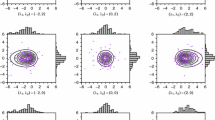
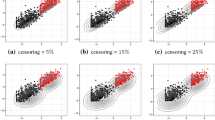
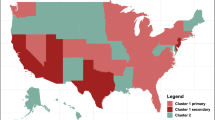
Abstract
We establish computationally flexible tools for the analysis of multivariate skew normal mixtures when missing values occur in data. To facilitate the computation and simplify the theoretical derivation, two auxiliary permutation matrices are incorporated into the model for the determination of observed and missing components of each observation and are manifestly effective in reducing the computational complexity. We present an analytically feasible EM algorithm for the supervised learning of parameters as well as missing observations. The proposed mixture analyzer, including the most commonly used Gaussian mixtures as a special case, allows practitioners to handle incomplete multivariate data sets in a wide range of considerations. The methodology is illustrated through a real data set with varying proportions of synthetic missing values generated by MCAR and MAR mechanisms and shown to perform well on classification tasks.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Anderson TW (2003) An introduction to multivariate statistical analysis, 3rd edn. Wiley and Sons, New York
Arellano-Valle RB, Azzalini A (2006) On the unification of families of skew-normal distributions. Scand J Statist 33: 561–574
Arellano-Valle RB, Bolfarine H, Lachos VH (2007) Bayesian inference for skew-normal linear mixed models. J Appl Stat 34: 663–682
Arellano-Vallea RB, Genton MG (2005) On fundamental skew distributions. J Multivariate Anal 96: 93–116
Azzalini A (2005) The skew-normal distribution and related multivariate families (with discussion). Scand J Statist 32: 159–200
Azzalini A, Capitanio A (1999) Statistical applications of the multivariate skew-normal distribution. J R Stat Soc Ser B 61: 579–602
Azzalini A, Dalla Valle A (1996) The multivariate skew-normal distribution. Biometrika 83: 715–726
Basford KE, McLachlan GJ (1985) Estimation of allocation rates in a cluster analysis text. J Am Stat Assoc 80: 286–293
Box GEP, Cox DR (1964) An analysis of transformation. J R Stat Soc Ser A 26: 211–252
Cook RD, Weisberg S (1994) An introduction to regression graphics. Wiley, New York
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB (1977) Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm (with discussion). J R Stat Soc Ser B 39: 1–38
Diebolt J, Robert CP (1994) Estimation of finite mixture distributions through Bayesian sampling. J R Stat Soc Ser B 56: 363–375
Escobar MD, West M (1995) Bayesian density estimation and inference using mixtures. J Am Stat Assoc 90: 577–588
Frühwirth-Schnatter S (2006) Finite mixture and Markov switching models. Springer, New York
Ghahramani Z, Jordan MI (1994) Supervised learning from incomplete data via an EM approach. In: Cowan JD, Tesarro G, Alspector J (eds) Advances in neural information processing systerms, vol 6. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Francisco, pp 120–127
Hastings WK (1970) Monte Carlo sampling methods using Markov chains and their applications. Biometrika 57: 97–109
Hollander M, Wolfe DA (1999) Nonparametric statistical methods, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Lin TI (2009a) Maximum likelihood estimation for multivariate skew normal mixture models. J Multivariate Anal 100: 257–265
Lin TI (2009b) Robust mixture modeling using multivariate skew t distributions. Stat Comput. doi:10.1007/s11222-009-9128-9 (in press)
Lin TI, Lee JC, Ni HF (2004) Bayesian analysis of mixture modelling using the multivariate t distribution. Stat Comput 14: 119–130
Lin TI, Lee JC, Ho HJ (2006) On fast supervised learning for normal mixture models with missing information. Pattern Recogn 39: 1177–1187
Lin TI, Lee JC, Hsieh WJ (2007a) Robust mixture modeling using the skew t distribution. Stat Comput 17: 81–92
Lin TI, Lee JC, Yen SY (2007b) Finite mixture modelling using the skew normal distribution. Statist Sinica 17: 909–927
Lin TI, Ho HJ, Shen PS (2009) Computationally efficient learning of multivariate t mixture models with missing information. Comp Stat 24: 375–392
Little RJA, Rubin DB (2002) Statistical analysis with missing data, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Liu CH, Rubin DB, Wu Y (1998) Parameter expansion to accelerate EM: the PX-EM algorithm. Biometrika 85: 755–770
McLachlan GJ, Basford KE (1988) Mixture models: inference and application to clustering. Marcel Dekker, New York
McLachlan GJ, Peel D (2000) Finite mixture models. Wiely, New York
Pearson K (1894) Contributions to the theory of mathematical evolution, Phi. Trans Roy Soc London A 185: 71–110
Peel D, McLachlan GJ (2000) Robust mixture modeling using the t distribution. Stat Comput 10: 339–348
Pyne S, Hu X, Wang K, Rossin E, Lin TI, Maier L, Baecher-Allan C, McLachlan GJ, Tamayo P, Hafler DA, De Jager PL, Mesirov JP (2009) Automated high-dimensional flow cytometric data analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 8519–8524
Rubin DB (1976) Inference and missing data. Biometrika 63: 581–592
Sahu SK, Dey DK, Branco MD (2003) A new class of multivariate skew distributions with applications to bayesian regression models. Canad J Statist 31: 129–150
Schafer JL (1997) Analysis of incomplete multivariate data. Chapman and Hall, London
Shoham S (2002) Robust clustering by deterministic agglomeration EM of mixtures of multivariate t-distributions. Pattern Recogn 35: 1127–1142
Shoham S, Fellows MR, Normann RA (2003) Robust, automatic spike sorting using mixtures of multivariate t-distributions. J Neurosci Methods 127: 111–122
Tanner MA, Wong WH (1987) The calculation of posterior distributions by data augmentation (with discussion). J Am Stat Assoc 82: 528–550
Titterington DM, Smith AFM, Markov UE (1985) Statistical analysis of finite mixture distributions. Wiely, New York
Wang HX, Zhang QB, Luo B, Wei S (2004) Robust mixture modelling using multivariate t distribution with missing information. Pattern Recogn Lett 25: 701–710
Zio MD, Guarnera U, Luzi O (2007) Imputation through finite Gaussian mixture models. Comp Stat Data Anal 51: 5305–5316
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, TC., Lin, TI. Supervised learning of multivariate skew normal mixture models with missing information. Comput Stat 25, 183–201 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-009-0169-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-009-0169-5