Abstract
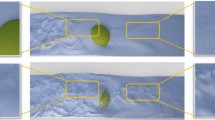
A detailed description of turbulent fluids based on numerical simulation is an important research topic required by many visual effects. We propose a novel method to simulate fluids with turbulent small-scale details. By inserting diffusive derivatives and divergence-free constraints to moving least-squares (MLS) fitting, we upgrade the velocity interpolation method for existing fluid solvers to enhance the subgrid accuracy. The time-step restriction of asymptotic property of diffusive derivatives is resolved by means of coupling to the constrained interpolation profile (CIP) advection framework. The proposed constrained moving least-squares interpolation profile (CMIP) method provides intuitive control over turbulence through the adjustment of one parameter as though controlling the Reynolds number with an inviscid model. The proposed method generates improved visuals of the highly turbulent fluid and is complementary to existing techniques that are currently being used.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bridson, R., Houriham, J., Nordenstam, M.: Curl-noise for procedural fluid flow. ACM Trans. Graph. 26(3), 46 (2007). SIGGRAPH Proc.
Chorin, A.: A numerical method for solving incompressible viscous flow problems. J. Comput. Phys. 2, 12–26 (1967)
Fedkiw, R., Stam, J., Jensen, H.: Visual simulation of smoke. In: Proc. of SIGGRAPH 01, pp. 15–22 (2001)
Feldman, B., O’Brien, J., Klingner, B.: Animating gases with hybrid meshes. ACM Trans. Graph. 24(3), 904–909 (2005). SIGGRAPH Proc.
Foster, N., Metaxas, D.: Realistic animation of liquids. Graph. Models Image Process. 58, 471–483 (1996)
Foster, N., Metaxas, D.: Modeling the motion of a hot, turbulent gas. In: Proc. of SIGGRAPH ’97, pp. 181–188 (1997)
Fresch, U.: Turbulence: The Legacy of A. N. Kolmogorov. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1996)
Gao, Y., Li, C.F., Hu, S.M., Barsky, B.A.: Simulating gaseous fluids with low and high speeds. Comput. Graph. Forum 28(7), 1845–1852 (2009). Proc. Pacific Graphics, 2009
Greenwood, S.T., House, D.H.: Better with bubbles: enhancing the visual realism of simulated fluid. In: Proc. of the 2004 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comput. Animat., pp. 287–296 (2004)
Hong, J.M., Kim, C.H.: Discontinuous fluids. ACM Trans. Graph. 24(3), 915–920 (2005). SIGGRAPH Proc.
Hong, J.M., Shinar, T., Fedkiw, R.: Wrinkled flames and cellular patterns. ACM Trans. Graph. 26(3), 471–476 (2007). SIGGRAPH Proc.
Hong, J.M., Lee, H.Y., Yoon, J.C., Kim, C.H.: Bubbles alive. ACM Trans. Graph. 27(3), 481–484 (2008). SIGGRAPH Proc.
Hong, J.M., Yoon, Y.C., Kim, C.H.: Divergence-constrained moving least squares for fluid simulation. Comput. Animat. Virtual Worlds 19(3–4), 469–477 (2008). CASA Proc.
Huerta, A., Vidal, Y., Villon, P.: Pseudo-divergence-free element free Galerkin method for incompressible fluid flow. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 193, 1119–1136 (2004)
Kim, J., Cha, D., Chang, B., Koo, B., Ihm, I.: Practical animation of turbulent splashing water. In: Proc. of the 2006 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comput. Animat., pp. 335–344 (2006)
Kim, B., Liu, Y., Llamas, I., Rossignac, J.: Advections with significantly reduced dissipation and diffusion. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 13, 135–144 (2007)
Kim, D., Song, O., Ko, H.S.: A semi-Lagrangian CIP fluid solver without dimensional splitting. Comput. Graph. Forum 27(2), 467–475 (2008). Proc. Eurographics
Kim, T., Thurey, N., James, D., Gross, M.: Wavelet turbulence for fluid simulation. ACM Trans. Graph. 27(3), 50 (2008). SIGGRAPH Proc.
Kim, D., Song, O.Y., Ko, H.S.: Stretching and wiggling liquids. ACM Trans. Graph. 28(5), 120 (2009)
Lentine, M., Zheng, W., Fedkiw, R.: A novel algorithm for incompressible flow using only a coarse grid projection. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 114:1–114:9 (2010)
Lorenz, E.N.: The Essence of Chaos. University of Washington Press, Seattle (1996)
Losasso, F., Talton, J., Kwatra, N., Fedkiw, R.: Two-way coupled SPH and particle level set fluid simulation. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 14(4), 797–804 (2008)
Narain, R., Sewall, J., Carlson, M., Lin, M.: Fast animation of turbulence using energy transport and procedural synthesis. ACM Trans. Graph. 27(5), 166 (2008). SIGGRAPH Asia Proc.
Nayroles, B., Touzot, G., Villon, P.: Generalizing the finite element method: diffuse approximation and diffuse elements. Comput. Mech. 10, 307–318 (1992)
Nealen, A.: An as-short-as possible introduction to the least squares, weighted least squares and moving least squares methods for scattered data approximation and interpolation. Tech. rep., TU Darmstadt (2004)
Nguyen, D., Fedkiw, R., Jensen, H.: Physically based modeling and animation of fire. ACM Trans. Graph. 29, 721–728 (2002). SIGGRAPH Proc.
Pfaff, T., Thuerey, N., Gross, M.: Lagrangian vortex sheets for animating fluids. ACM SIGGRAPH 2012 Papers (2012)
Schechter, H., Bridson, R.: Evolving sub-grid turbulence for smoke animation. In: Proc. of the 2008 ACM/Eurographics Symp. on Comput. Animat. (2008)
Selle, A., Rasmussen, N., Fedkiw, R.: A vortex particle method for smoke, water and explosions. ACM Trans. Graph. 24(3), 910–914 (2005). SIGGRAPH Proc.
Selle, A., Fedkiw, R., Kim, B.M., Liu, Y., Rossignac, J.: An unconditionally stable MacCormack method. J. Sci. Comput. 35, 350–371 (2008)
Shen, C., O’Brien, J.F., Shewchuk, J.: Interpolating and approximating implicit surfaces from polygon soup. ACM Trans. Graph. 31, 321–328 (2004). SIGGRAPH Proc.
Song, O., Shin, H., Ko, H.S.: Stable but non-dissipative water. ACM Trans. Graph. 24(1), 81–97 (2005)
Stam, J.: Stable fluids. In: Proc. of SIGGRAPH 99, pp. 121–128 (1999)
Thuerey, N., Sadlo, F., Schirm, S., Muller-Fischer, M., Gross, M.: Real-time simulations of bubbles and foam within a shallow water framework. In: Proc. of the 2007 ACM SIGGRAPH/Eurographics Symp. on Comput. Animat., pp. 191–198 (2007)
Yabe, T., Aoki, T.: A universal solver for hyperbolic equations by cubic-polynomial interpolation I. One-dimensional solver. Comput. Phys. Commun. 66(2–3), 219–232 (1991)
Yabe, T., Ishikawa, T., Wang, P.Y., Aoki, T., Kadota, Y., Ikeda, F.: A universal solver for hyperbolic equations by cubic-polynomial interpolation II. Two- and three-dimensional solvers. Comput. Phys. Commun. 66(2–3), 233–242 (1991)
Acknowledgements
This Research is supported by Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism (MCST) and Korea Creative Content Agency (KOCCA) in the Culture Technology (CT) Research & Development Program 2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
(MPG 31.4 MB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, ST., Hong, JM. Visual simulation of turbulent fluids using MLS interpolation profiles. Vis Comput 29, 1293–1302 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-012-0770-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-012-0770-4