Abstract
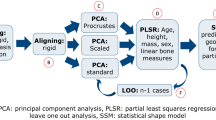
We propose a new method for recovering the pelvis of an ancient skeleton from its three component bones with collapsed surfaces. The proposed method uses four types of statistical shape models (SSMs) for the bones. The SSM for each bone describes the mean shape and shape variations of a class of bones. The SSMs for the three component bones are employed to restore the shapes of the component bones. The SSM for the whole pelvis provides the natural anatomical shape of the pelvis and the spatial relationship among the sacrum and the hip bones. Therefore, the three component bones are aligned by using the SSM for the pelvis. The experimental results show that our method achieves reliable reconstruction of the ancient pelvis shape despite having collapsed surfaces in its component bones.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht, T., Vetter, T.: Automatic fracture reduction. In: Proceedings of Mesh Processing in Medical Image Analysis 2012, pp. 22–29 (2012)
Andrews, S., Laidlaw, D.: Toward a framework for assembling broken pottery vessels. In: Proceeding of Eighteenth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 945–946 (2002)
Besl, P., McKay, N.: A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 14(2), 239–256 (1992)
Gong, R., Stewart, J., Abolmaesumi, P.: Reduction of multi-fragment fractures of the distal radius using atlas-based 2D/3D registration. In: Proceedings of the SPIE Medical Imaging 2009: Visualization, Image-Guided Procedures, and Modeling, vol. 7261 (2009)
Gray, H.: Anatomy of the Human Body. Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia (1918)
Harders, M., Barlit, A., Gerber, C., Hodler, J., Székely, G.: An optimized surgical planning environment for complex proximal humerus fractures. In: MICCAI Workshop on Interaction in Medical Image Analysis and Visualization, pp. 1–9 (2007)
Heimann, T., Meinzer, H.: Statistical shape models for 3D medical image segmentation: a review. Med. Image Anal. 13(4), 543–563 (2009)
Huber, P.: Robust estimation of a location parameter. Ann. Math. Stat. 35(1), 73–101 (1964)
Kaick, O., Zhang, H., Hamarneh, G., Cohen-Or, D.: A survey on shape correspondence. In: Eurographics 2010: State of the Art Reports, pp. 61–82 (2011)
Krogman, W., Iscan, M.: The Human Skeleton in Forensic Medicine. C.C Thomas Pub Ltd., Springfield (1986)
Kruggel, F.: Robust parametrization of brain surface meshes. Med. Image Anal. 12(3), 291–299 (2008)
Liu, B., Luoa, X., Huanga, R., Wanb, C., Zhangc, B., Hua, W., Yued, Z.: Virtual plate pre-bending for the long bone fracture based on axis pre-alignment. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 38(4), 233–244 (2014)
Miyauchi, S., Morooka, K., Tsuji, T., Miyagi, Y., Fukuda, T., Kurazume, R.: Area-and angle-preserving parameterization for vertebra surface mesh. Recent Adv. Comput. Methods Clin. Appl. Spine Imaging 13(4), 187–198 (2015)
Miyauchi, S., Morooka, K., Tsuji, T., Miyagi, Y., Fukuda, T., Kurazume, R.: Fast modified self-organizing deformable model: geometrical feature-preserving mapping of organ models onto target surfaces with various shapes and topologies. Comput. Methods Progr. Biomed. 157(4), 237–250 (2018)
Moore, P., Molloy, D.: A survey of computer-based deformable models. In: Proceeding of International Machine Vision and Image Processing Conference 2007, pp. 55–66 (2007)
Morooka, K., Nagahashi, H.: Self-organizing deformable model: a new method for fitting mesh model to given object surface. In: Proceedings of Advances in Visual Computing, pp. 151–158 (2005)
Morooka, K., Nakamoto, M., Sato, Y.: A survey on statistical modeling and machine learning approaches to computer assisted medical intervention: intraoperative anatomy modeling and optimization of interventional procedures. IEICE Trans. Inf. Syst. 96(3), 748–797 (2013)
Otomaru, I., Nakamoto, M., Kagiyama, Y., Takao, M., Sugano, N., Tomiyama, N., Tada, Y., Sato, Y.: Automated preoperative planning of femoral stem in total hip arthroplasty from 3D CT data: Atlas-based approach and comparative study. Med. Image Anal. 16(2), 415–426 (2012)
Scheuering, M., Salama, C., Eckstein, C., Hormann, K., Greiner, G.: Interactive repositioning of bone fracture segments. In: Proceedings of Vision, Modeling and Visualization (VMV), pp. 499–505 (2001)
Sederberg, T., Parry, S.: Free-form deformation of solid geometric models. ACM Siggraph Comput. Graph. 20(4), 151–160 (1986)
Shi, R., Zeng, W., Su, Z., Damasio, H., Lu, Z., Wang, Y., Yau, S., Gu, X.: Hyperbolic harmonic mapping for constrained brain surface registration. In: Proceeding of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2531–2538 (2013)
Su, Z., Wang, Y., Shi, R., Zeng, W., Sun, J., Luo, F., Gu, X.: Optimal mass transport for shape matching and comparison. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37(11), 2246–2259 (2015)
Wang, Y., Shi, J., Yin, X., Gu, X., Chan, T., Yau, S., Toga, A., Thompson, P.: Brain surface conformal parameterization with the Ricci flow. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 31(2), 251–264 (2012)
Watanabe, N.: The preservation of bony substances in the soil of prehistoric sites. J. Anthropol. Soc. Nippon 61(2), 67–74 (1950)
Willis, A., Anderson, D., Thomas, T., Brown, T., Marsh, J.: 3D reconstruction of highly fragmented bone fractures. In: Proceedings of the SPIE Conference on Medical Imaging 2007: Image Processing, vol. 6512, pp. P1–P10 (2007)
Wu, Z., Song, S., Khosla, A., Yu, F., Zhang, L., Tang, X., Xiao, J.: 3D shapenets: a deep representation for volumetric shape modeling. In: Proceedings of 28th IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR2015), pp. 1912–1920 (2015)
Zhao, X., Su, Z., Gu, X., Kaufman, A., Sun, J., Gao, J., Luo, F.: Area-preservation mapping using optimal mass transport. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 19(12), 2838–2847 (2013)
Zhou, B., Willis, A., Sui, Y., Anderson, D., Brown, T., Thomas, T.: Virtual 3D bone fracture reconstruction via inter-fragmentary surface alignment. In: Proceedings of IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, pp. 1809–1816 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by JST CREST Grant Number JPMJCR1786, Japan. JSPS KAKENHI Grant Nos. 16K00243, 17H05299, and Takahashi Industrial and Economic Research Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morooka, K., Matsubara, R., Miyauchi, S. et al. Ancient pelvis reconstruction from collapsed component bones using statistical shape models. Machine Vision and Applications 30, 59–69 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-018-0972-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-018-0972-5