Abstract
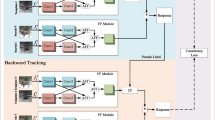
Feature-level or pixel-level fusion is a common technique for integrating different modes of information in RGB-T object tracking. A good fusion method between modalities can significantly improve the tracking performance. In this paper, a multi-modal and multi-level fusion model based on Siamese network (SiamMMF) is proposed. SiamMMF consists of two main subnetworks: a pixel-level fusion network and a feature-level fusion network. The pixel-level fusion network fuses the infrared images and the visible light images by taking the maximum values of the pixels corresponding to the different images, and the combined images are used to replace the visible light images. The infrared images and the visible light images are each input to the backbone with dual-stream structure for processing. After the extraction of deep features, the visible and infrared features from the two branches are cross-correlated to obtain a fusion result that is sent to the tracking head for tracking. Based on numerous experiments, it was found that the best tracking effect is obtained when the weighting ratio between the visible and infrared modality is set to 6:4. Nineteen pairs of RGB-T video sequences with different attributes were used to test our model and compared it with 15 trackers. For the two evaluation criteria, success rate and precision rate, our network achieved the best results.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grabner, H., Grabner, M., Bischof, H.: Real-time tracking via on-line boosting. In: Proceedings of the 2006 British Machine Vision, pp. 47–56 (2006)
Avidan, S.: Ensemble tracking. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 29(2), 261–271 (2007)
Grabner, H., Leistner, C., Bischof, H.: Semi-supervised on-line boosting for robust tracking. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 234–247 (2008)
Zhang, J. M., Ma, S.G., Sclaroff, S.: MEEM: robust tracking via multiple experts using entropy minimization. In: European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 188–203 (2014)
Hare, S., Golodetz, S., Saffari, A.: Struck: structured output tracking with kernels. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(10), 2096–2109 (2015)
Bertinetto, L., Valmadre, J., Henriques, J. F., Vedaldi, A., Torr, P. H. S.: Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking, Computer Vision - ECCV 2016 Workshops, pp. 850–865 (2016)
Li, B., Yan, J.J., Wu, W., Zhu, Z., Hu, X.L.: High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In: 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2018), pp. 8971–8980(2018)
Li, B., Wu, W., Wang, Q., Zhang, F. Y., Xing, J. L., Yan, J. J.: SiamRPN++: evolution of siamese visual tracking with very deep networks. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR 2019), pp. 4277–4286 (2019)
Guo, D.Y., Wang, J., Cui, Y., Wang, Z.H., Chen, S.Y.: SiamCAR: siamese fully convolutional classification and regression for visual tracking. In: The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2020)
Liu, H.P., Sun, F.C.: Fusion tracking in color and infrared images using joint sparse representation, Science China: Information Sciences, pp. 104–113 (2012)
Zhang, X.C., Ye, P., Leung, H., Gong, K., Xiao, G.: Object fusion tracking based on visible and infrared images: A comprehensive review, Information Fusion, pp. 166–187 (2020)
Li, C.L., Liang, X.Y., Lu, Y.J.: RGB-T object tracking: benchmark and baseline, Pattern Recognition (2018)
Dalal, N., Triggs, B.: Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection, In CVPR (2005)
Lowe, D.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints, IJCV (2004)
Wu, Y., Blasch, E., Chen, G.S.: Multiple source data fusion via sparse representation for robust visual tracking. In: 14th International Conference on Information Fusion, pp. 1–8 (2011)
Lan, X.Y., Ma, A.J., Yuen, P.C.: Multi-cue visual tracking using robust feature-level fusion based on joint sparse representation. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), pp. 1194–1201 (2014)
Li, C.L., Cheng, H., Hu, S.Y.: Learning collaborative sparse representation for grayscale-thermal tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(12), 5743–5756 (2016)
Lan, X.Y., Ye, M., Zhang, S.P.: Robust collaborative discriminative learning for RGB-infrared tracking. In: 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp. 7008–7015 (2018)
Bolme, D.S., Beveridge, J.R., Draper, B.A.: Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In: The 23rd IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (2010)
Zhao, S., Zhang, Z., Zhang, T., Guo, W., Luo, Y.: Transferable SAR image classification crossing different satellites under open set condition. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 19, 1–5 (2022)
Zhang, T., Quan, S.N., Yang, Z., Guo, W.W., Zhang, Z.H., Gan, H.P.: A two-stage method for ship detection using PolSAR image. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 99, 1–19 (2022)
Bai, B., Zhong, B.N., Ouyang, G.: Kernel correlation filters for visual tracking with adaptive fusion of heterogeneous cues. Neurocomputing 286, 109–120 (2018)
Zhai, S.Y., Shao, P.P., Liang, X.Y.: Fast RGB-T tracking via cross-modal correlation filters. Neurocomputing 334, 172–181 (2019)
Wang, Y. L., Li, C.L., Tang, J.: Learning soft-consistent correlation filters for RGB-T object tracking. In: Chinese Conference on Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision (PRCV), pp. 295–306 (2018)
Li, C.L., Wu, X.H., Zhao, N.: Fusing two-stream convolutional neural networks for RGB-T object tracking. Neurocomputing 281, 78–85 (2018)
Zhu, Y.B., Li, C.L., Luo, B.: Dense feature aggregation and pruning for RGBT tracking. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM Intermational Conference on Multimedia, pp. 465–472 (2019)
Li, C.L., Lu, A.D., Zheng, A.H.: Multi-adapter RGBT tracking, arXiv Preprint, (2019)
Yang, R., Zhu, Y.B., Wang, X.: Learning target-oriented dual attention for robust RGB-T tracking. In: 2019 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP) (2019)
Ma, J., Chen, C., Li, C.: Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization, Information Fusion, pp. 100–109 (2016)
Liu, C.H., Qi, Y., Ding, W.R.: Infrared and visible image fusion method based on saliency detection in sparse domain, Infrared Physics and Technology, pp. 94–102 (2017)
Zhu, Y.B., Li, C. L., Lu, Y.: FANet: quality-aware feature aggregation network for RGB-T tracking, arXiv Preprint (2018)
Zhang, X. C., Ye, P., Peng, S.Y., Liu, J., Gong, K., Xiao, G.: SiamFT: an RGB-infrared fusion tracking method via fully convolutional siamese networks, IEEE Access (2019)
Zhang, X.C., Ye, P., Peng, S.Y., Liu, J., Xiao, G.: DSiamMFT: an RGB-T fusion tracking method via dynamic siamese networks using multi-layer feature fusion, Signal Process.-Image Commun. (2020)
Liu, J., Zhang, S., Wang, S., Metaxas, D.: Multispectral deep neural networks for pedestrian detection. In: British Machine Vision Conference 2016, pp. 73.1-73.13 (2016)
Yin, H.: Tensor sparse representation for 3-D medical image fusion using weighted average rule. IEEE Trans. 65(11), 2622–2633 (2018)
Hill, P., Al-Mualla, M.E., Bull, D.: Perceptual image fusion using wavelets. IEEE Trans. 26(3), 1076–1088 (2017)
Li, C.L., Lu, A.D., Zheng, A.H., Tu, Z.Z., Tang, J.: Multi-Adapter RGBT Tracking. In: 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), pp. 2262-2270 (2019)
Zhang, P., Zhao, J., Wang, D., Lu, H., Yang, X.: Jointly modeling motion and appearance cues for robust RGB-T tracking, arXiv preprint (2020)
Russakovsky, O., Deng, J., Su, H., Krause, J., Satheesh, S., Ma, S., Huang, Z., Karpathy, A., Khosla, A., Bernstein, M.: Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge, IJCV (2015)
Ma, C., Huang, J.B., Yang, X.K., Yang, M.H.: Robust visual tracking via hierarchical convolutional features, TPAMI (2018)
Li, B., Wu, W., Wang, Q., Zhang, F.Y., Xing, J.L., Yan, J.J.: Siamrpn++: evolution of siamese visual tracking with very deep networks, In CVPR (2019)
Danelljan, M., Robinson, A., Khan, F.S., Felsberg, M.: Beyond correlation filters: learning continuous convolution operators for visual tracking. In: Proc. Eur. Conf. pp. 472–488 (2016)
Danelljan, M., Khan, F.S., Felsberg, M., Weijer, J.V.: Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit, pp. 1090-1097 (2014)
Henriques, J.F., Caseiro, R., Martins, P., Batista, J.: Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels. In: Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., pp. 702-715. Berlin, Germany, Springer (2012)
Wang, D., Lu, H.: Visual tracking via probability continuous outlier model. In: Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit, pp. 3478–3485 (2014)
Danelljan, M., Bhat, G., Khan, F.S., Felsberg, M.: ECO: efficient convolution operators for tracking, inProc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit, pp. 6638–6646 (2017)
Li, C., Zhu, C., Zhang, J., Luo, B., Wu, X., Tang, J.: Learning local-global multi-graph descriptors for RGB-T object tracking, IEEE Trans (to be published)
Babenko, B., Yang, M.-H., Belongie, S.: Robust object tracking with online multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33(8), 1619–1632 (2011)
Li, Y., Zhu, J., Hoi, S.C.: Reliable patch trackers: robust visual tracking by exploiting reliable patches, inProc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit, pp. 353–361 (2015)
Kalal, Z., Mikolajczyk, K., Matas, J.: Tracking-learning-detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(7), 1409–1422 (2012)
Hare, S., Golodetz, S., Saffari, A., Vineet, V., Cheng, M.-M., Hicks, S.L., Torr, P.H.: Struck: structured output tracking with kernels. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38(10), 2096–2109 (2016)
Zhang, K., Zhang, L., Yang, M.-H.: Real-time compressive tracking. In: Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. pp. 864-877, Berlin, Germany, Springer (2012)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62261026), supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62061019), General Project of Jiangxi Natural Science Foundation (20212BAB202013), the Key Project of Jiangxi Education Department (GJJ201107), and Key Laboratory of System Control and Information Processing, Ministry of Education (Scip202106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Z., Huang, P., He, D. et al. SiamMMF: multi-modal multi-level fusion object tracking based on Siamese networks. Machine Vision and Applications 34, 7 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-022-01354-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-022-01354-2