Abstract
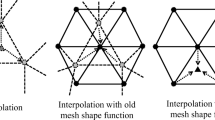
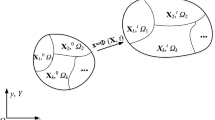
In this study, an automated adaptive mesh control scheme, based on local mesh modifications, is developed for the finite element simulations of 3D metal-forming processes. Error indicators are used to control the mesh discretization errors, and an h-adaptive procedure is conducted. The mesh size field used in the h-adaptive procedure is processed to control the discretization and geometric approximation errors of the evolving workpiece mesh. Industrial problems are investigated to demonstrate the capabilities of the developed scheme.







































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng JH, Kikuchi N (1986) A mesh rezoning technique for finite element simulation of metal forming processes. Int J Numer Methods Eng 23:219–228
Habraken A, Cescotto S (1990) An automatic remeshing technique for finite element simulation of forming processes. Int J Numer Meth Eng 30:1503–1525
Hattangady NV, Shephard MS, Chaudhary AB (1999) Towards realistic automated 3D modelling of metal forming problems. Eng Comput 15:356–374
Ravindranath MN, Kumar RK (2000) Simulation of cold forging using contact and practical adaptive meshing algorithms. J Mater Proc Technol 104:110–126
Chand CP, Kumar RK (1998) Remeshing issues in the finite element analysis of metal forming problems. J Mater Proc Technol 75:63–74
Zhu YY, Zacharia T, Cescotto S (1997) Application of fully automatic remeshing to complex metal-forming analyses. Comput Struct 62(3):417–427
Mathisen KM, Hopperstad OS, Okstad KM, Berstad T (1999) Error estimation and adaptivity in explicit nonlinear finite element simulation of quasi-static problems. Comput Struct 72:627–644
Kwak DY, Cheon JS, Im YT (2002) Remeshing for metal forming simulations. Part I: two-dimensional quadrilateral remeshing. Int J Numerical Methods Eng 53:2463–2500
Coupez T (1995) Automatic remeshing in three-dimensional moving mesh finite element analysis of industrial forming. In: Shen SF, Dawson PR (eds) Simulation of material processing: theory, practice, methods and applications. Balkema, Rotterdam, pp 407–412
Fluhrer J (2004) DEFORM 3DTM Version 5.0 User’s Manual. Scientific Forming Technologies Corporation, Columbus, OH
Kobayashi S, OH S-I, Altan T (1989) Metal forming and the finite element method. Oxford University Press, New York
Freitag LA, Ollivier-Gooch C (1997) Effect of mesh quality on solution efficiency. In: Proceedings of the 6th international meshing roundtable. Park City, Utah, October 1997, pp 249–260
Fried L (1972) Accuracy of complex finite elements. AIAA J 10:347–349
Hughes TJR (2000) The finite element method: linear static and dynamic finite element analysis. Dover, Mineola
Liu A, Joe B (1994) Relationship between tetrahedron shape measures. BIT 34:268–287
Zienkiewicz OC, Zhu JZ (1992) The superconvergent patch recovery and a posteriori error estimates. Part 1: the recovery technique. Int J Numer Meth Eng 33:1331–1364
Baehmann PL, Shephard MS, Flaherty JE (1992) A posteriori error for trianglular and tetrahedral quadratic elements using interior residuals. Int J Numer Meth Eng 34:979–996
Baehmann PL, Shephard MS, Ashley R, Jay A (1988) Automated metal forming modeling utilizing adaptive remeshing and evolving geometry. Comput Struct 30:319–325
Baehmann PL, Collar RR, Hattangady NV, Shephard MS (1992) Geometry and mesh control for automated bulk forming simulations. In: Proceedings of ASME winter annual meeting. Anaheim, CA, pp 45–57
George PL (1991) Automatic mesh generation: application to finite element methods. Wiley, Chichester
Shephard MS, Baehmann PL, Collar RR, Hattangady NV, Niu Q (1993) Automated remodeling techniques in finite element analysis. Advances in CAD/CAE, Academic, New York
Beall MW, Shephard MS (1997) A general topology-based mesh data structure. Int J Numer Meth Eng 40:1573–1593
Li X, Shephard MS, Beal MW (2003) 3D anisotropic mesh adaptation by mesh modifications. Comp Meth Appl Mech Eng (Submitted)
Braack M, Becker R, Rannacher R (1997) An adaptive finite element method for combustion problems. In: Proceedings of the third summer conference, numerical modelling in continuum mechanics. Charles Universirt, Prague, Czech Republic, pp 91–100
Hattangady NV (1999) Automatic remeshing in 3D analysis of forming process. Int J Numer Meth Eng 45:553–568
Shephard MS, Georges MK (1991) Automatic three-dimensional mesh generation by the finite octree technique. Int J Numer Meth Eng 32(4):709–749
Li X, Shephard MS, Beall MW (2003) Accounting for curved domains in mesh adaptation. Int J Numer Meth Eng 58:247–276
Zorin D, Schroder P, Sweldens W (1996) Interpolating subdivision with arbitrary topology. In: Proceedings of computer graphic, ACM SIGGRAPH, pp 189–192
Lee CK (2003) Automatic metric 3D surface mesh generation using subdivision surface geometrical model. Part I: construction of underlying geometric model. Int J Numer Meth Eng 56:1593–1614
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge GE Corp for funding this work. Technical assistance from A. Majorell, D. Mika and P. R. Myers from GE, and C. Fischer from SFTC is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, J., Kocak, S. & Shephard, M.S. Automated adaptive 3D forming simulation processes. Engineering with Computers 21, 47–75 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-005-0001-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-005-0001-y