Abstract
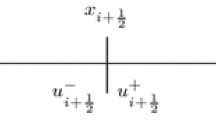
In this paper, based on the cubic B-spline finite element (CBSFE) and the radial basis functions (RBFs) methods, the inverse problems of finding the nonlinear source term for system of reaction–diffusion equations are studied. The approach of the proposed methods are to approximate unknown coefficients by a polynomial function whose coefficients are determined from the solution of minimization problem based on the overspecified data. In fact, this work considers a comparative study between the cubic B-spline finite element method and radial basis functions method. The stability and convergence analysis for these problems are investigated and some examples are given to illustrate the results.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck JV, Blackwell B, Haji-sheikh A (1996) Comparison of some inverse heat conduction methods using experimental data. Int J Heat Mass Transf 3:3649–3657
Pourgholi R, Azizi N, Gasimov YS, Aliev F, Khalafi HK (2009) Removal of numerical instability in the solution of an inverse heat conduction problem. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 14(6):2664–2669
Pourgholi R, Dana H, Tabasi SH (2014) Solving an inverse heat conduction problem using genetic algorithm: sequential and multi-core parallelization approach. Appl Math Model 38(7):1948–1958
Shenefelt JR, Luck R, Taylor RP, Berry JT (2002) Solution to inverse heat conduction problems employing singular value decomposition and model-reduction. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:67–74
Tikhonov AN, Arsenin VY (1977) Solution of ill-posed problems. V.H. Winston and Sons, Washington
Alifanov OM (1994) Inverse heat transfer problems. Springer, New York
Pourgholi R, Rostamian M (2010) A numerical technique for solving IHCPs using Tikhonov regularization method. Appl Math Model 34(8):2102–2110
Beck JV, Blackwell B, St CR (1985) Clair, inverse heat conduction: ill posed problems. Wiley, New York
Duchateau P, Rundell W (1985) Unicity in an inverse problem for an unknown reaction term in a reaction diffusion equation. J Differ Equ 59(2):155–164
Muzylev NV (1980) Uniqueness theorems for some convergence problems of heat conduction. USSR Comput Math Phys 20(2):120–134
Pilant MS, Rundell W (1986) An inverse problem for a nonlinear parabolic equation. Commun Partial Differ Equ 11(4):445–457
Pilant MS, Rundell W (1988) Fixed point methods for a nonlinear parabolic inverse coefcient problem. Commun Partial Differ Equ 13(4):469–549
Anger G (1990) Inverse problems in differential equations. Plenum, New York
Nanda A, Das PC (2000) Determination of the non-linear reaction term in a coupled reaction–diffusion system. Numer Funct Anal Optim 21(3&4):489–508
Courant R (1943) Variational methods for the solution of problems of equilibrium and vibrations. Bull Am Math Soc 49:1–23
Bangerth W, Joshi A (2009) Adaptive finite element methods for nonlinear inverse problems. In: Proceedings of the 2009 ACM symposium on Applied Computing, pp 1002–1006
Beilina L, Johnson C (2001) A hybrid FEM/FDM method for an inverse scattering problem. In: Numerical Mathematics and Advanced Applications - ENUMATH 2001. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 545–556
Beilina L (2003) Adaptive finite element/difference method for inverse elastic scattering waves. Appl Comput Math 2:119–134
Ling X, Keanini RG, Cherukuri HP (2003) A non-iterative finite element method for inverse heat conduction problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 56:1315–1334
Kansa EJ (1990) Multiquadricsa scattered data approximation scheme with applications to computational fluid dynamics—I. Comput Math Appl 19:127–145
Hardy RL (1971) Multiquadric equations of topography and other irregular surfaces. J Geophys Res 76:1905–1915
Hon YC, Mao XZ (1998) An efficient numerical scheme for Burgers equation. Appl Math Comput 95:37–50
Hon YC, Cheung KF, Mao XZ, Kansa EJ (1999) Multiquadric solution for shallow water equations. J Hydraul Eng 125:524–533
Zerroukat M, Power H, Chen CS (1992) A numerical method for heat transfer problem using collocation and radial basis functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 42:1263–1278
Hon YC, Mao XZ (1999) A radial basis function method for solving options pricing model. Financ Eng 8(1):31–49
Marcozzi M, Choi S, Chen CS (2001) On the use of boundary conditions for variational formulations arising in financial mathematics. Appl Math Comput 124:197–214
Fasshauer GE (2007) Meshfree Approximation Methods with Matlab: (With CD-ROM), vol 6. World Scientific Publishing Co Inc
Hon YC, Wu Z (2000) A numerical computation for inverse boundary determination problem. Eng Anal Bound Elem 24:599–606
Li J (2004) A radial basis meshless method for solving inverse boundary value problems. Commun Numer Methods Eng 20:51–60
Li J (2005) Application of radial basis meshless methods to direct and inverse biharmonic boundary value problems. Commun Numer Methods Eng 21:169–182
Cheng AH-D, Cabral JJSP (2005) Direct solution of ill-posed boundary value problems by radial basis function collocation method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 64:45–64
Ma L, Wu Z (2011) Radial basis functions method for parabolic inverse problem. Int J Comput Math 88(2):384–395
Bayona V, Moscoso M, Carretero M, Kindelan M (2010) RBF-FD formulas and convergence properties. J Comput Phys 229:8281–8295
Fasshauer GE, Zhang JG (2007) On choosing “optimal” shape parameters for RBF approximation. Numer Algorithm 45:345–368
Tikhonov AN, Arsenin VY (1977) On the solution of ill-posed problems. Wiley, New York
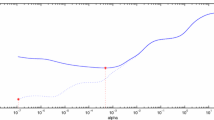
Hansen PC (1992) Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-curve. SIAM Rev 34:561–580
Lawson CL, Hanson RJ (1995) Solving least squares problems. SIAM, Philadelphia
Elden L (1984) A note on the computation of the generalized cross-validation function for ill-conditioned least squares problems. BIT 24:467–472
Golub GH, Heath M, Wahba G (1979) Generalized cross-validation as a method for choosing a good ridge parameter. Technometrics 21:215–223
Wahba G (1990) Spline models for observational data. SIAM, Philadelphia
Martin L, Elliott L, Heggs PJ, Ingham DB, Lesnic D, Wen X (2006) Dual reciprocity boundary element method solution of the Cauchy problem for Helmholtz-type equations with variable coefficients. J. Sound Vib 297:89–105
Dehghan M, Tatari M (2006) Determination of a control parameter in a one-dimensional parabolic equation using the method of radial basis functions. Mathematical and Computer Modelling 44:1160–1168
Cabeza JMG, Garcia JAM, Rodriguez AC (2005) A Sequential Algorithm of Inverse Heat Conduction Problems Using Singular Value Decomposition. International Journal of Thermal Sciences 44:235–244
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pourgholi, R., Tabasi, S.H. & Zeidabadi, H. Numerical techniques for solving system of nonlinear inverse problem. Engineering with Computers 34, 487–502 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0554-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-017-0554-6
Keywords
- Cubic B-spline
- Finite element method
- Radial basis functions method
- Inverse problems
- Stability analysis
- Convergence analysis
- Tikhonov regularization method
- Ill-posed problems
- Noisy data