Abstract
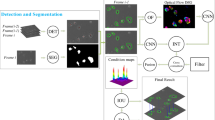
In this work, we propose a new joint detection and tracking method for cell tracking. First, we develop a new procedure for generating an over-complete set of detection hypotheses via ellipse fitting, and then, we define several local events and their corresponding labeling variables to account for both biological behavior of cells and segmentation errors. The task of cell tracking is formulated as an integer linear programming problem with constraints and solved efficiently using commercial software. In addition, instead of learning local classifiers independently, we exploit block-coordinate Frank–Wolfe algorithm to learn the optimal parameters of our model under the framework of structured SVM. We also present the kernelized version of the learning algorithm which can boost the tracking performance further. Experimental results on public datasets show that our method is competitive with the state-of-the-art ones.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krzic, U., Gunther, S., Saunders, T.E., Streichan, S.J., Hufnagel, L.: Multiview light-sheet microscope for rapid in toto imaging. Nat. Methods 9(7), 730–733 (2012)
Tomer, R., Khairy, K., Amat, F., Keller, P.J.: Quantitative high-speed imaging of entire developing embryos with simultaneous multiview light-sheet microscopy. Nat. Methods 9(7), 755–763 (2012)
Meijering, E., Dzyubachyk, O., Smal, I., van Cappellen, W.A.: Tracking in cell and developmental biology. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 20(8), 894–902 (2009)
Kanade, T., Yin, Z., Bise, R., Huh, S., Eom, S., Sandbothe, M.F., Chen, M.: Cell image analysis: algorithms, system and applications. In: 2011 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision, 5-7 Jan. 2011, pp. 374–381 (2011)
Meijering, E., Dzyubachyk, O., Smal, I.: Methods for cell and particle tracking. Methods Enzymol. 504, 183–200 (2012). doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-391857-4.00009-4
González Serrano, G., Fusco, L., Pertz, O., Smith, K.: Automated quantification of morphodynamics for high-throughput live cell imaging datasets. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, pp. 664–667 (2013)
Maska, M., Ulman, V., Svoboda, D., Matula, P., Matula, P.: A benchmark for comparison of cell tracking algorithms. Bioinformatics 30(11), 1609–1617 (2014)
Dufour, A., Shinin, V., Tajbakhsh, S., Guillen-Aghion, N., Olivo-Marin, J.C., Zimmer, C.: Segmenting and tracking fluorescent cells in dynamic 3-D microscopy with coupled active surfaces. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 14(9), 1396–1410 (2005)
Li, K., Miller, E.D., Chen, M., Kanade, T., Weiss, L.E., Campbell, P.G.: Cell population tracking and lineage construction with spatiotemporal context. Med. Image Anal. 12(5), 546–566 (2008)
Dzyubachyk, O., van Cappellen, W.A., Essers, J., Niessen, W.J., Meijering, E.: Advanced level-set-based cell tracking in time-lapse fluorescence microscopy. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 29(3), 852–867 (2010)
Dufour, A., Thibeaux, R., Labruyere, E., Guillen, N., Olivo-Marin, J.C.: 3-D active meshes: fast discrete deformable models for cell tracking in 3-D time-lapse microscopy. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 20(7), 1925–1937 (2011)
Delgado-Gonzalo, R., Chenouard, N., Unser, M.: Fast parametric snakes for 3D microscopy. IEEE Int. Symp. Biomed. Imag. 2–5(2012), 852–855 (2012)
Maska, M., Danek, O., Garasa, S., Rouzaut, A., Munoz-Barrutia, A., Ortiz-de-Solorzano, C.: Segmentation and shape tracking of whole fluorescent cells based on the Chan-Vese model. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 32(6), 995–1006 (2013)
Amat, F., Lemon, W., Mossing, D.P., McDole, K., Wan, Y., Branson, K., Myers, E.W., Keller, P.J.: Fast, accurate reconstruction of cell lineages from large-scale fluorescence microscopy data. Nat. Methods 11(9), 951–958 (2014)
Chenouard, N., Bloch, I., Olivo-Marin, J.C.: Multiple hypothesis tracking for cluttered biological image sequences. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 35(11), 2736–3750 (2013)
Li, F., Zhou, X., Ma, J., Wong, S.T.: Multiple nuclei tracking using integer programming for quantitative cancer cell cycle analysis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 29(1), 96–105 (2010)
Kausler, B.X., Schiegg, M., Andres, B., Lindner, M.: A discrete chain graph model for 3d+t cell tracking with high misdetection robustness. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 144–157 (2012)
Lou, X., Schiegg, M., Hamprecht, F.A.: Active structured learning for cell tracking: algorithm, framework, and usability. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 33(4), 849–860 (2014)
Magnusson, K.E.G., Jaldén, J.: A batch algorithm using iterative application of the Viterbi algorithm to track cells and construct cell lineages. In: IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, pp. 382–385 (2012)
Padfield, D., Rittscher, J., Roysam, B.: Coupled minimum-cost flow cell tracking for high-throughput quantitative analysis. Med. Image Anal. 15(4), 650–668 (2011)
Schiegg, M., Hanslovsky, P., Kausler, B.X., Hufnagel, L., Hamprecht, F.A.: Conservation tracking. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2928–2935 (2013)
Schiegg, M., Hanslovsky, P., Haubold, C., Koethe, U., Hufnagel, L., Hamprecht, F.A.: Graphical model for joint segmentation and tracking of multiple dividing cells. Bioinformatics 31(6), 948–956 (2015)
Magnusson, K.E., Jalden, J., Gilbert, P.M., Blau, H.M.: Global linking of cell tracks using the Viterbi algorithm. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 34(4), 911–929 (2015)
Turetken, E., Wang, X., Becker, C.J., Haubold, C., Fua, P.: Network flow integer programming to track elliptical cells in time-lapse sequences. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 36, 942 (2016). doi:10.1109/TMI.2016.2640859
Lacoste-Julien, S., Jaggi, M., Schmidt, M., Pletscher, P.: Block-coordinate frank-wolfe optimization for structural SVMs. In: International Conference on Machine Learning, Atlanta, United States, pp. 53–61 (2013)
Schindelin, J., Arganda-Carreras, I., Frise, E., Kaynig, V., Longair, M., Pietzsch, T., Preibisch, S., Rueden, C., Saalfeld, S., Schmid, B., Tinevez, J.Y., White, D.J., Hartenstein, V., Eliceiri, K., Tomancak, P., Cardona, A.: Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 9(7), 676–682 (2012)
Kovesi, P.: MATLAB and octave functions for computer vision and image processing. http://www.peterkovesi.com/
Prasad, D.K., Quek, C., Leung, M.K.H., Cho, S.Y.: A parameter independent line fitting method. In: Asian Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp. 441–445 (2011)
Prasad, D.K., Leung, M.K.H., Quek, C.: ElliFit: An unconstrained, non-iterative, least squares based geometric Ellipse Fitting method. Pattern Recognit. 46(5), 1449–1465 (2013)
Nowozin, S., Lampert, C.H.: Structured learning and prediction in computer vision. Found. Trends Comput. Graph. Vision 6(3–4), 185–365 (2011)
Solorzano, C.O., Kozubek, M., Meijering, E., noz Barrutia, A.M.: ISBI Cell Tracking Challenge (2014). http://www.codesolorzano.com/celltrackingchallenge/Cell_Tracking_Challenge/Welcome.html
Lofberg, J.: YALMIP : a toolbox for modeling and optimization in MATLAB. In: 2004 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp. 284–289 (2004)
Bensch, R., Ronneberger, O.: Cell segmentation and tracking in phase contrast images using graph cut with asymmetric boundary costs. In: International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging, pp. 1220–1223 (2015)
Achanta, R., Shaji, A., Smith, K., Lucchi, A., Fua, P., Süsstrunk, S.: SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(11), 2274–2282 (2012)
Matula, P., Maska, M., Sorokin, D.V., Matula, P., Ortiz-de-Solorzano, C., Kozubek, M.: Cell tracking accuracy measurement based on comparison of acyclic oriented graphs. PloS ONE 10(12), e0144959 (2015)
IBM CPLEX. http://www-01.ibm.com/software/commerce/optimization/cplex-optimizer/
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, under Grant No.61174020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiuqing, W., Xu, C. & Xianhang, Z. Cell tracking via Structured Prediction and Learning. Machine Vision and Applications 28, 859–874 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-017-0872-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-017-0872-0