Abstract
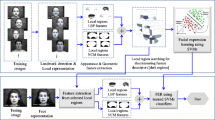
This paper proposes a method for facial expression recognition in image sequences. Face is detected from the scene and then facial features are detected using image normalization, and thresholding techniques. Using an optimization algorithm the Candide wire frame model is adapted properly on the first frame of face image sequence. In the subsequent frames of image sequence facial features are tracked using active appearance algorithm. Once the model fits on the first frame, animation parameters of model are set to zero, to obtain the shape of model for the neutral facial expression of the same face. The last frame of the image sequence corresponds to greatest facial expression intensity. The geometrical displacement of the Candide wire frame nodes, between the neutral expression frame and the last frame, is used as an input to the multiclass support vector machine, which classifies facial expression into one of the class such as happy, surprise, sadness, anger, disgust, fear and neutral. This method is applicable for frontal as well as tilted faces with angle \(\pm 30\,^{\circ }, \pm 45\,^{\circ }, \pm 60\,^{\circ }\) with respect to y axis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ekman, P., Friesen, W.V.: Facial Action Coding System Manual. Palo Alto Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto (1978)
Fasel, B., Luettin, J.: Automatic facial expression analysis: a survey. Pattern Recognit. 36(1), 259–275 (2003)
Pantic, M., Rothkrantz, L.J.M.: Automatic analysis of facial expressions: the state of the art. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 22, 1424–1445 (2000)
Lajevardi, S., Lech, M.: Facial expression recognition from image sequences using optimized feature selection. In: 23rd International Conference on Image and Vision Computing, pp. 1–6. New Zealand (2008)
Viola, P., Jones, M.: Robust real-time object detection. Technical Report, Cambridge Research Laboratory, Technical Report Series (2001)
Yacoob, Y., Davis, L.: Recognizing human facial expressions from long image sequences using optical flow. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 18(6), 636–642 (1996)
Essa, I.A., Pentland, A.P.: Coding, analysis, interpretation, and recognition of facial expressionsl. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 19, 757–763 (1997)
Pentland, A., Moghaddam, B., starner, T.: View based and modular eigenspaces for face recognition. In: Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 84–91 (1994)
Simoncelli, E.: Distributed representation and analysis of visual motion. Ph.D. thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1993)
Kimura, S., Yachida, M.: Facial expression recognition and its degree estimation. In: Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 295–300 (1997)
Wu, H., Yokoyama, T., Pramadihanto, D., Yachinda, M.: Face and facial feature extraction from color image. In: Proceedings of the International Conference Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 343–350 (1996)
Cohn, J. F., Ziochower, A. J., lien, J. J., kanade, T.: Feature point tracking by optical flow discriminates subtle differences in facial expression. In: Proceedings of the International Conference Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 396–401 (1998)
Lucas, B., Kanade, T.: An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision. In: Proceedings of the Joint Conference Artificial Intelligence, pp. 674–680 (1981)
Wang, M., Iwai, Y., Yachindai, M.: Expression recognition from time-sequential facial images by use of expression change model. In: Proceedings of the International Conference Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 324–329 (1998)
Buhmann, J., Lange, J., von der Malsburg, C.: Distortion invariant object recognition matching hierarchically labelled graphs. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference Neural Networks, pp. 155–159 (1989)
Valstar, M., Patras, I., Pantic, M.: Facial action unit recognition using temporal templates. In: 13th IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human Interactive, Communication, pp. 253–258 (2004)
Bobick, A., Davis, J.: The recognition of human movement using temporal templates. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 23(3), 257–267 (2001)
Isard, M., Blake, A.: Condensation—conditional density propagation for visual tracking. Int. J. Comput Vis. 29, 5–28 (1998)
Cohen, I., Sebe, N., Garg, A., Chen, L.S., Huang, T.S.: Facial expression recognition from video sequences: temporal and static modeling. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 91, 160–187 (2003)
Hai, T., Huang, T.: Connected vibrations: a modal analysis approach for non-rigid motion tracking. IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 735–740, June 1998
Black, M.J., Yacoob, Y.: Recognizing facial expressions in image sequences using local parameterized models of image motion. lnt. J. Comput. Vis. 25(1)), 23–48 (1997)
Kotsia, I., Pitas, I.: Facial expression recognition in image sequences using geometric deformation features and support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 16, 172–187 (2007)
Bouguet, J.Y.: Pyramidal implementation of the Lucas-Kanade feature tracker. Technical Report Intel Corporation, Microprocessor Research Labs (1999)
Cootes, T.F., Edwards, G., Taylor, C.J.: Active appearance models. In: Proceedings of the 5th European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 484–498 (1998)
Patil, R., Sahula, V., Mandal, A.: Automatic detection of facial feature points in image sequences. International Conference on Image Information Processing ICIIP, Nov 2011
Welsh, B.: Model based coding of images. Ph.D. dessertation, British Telecom Research Lab, Jan 1991
Ahlberg, J.: Wincandide 1.3 user’s manual. Technical Report. Report No. LiTH-ISY-R-2344, Department of EE, Linkoping University (2001)
Weisstein, E. W.: Barycentric coordinates, MathWorld-A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/BarycentricCoordinates.html. Accessed 24 Jan 2010
Ahlberg, J.: Fast image warping for active models. Technical Report. Report No. LiTH-ISY-R-2355, Department of EE, Linkoping University (2001)
Ahlberg, J.: An active model for facial feature tracking. EURASIP J. Appl. Signal Process. 2002, 566–571 (2001)
Hsu, C.-W., Chang, C.-C., Lin, C.-J.: A practical guide to support vector classification. National Taiwan University, Taipei 106, Taiwan
Kanade, T., Cohn, J., Tian, Y.: Comprehensive database for facial expression analysis. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 46–53, March 2000
Nordstrøm, M. M., Larsen, M., Sierakowski, J., Stegmann, M. B.: The IMM face database—an annotated dataset of 240 face images. May 2004
Kyrkou, C., Theocharides, T.: Scope: towards a systolic array for SVM object detection. Embed. Syst. Lett. IEEE 1, 46–49 (2009)
Mathur, A., Foody, G.: Multiclass and binary SVM classification: implications for training and classification users. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. IEEE 5, 241–245 (2008)
Liu, H., wei Huang, Y., Liu, D.: Multi-class surface EMG classification using support vector machines and wavelet transform. In: 8th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, pp. 2963–2967, July 2010
Hsu, C.W., Lin, C.J.: A comparison of methods for multiclass support vector machines. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 13, 415–425 (2002)
Weston, J., Watkins, C.: Multi-class support vector machines. Technical Report. CSD-TR-98-04 (2004)
Strom, J., Davoine, F., Ahlberg, J.: Very low bit rate facial texture coding. In: Proceedings of the International Workshop on Synthetic/Natural Hybrid Coding and 3D, Imaging, pp. 237–240, Sept 1997
Burges, C. J.: A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition. J. Data Min. Knowl. Disc 2, 121–167 (1998)
Cootes, T., Taylor, C., Cooper, D., Graham, J.: Active shape models-training and application. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 61(1), 38–59 (1995)
Anderson, K., Peter, W.: A real time automated system for the recognition of human facial expressions. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 36, 96–105 (2006)
Lanitis, A., Taylor, C., Cootes, T.: Automatic interpretation and coding of face images using flexible models. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 19(7), 743–756 (1997)
Lien, C. J., Kanade, T., Cohn, J. F., Li, C.: Detection, tracking, and classification of action units in facial expressions. J. Robot Auton. Syst. (1999)
Tian, Y., Kanade, T., Cohn, J.: Recognizing action units for facial expression analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 23, 97–115 (2001)
Ming-Hsuan, Y., Kriegman, D.J., Ahuja, N.: Detecting faces in images: a survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 24(1), 34–58 (2002)
Gokturk, S. B., Tomasi, C., Girod, B., Bouguet, J.-Y.: Model-based face tracking for view-independent facial expression recognition. In: Proceedings of the 5th IEEE International Conference Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, pp. 287–293, May 2002
Pontil, M., Verri, A.: Support vector machines for 3D object recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 20, 637–646 (1998)
Drucker, H., Donghui, W., Vapniki, V.: Support vector machines for spam categorization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 10, 1048–1054 (1999)
Canu, S., Grandvalet, Y., Guigue, V., Rakotomamonjy, A.: SVM and Kernel Methods Matlab Toolbox. Perception Systems Information. INSA de Rouen, France (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, R.A., Sahula, V. & Mandal, A.S. Features classification using geometrical deformation feature vector of support vector machine and active appearance algorithm for automatic facial expression recognition. Machine Vision and Applications 25, 747–761 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-014-0594-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-014-0594-5