic ensemble methods that try to build more robust models by combining different classifiers. The results show that the proposed frequency domain steganalysis method with 95% accuracy performs better than the previous methods in the time domain.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Abbas, M. Schuld, F. Petruccione, On quantum ensembles of quantum classifiers. Quant. Mach. Intell. 2(1), 1–8 (2020)
M.J. Chaharlang, S. Mosleh, H. Rasouli, A novel quantum audio steganography–steganalysis approach using LSFQ-based embedding and QKNN-based classifier. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 39(8), 3925–3957 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-020-01345-6
J. Chaharlang, M. MoslehS, A. Rasouli-Heikalabad, A novel quantum steganography-Steganalysis system for audio signals. Multimedia Tools Appl. 79(25), 17551–17577 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-020-08694-z
K. Chen, F. Yan, A.M. Iliyasu, J. Zhao, Exploring the implementation of steganography protocols on quantum audio signals. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(2), 476–494 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-017-3580-7
S.A. Cuccaro, T.G. Draper, S.A. Kutin, D.P. Moulton, A new quantum ripple-carry addition circuit. arXiv preprint quant-ph/0410184. (2004). https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.quant-ph/0410184
A. GalindoM, A. Martin-Delgado, Information and computation: classical and quantum aspects. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74(2), 347 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.74.347
H. GhasemzadehM, H. Kayvanrad, Comprehensive review of audio steganalysis methods. IET Signal Proc. 12(6), 673–687 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-spr.2016.0651
S. Gulde, M. Riebe, G.P. Lancaster, C. Becher, J. Eschner, H. Häffner, F. Schmidt-Kaler, I.L. Chuang, R. Blatt, Implementation of the Deutsch-Jozsa algorithm on an ion-trap quantum computer. Nature 421(6918), 48–50 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01336
P. Li, X. Liu, Bilinear interpolation method for quantum images based on quantum Fourier transform. Int. J. Quant. Inform. 16(04), 1850031 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219749918500314
P. Li, B. Wang, H. Xiao, X. Liu, Quantum representation and basic operations of digital signals. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(10), 3242–3270 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-018-3841-0
Q. Liu, A.H. Sung, M. Qiao. Spectrum steganalysis of WAV audio streams, in International Workshop on Machine Learning and Data Mining in Pattern Recognition. (2009). Springer
Q. Liu, A.H. Sung, M. Qiao, Temporal derivative-based spectrum and mel-cepstrum audio steganalysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 4(3), 359–368 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIFS.2009.2024718
X. Lu, N. Jiang, H. HuZ, Ji, Quantum adder for superposition states. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 57(9), 2575–2584 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/S10773-018-3779-2
M.A. NielsenI, L. Chuang, Quantum computation and quantum information. Am. J. Phys. 26(4), 37 (2010)
C.-Y. Pang, R.-G. Zhou, B.-Q. Hu, W. Hu, A. El-Rafei, Signal and image compression using quantum discrete cosine transform. Inf. Sci. 473, 121–141 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2018.08.067
P. Rao, Audio Signal Processing. (2007). p. 169–189.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-75398-8_8
E. Şahin, I. Yilmaz, QRMA: quantum representation of multichannel audio. Quant. Inf. Process. 18(7), 1–30 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-019-2317-3
M. Schuld, F. Petruccione, Quantum ensembles of quantum classifiers. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 1–12 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-20403-3
Y. Takahashi, N. Kunihiro, A linear-size quantum circuit for addition with no ancillary qubits. Quant. Inf. Comput. 5(6), 440–448 (2005)
S. Tang, The Principle of Computer Composition (Higher Education Process, Beijing, 2008), pp.258–269
V. Vedral, A. Barenco, A. Ekert, Quantum networks for elementary arithmetic operations. Phys. Rev. A 54(1), 147 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.54.147
D. Wang, Z.-H. Liu, W.-N. Zhu, S.-Z. Li, Design of quantum comparator based on extended general Toffoli gates with multiple targets. Comput. Sci. 39(9), 302–306 (2012)
J. Wang, QRDA: quantum representation of digital audio. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 55(3), 1622–1641 (2016)
Y. Wei, L. Guo, Y. Wang, C. Wang, A blind audio steganalysis based on feature fusion. J. Electron. 28(3), 265–276 (2011)
F. Yan, K. Chen, A.M. Iliyasu, K. Hirota, Circuit-based modular implementation of quantum ghost imaging. IEEE Access. 8, 23054–23068 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2970016
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Norouzi Larki, S., Mosleh, M. & Kheyrandish, M. Quantum Audio Steganalysis Based on Quantum Fourier Transform and Deutsch–Jozsa Algorithm. Circuits Syst Signal Process 42, 2235–2258 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02208-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00034-022-02208-y