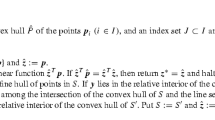1
optimization under linear inequality constraints based upon iteratively reweighted iterative projection (or IRIP). IRIP is compared to a linear programming (LP) strategy for L1 minimization (Späth 1987, Chapter 5.3) using the ultrametric condition as an exemlar class of constraints to be fitted. Coded for general constraints, the LP approach proves to be faster. Both methods, however, suffer from a serious limitation in being unable to process reasonably-sized data sets because of storage requirements for the constraints. When the simplicity of vector projections is used to allow IRIP to be coded for specific (in this case, ultrametric) constraints, we obtain a fast and efficient algorithm capable of handling large data sets. It is also possible to extend IRIP to operate as a heuristic search strategy that simultaneously identifies both a reasonable set of constraints to impose and the optimally-estimated parameters satisfying these constraints. A few noteworthy characteristics of L1 optimal ultrametrics are discussed, including other strategies for reformulating the ultrametric optimization problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, T. L 1 Optimization under Linear Inequality Constraints. J. of Classification 17, 225–242 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003570000020
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003570000020