Abstract
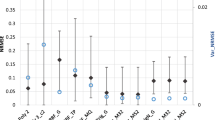
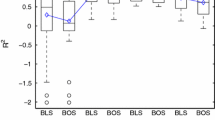
In this research, influences of two factors in adaptive metamodeling, noise level of samples and initial size of samples, are investigated through comparative study. Two cases of adaptive metamodeling considering the best output point for optimization and the best fit in a specific output parameter space are considered. Three different metamodels, kriging, radial basis function, and multivariate polynomial, are employed in this study. Various test functions are used to create the sample data and evaluate the quality and efficiency of the adaptive metamodeling methods considering influences of noise and initial size of samples. The results of this research provide guidelines for selecting appropriate adaptive metamodeling methods to solve various engineering problems. Effectiveness of the developed guidelines has been demonstrated through case study applications.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crombecq K, Gorissen D, Deschri D, Dhaene T (2011) A novel hybrid sequential design strategy for global surrogate modeling of computer experiments. SIAM J Sci Comput 33(4):1948–1974
Fang KT, Li R, Sudjianto A (2006) Design and modeling for computer experiments. Chapman & Hall/CRC, FL, USA
Hardy RL (1971) Multiquadratic equations of topography and other irregular surfaces. J Geophys Res 76(1):1905–1915
Hassing PM, Fang H, Wang Q (2010) Identification of material parameters for McGinty’s model using adaptive RBFs and optimization. Struct Multidisc Optim 42(2):233–242
Hickernell FJ (1998) A generalized discrepancy and quadrature error bound. Math Comput 67(221):299–322
Hickernell FJ, Liu MQ (2002) Uniform designs limit aliasing. Biometrika 89(4):893–904
Jeong S, Murayama M, Yamamoto K (2005) Efficient optimization design method using kriging model. J Aircr 42(2):413–420
Johnson ME, Morre LM, Ylvisaker D (1990) Minimax and maximum distance designs. J Stat Plan Inf 26(2):131–148
Jones DR, Schonlau A, Welch WJ (1998) Efficient global optimization of expensive black-box functions. J Global Optim 13(4):455–492
Li G, Aute V, Azarm S (2010) An accumulative error based adaptive design of experiments for offline metamodeling. Struct Multidisc Optim 40(1–6):137–155
Li M, Li G, Azarm S (2008) A kriging metamodel assisted multi-objective genetic algorithm for design optimization. J Mech Des ASME Trans 130(3)
Lovison A, Rigoni E (2010) Adaptive sampling with a Lipschitz criterion for accurate metamodeling. Commun Appl Indus Math 1(2):110–126
Matheron G (1963) Principals of geostatistics. Econ Geol 58(8):1246–1266
McKay MD, Beckman RJ, Conover WJ (1979) Comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Technometrics 21(2):239–245
Morris MD, Mitchell TJ (1995) Exploratory designs for computer experiments. J Stat Plan Inf 43(3):381–402
Mourelatos Z, Kuczera R, Latcha M (2006) An efficient Monte Carlo reliability analysis using global and local metamodels. In: Proceedings of 11th AIAA/ISSMO multidisciplinary analysis and optimization conference, Portsmouth
Myers RH, Montgomery DC (1995) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. John Wiley & Sons, NY, USA
Picheny V, Ginsbourger D, Roustant O, Haftka RH, Kim NH (2010) Adaptive designs of experiments for accurate approximation of a target region. J Mech Des ASME Trans 132(7)
Sacks J, Welch WJ, Mitchell TJ, Wynn HP (1989) Design and analysis of computer experiments. Stat Sci 4(4):409–435
Simpson TW, Peplinski JD, Koch PN, Allen JK (2001) Metamodels for computer-based engineering design: survey and recommendations. Eng Comp 17(2):129–150
Sobol IM (1967) On the distribution of points in a cube and the approximate evaluation of integrals. USSR Comput Math Mathem Phys 7(4):86–112
Villemonteix J, Vazquez E, Walter, E (2007) Identification of expensive-to-simulate parametric models using kriging and stepwise uncertainty reduction. In: Proceedings of the 46th IEEE conference on decision and control, New Orleans
Wang GG, Shan S (2007) Review of metamodeling techniques in support of engineering design optimization. J Mech Des ASME Trans 129:370–380
Wang L, Shan S, Wang GG (2004) Mode-pursuing sampling method for global optimization on expensive black-box functions. Eng Optim 36(4):419–438
Wei X, Wu Y, Chen L (2012) A new sequential optimal sampling method for radial basis functions. Appl Math Comput 218(19):9635–9646
Yang Q, Kianimanesh A, Park SS, Freiheit T, Xue D (2011) A semi-empirical model considering the influence of operating parameters on performance for a direct methanol fuel cell. J Power Sources 196(24):10640–10651
Zhao D, Xue D (2010) A comparative study of metamodeling methods considering sample quality merits. Struct Multidisc Optim 42(6):923–938
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada through its Discovery Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Q., Xue, D. Comparative study on influencing factors in adaptive metamodeling. Engineering with Computers 31, 561–577 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-014-0358-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-014-0358-x