Abstract
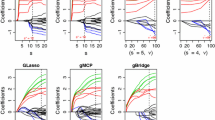
Prediction variables of the regression model are grouped in many application problems. For example, a factor in an analysis of variance can have several levels or each original prediction variable in additive models can be expanded into different order polynomials or a set of basis functions. It is essential to select important groups and individual variables within the selected groups. In this study, we propose the objective Bayesian group and individual variable selections within the selected groups in the regression model to reduce the computational cost, even though the number of regression variables is large. Besides, we examine the consistency of the proposed group variable selection procedure. The proposed objective Bayesian approach is investigated using simulation and real data examples. The comparisons between the penalized regression approaches, Bayesian group lasso and the proposed method are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike H (1973) Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In: Petrov BN, Csaki F (eds) Second international symposium on information theory. Akademiai Kiado, Budapest, pp 267–281
Abramovich F, Angelini C (2006) Bayesian maximum a posteriori multiple testing procedure. Sankhy\({\bar{a}}\) 68:436–460
Abramovich F, Grinshtein V, Pensky M (2007) On optimality of Bayesian testimation in the normal means problem. Ann Stat 35:2261–2286
Atkinson AC (1978) Posterior probabilities for choosing a regression model. Biometrika 65:39–48
Berger JO, Pericchi LR (1996) The intrinsic Bayes factor for model selection and prediction. J Am Stat Assoc 91:109–122
Box GEP, Meyer RD (1986) An analysis for unreplicated fractional factorials. Technometrics 28:11–18
Breheny P, Huang J (2009) Penalized methods for bi-level variable selection. Stat Interface 2:369–380
Breheny P, Zeng Y (2021) grpreg: regularization paths for regression models with grouped covariates. R Package Version 3(3):1
Casella G, Moreno E (2006) Objective Bayesian variable selection. J Am Stat Assoc 101:157–167
Casella G, Girón FJ, Martínez ML, Moreno E (2009) Consistency of Bayesian procedures for variable selection. Ann Stat 37:1207–1228
Chen RB, Chu CH, Yuan S, Wu YN (2016a) Bayesian sparse group selection. J Comput Graph Stat 25:665–683
Chen K, Lin Y, Wang Z, Ying Z (2016b) Least product relative error estimation. J Multivar Anal 144:91–98
Clyde M, DeSimone H, Parmigiani G (1996) Prediction via orthogonalized model mixing. J Am Stat Assoc 91:1197–1208
Fan J, Li R (2001) Variable selection via nonconcave penalized likelihood and its oracle properties. J Am Stat Assoc 96:1348–1360
George EI, McCulloch RE (1993) Variable selection via gibbs sampling. J Am Stat Assoc 88:881–889
George EI, McCulloch RE (1997) Approaches for variable selection. Stat Sin 7:339–373
Geweke J (1996) Variable selection and model comparison in regression. In: Bernardo JM et al (eds) Bayesian statistics, vol 5. Oxford University Press, London, pp 169–194
Girón FJ, Martínez ML, Moreno E, Torres F (2006) Objective testing procedures in linear models. Scand J Stat 33:765–784
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S (1989) Applied logistic regression. Wiley, NewYork
Huang H, Ma S, Xie H, Zhang C (2009) A group bridge approach for variable selection. Biometrika 96:339–355
Huang J, Breheny P, Ma S (2012) A selective review of group selection in high-dimensional models. Stat Sci 27:481–499
Kim Y, Kim J, Kim Y (2006) The blockwise sparse regression. Stat Sin 16:375–390
Kuo L, Mallick B (1998) Variable selection for regression models. Sankhy\({\bar{a}}\) 60:65–81
Liquet B, Mengersen K, Pettitt AN, Sutton M (2017) Bayesian variable selection regression of multivariate responses for group data. Bayesian Anal 12:1039–1067
Liquet B, Sutton M (2017) MBSGS: multivariate Bayesian sparse group selection with spike and slab. R Package Version 1(1)
Mallows C (1973) Some comments on \(C_p\). Technometrics 15:661–675
Mitchell TJ, Beauchamp JJ (1988) Bayesian variable selection in linear regression (with discussion). J Am Stat Assoc 83:1023–1036
Moreno E, Bertolino F, Racugno W (1998) An intrinsic limiting procedure for model selection and hypotheses testing. J Am Stat Assoc 93:1451–1460
Moreno E, Girón FJ (2005) Consistency of Bayes factors for intrinsic priors in normal linear models. Comptes Rendus Mathematique, Series I 340:911–914
Moreno E, Girón FJ (2008) Comparison of Bayesian objective procedures for variable selection in linear regression. Test 17:472–490
Pericchi LR (1984) An alternative to the standard Bayesian procedure for discrimination between normal linear models. Biometrika 71:575–586
Poirier DJ (1985) Bayesian hypothesis testing in linear models with continuously induced conjugate prior across hypotheses. In: Bernardo JM et al (eds) Bayesian statistics, vol 2. Elsevier, New York, pp 711–722
Sarkar SK, Chen J (2004) A Bayesian stepwise multiple testing procedure. Technical Report, Temple University
Schwarz G (1978) Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Stat 6:461–464
Simon N, Friedman J, Hastie T, Tibshirani R (2013) A Sparse Group Lasso. J Comput Graph Stat 22:231–245
Siri WE (1956) The gross composition of the body. Adv Biol Med Phys 4:239–280
Smith M, Kohn R (1996) Nonparametric regression using Bayesian variable selection. J Econom 75:317–344
Smith AFM, Spiegelhalter DJ (1980) Bayes factor and choice criteria for linear models. J R Stat Soc Ser B 42:213–220
Spiegelhalter DJ, Smith AFM (1982) Bayes factor for linear and log-linear models with vague prior information. J R Stat Soc Ser B 44:377–387
Wang L, Chen G, Li H (2007) Group SCAD regression analysis for microarray time course gene expression data. Bioinformatics 23:1486–1494
Xu X, Ghosh M (2015) Bayesian variable selection and estimation for group lasso. Bayesian Anal 10:909–936
Yuan M, Lin Y (2006) Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables. J R Stat Soc Ser B 68:49–67
Zhang CH (2010) Nearly unbiased variable selection under minimax concave penalty. Ann Stat 38:894–942
Zhao P, Rocha G, Yu B (2009) Grouped and hierarchical model selection though composite absolute penalties. Ann Stat 37:3468–3497
Zhou N, Zhu J (2010) Group variable selection via a hierarchical Lasso and Its Oracle property. Stat Interface 3:557–574
Acknowledgements
The research of Yongku Kim was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (No. 2018R1D1A1B07043352).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, S.G., Lee, W.D. & Kim, Y. Objective Bayesian group variable selection for linear model. Comput Stat 37, 1287–1310 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-021-01160-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-021-01160-w