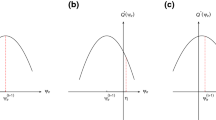
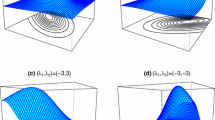
Abstract
Mixture of t factor analyzers (MtFA) have been shown to be a sound model-based tool for robust clustering of high-dimensional data. This approach, which is deemed to be one of natural parametric extensions with respect to normal-theory models, allows for accommodation of potential noise components, atypical observations or data with longer-than-normal tails. In this paper, we propose an efficient expectation conditional maximization (ECM) algorithm for fast maximum likelihood estimation of MtFA. The proposed algorithm inherits all appealing properties of the ordinary EM algorithm such as its stability and monotonicity, but has a faster convergence rate since its CM steps are governed by a much smaller fraction of missing information. Numerical experiments based on simulated and real data show that the new procedure outperforms the commonly used EM and AECM algorithms substantially in most of the situations, regardless of how the convergence speed is assessed by the computing time or number of iterations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Celeux G, Chrétien S, Forbes F, Mkhadri A (2001) A component-wise EM algorithm for mixtures. J Comput Graph Statist 10: 697–712
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB (1977) Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm (with discussion). J R Stat Soc Ser B 39: 1–38
Fessler JA, Hero AO (1994) Space-alternating generalized expectation-maximisation algorithm. IEEE Tran Sig Proc 42: 2664–2677
Frey BJ, Colmenarez A, Huang TS (1998) Mixtures of local linear subspaces for face recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 32–37
Ghahramani Z, Beal M (2000) Variational inference for Bayesian mixture of factor analysers. In: Solla S, Leen T, Muller K-R (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems 12. MIT Press, Cambridge, pp 449–455
Ghahramani Z, Hinton GE (1997) The EM algorithm for mixtures of factor analyzers. Technical report no. CRG-TR-96-1, University of Toronto
Ho HJ, Pyne S, Lin TI (2012) Maximum likelihood inference for mixtures of skew Student-t-normal distributions through practical EM-type algorithms. Stat Comput 22: 287–299
Jamshidian M, Jennrich RI (1993) Conjugate gradient acceleration of the EM algorithm. J Am Stat Assoc 88: 221–228
Lin TI (2009) Maximum likelihood estimation for multivariate skew normal mixture models (In press). J Multivar Anal 100: 257–265
Lin TI (2010) Robust mixture modeling using multivariate skew t distributions. Stat Comput 20: 343–356
Lin TI, Ho HJ, Shen PS (2009) Computationally efficient learning of multivariate t mixture models with missing information. Comp Stat 24: 375–392
Lin TI, Lee JC, Ni HF (2004) Bayesian analysis of mixture modelling using the multivariate t distribution. Stat Comput 14: 119–130
Lin TC, Lin TI (2010) Supervised learning of multivariate skew normal mixture models with missing information. Comput Stat 25: 183–201
Liu CH, Rubin DB (1994) The ECME algorithm: a simple extension of EM and ECM with faster monotone convergence. Biometrika 81: 633–648
Liu CH, Rubin DB (1995) ML estimation of the t distribution using EM and its extensions, ECM and ECME. Stat Sin 5: 19–39
Louis TA (1982) Finding the observed information matrix when using the EM algorithm. J R Stat Soc Ser B 44: 226–233
McLachlan GJ, Bean RW, Jones BT (2007) Extension of the mixture of factor analyzers model to incorporate the multivariate t-distribution. Comput Stat Data Anal 51: 5327–5338
McLachlan GJ, Bean RW, Peel D (2002) A mixture model-based approach to the clustering of microarray expression data. Bioinformatics 18: 413–422
McLachlan GJ, Peel D (2000) Finite mixture models. Wiley, New York
McLachlan GJ, Peel D, Bean RW (2003) Modelling high-dimensional data by mixtures of factor analyzers. Comput Stat Data Anal 41: 379–388
Meilijson I (1989) A fast improvement to the EM algorithm in its own terms. J R Stat Soc Ser B 51: 127–138
Meng XL, Rubin DB (1993) Maximum likelihood estimation via the ECM algorithm: a general framework. Biometrika 80: 267–278
Meng XL, Dyk D (1997) The EM algorithm—an old folk-song sung to a fast new tune. J Roy Stat Soc B 59: 511–567
Shoham S (2002) Robust clustering by deterministic agglomeration EM of mixtures of multivariate t-distributions. Pattern Recogn 35: 1127–1142
Shoham S, Fellows MR, Normann RA (2003) Robust, automatic spike sorting using mixtures of multivariate t-distributions. J Neurosci Methods 127: 111–122
Tipping ME, Bishop CM (1999) Mixtures of probabilistic principal component analyzers. Neural Comput 11: 443–482
Ueda N, Nakano R, Ghahramani Z, Hinton GE (2000) SMEM algorithm for mixture models. Neural Comput 12: 2109–2128
Utsugi A, Kumagai T (2001) Bayesian analysis of mixtures of factor analyzers. Neural Comp 13: 993–1002
Zhao JH, Yu PLH (2008) Fast ML estimation for the mixture of factor analyzers via an ECM algorithm. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 19: 1956–1961
Zhao JH, Yu PLH, Jiang Q (2008) ML estimation for factor analysis: EM or non-EM. Stat Comput 18: 109–123
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, WL., Lin, TI. An efficient ECM algorithm for maximum likelihood estimation in mixtures of t-factor analyzers. Comput Stat 28, 751–769 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-012-0327-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-012-0327-z