Abstract
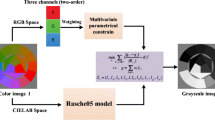
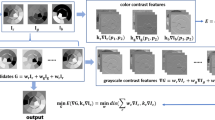
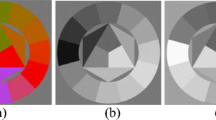
This paper presents a novel semi-reference inspired color-to-gray conversion model for faithfully preserving the contrast details of the color image, essentially differs from most of the no-reference and reference approaches. In the proposed model, on the basic assumption that a good gray conversion should make the conveyed gradient values (i.e., contrast) to be maximal, we present a projection maximum function to model the decolorization procedure. We further incorporate weights of the original gradients into the maximum function. The Gaussian weighted factor consisting of the gradients of each channel of the input color image is employed to better reflect the degree of preserving feature discriminability and color ordering in color-to-gray conversion. The projected gradient descent and discrete searching techniques are developed to solve the proposed model with and without nonnegative constraint, respectively. Extensive experimental evaluations on two existing datasets, containing abundant colors and patterns, show that the proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art methods quantitatively and qualitatively.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bala, R., Eschbach, R.: Spatial color-to-grayscale transform preserving chrominance edge information. In: Color Imaging Conference, pp. 82–86 (2004)
Neumann, L., Cadık, M., Nemcsics, A.: An efficient perception-based adaptive color to gray transformation. In: Computational Aesthetics, pp. 73–80 (2007)
Smith, K., Landes, P.E., Thollot, J., Myszkowski, K.: Apparent greyscale: a simple and fast conversion to perceptually accurate images and video. Comput. Gr. Forum 27(2), 193–200 (2008)
Jin, Z., Li, F., Ng, M.K.: A variational approach for image decolorization by variance maximization. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 7(2), 944–968 (2014)
Du, H., He, S., Sheng, B., et al.: Saliency-guided color-to-gray conversion using region-based optimization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(1), 434–443 (2015)
Gooch, A.A., Olsen, S.C., Tumblin, J., Gooch, B.: Color2gray: salience-preserving color removal. ACM Trans. Gr. 24(3), 634–639 (2005)
Rasche, K., Geist, R., Westall, J.: Re-coloring images for gamuts of lower dimension. Comput. Gr. Forum 24(3), 423–432 (2005)
Kim, Y., Jang, C., Demouth, J., Lee, S.: Robust color-to gray via nonlinear global mapping. ACM Trans. Gr. 28(5), 1–4 (2009)
Kuk, J.G., Ahn, J.H., Cho, N.I.: A color to grayscale conversion considering local and global contrast. Proc. ACCV 4, 513–524 (2010)
Song, M., Tao, D., Chen, C., Li, X., Chen, C.W.: Color to gray: visual cue preservation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(9), 1537–1552 (2010)
Lu, C., Xu, L., Jia, J.: Contrast preserving decolorization. In: IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), pp. 1–7 (2012)
Song, Y., Bao, L., Xu, X., Yang, Q.: Decolorization: is rgb2gray () out? In: ACM SIGGRAPH Asia Technical Briefs (2013)
Liu, Q., Liu, P.X., Xie, W., Wang, Y., Liang, D.: GcsDecolor: gradient correlation similarity for efficient contrast preserving decolorization. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(9), 2889–2904 (2015)
Grundland, M., Dodgson, N.A.: Decolorize: fast, contrast enhancing, color to grayscale conversion. Pattern Recognit. 40(11), 2891–2896 (2007)
Song, M., Tao, D., Bu, J., Chen, C., Yang, Y.: Color-to-gray based on chance of happening preservation. Neurocomputing 119, 222–231 (2013)
Lu, C., Xu, L., Jia, J.: Real-time contrast preserving decolorization. In: ACM SIGGRAPH Asia Technical Berief (2012)
Lu, C., Xu, L., Jia, J.: Contrast preserving decolorization with perception-based quality metrics. Int J. Comput. Vis. 110, 222–239 (2014)
Ancuti, C.O., Ancuti, C., Bekaert, P.: Enhancing by saliency guided decolorization. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on CVPR, pp. 257–264 (2011)
Cad’ık, M.: Perceptual evaluation of color-to-grayscale image conversions. Comput. Gr. Forum 27(7), 1745–1754 (2008)
Ancuti, C.O., Ancuti, C., Hermans, C.: Image and video decolorization by fusion. In: Computer Vision, pp. 79–92 (2010)
Lau, C., Heidrich, W., Mantiuk, R.: Cluster-based color space optimizations. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, ICCV, pp. 1172–1179 (2011)
Song, Y., Bao, L., Yang, Q.: Real-time video decolorization using bilateral filtering. In: IEEE Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 159–166 (2014)
Yoo, M.J., Lee, I.K., Lee, S.: Color sequence preserving decolorization. Comput. Gr. Forum 34, 373–383 (2015)
Zhu, W., Hu, R., Liu, L.: Grey conversion via perceived-contrast. Vis. Comput. 30(3), 299–309 (2014)
Kuhn, G.R., Oliveira, M.M., Fernandes, L.A.F.: An improved contrast enhancing approach for color-to-grayscale mappings. Vis. Comput. 24(7), 505–514 (2008)
Ji, Z., Fang, M.E., Wang, Y., et al.: Efficient decolorization preserving dominant distinctions. Vis. Comput. 32(12), 1–11 (2016)
Farbman, Z., Fattal, R., Lischinski, D., Szeliski, R.: Edge-preserving decompositions for multi-scale tone and detail manipulation. ACM Trans. Gr. 27(3), 67 (2008)
Tomasi, C., Manduchi, R.: Bilateral filtering for gray and color images. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 839–846 (1998)
Liu, Q., Luo, J., Zhu, Y.: Adaptive image decomposition by improved bilateral filter. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 23(7), 16–22 (2011)
Liu, Q., Xiong, B., Zhang, M.: Adaptive sparse norm and nonlocal total variation methods for image smoothing. Math. Probl. Eng. 2014, 18 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/426125. (Article ID 426125)
He, X., Yan, S., Hu, Y., Niyogi, P., Zhang, H.: Face recognition using Laplacianfaces. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 27(3), 328–340 (2005)
Calamai, Paul H., Mor’e, Jorge J.: Projected gradient methods for linearly constrained problems. Math. Program. 39, 93–116 (1987)
Liu, Q., Liang, D., Song, Y., Luo, J., Zhu, Y., Li, W.: Augmented Lagrangian based sparse representation method with dictionary updating for image deblurring. SIAM J. Imaging Sci. 6(3), 1689–1718 (2013)
Martin, D., Fowlkes, C., Tal, D., Malik, J.: A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. Proc. IEEE Conf. ICCV 2, 416–423 (2001)
Ma, K., Zhao, T., Zeng, K., Wang, Z.: Objective quality assessment for color-to-gray image conversion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(12), 4673–4685 (2015)
Kline, D.M., Berardi, V.L.: Revisiting squared-error and cross-entropy functions for training neural network classifiers. Neural Comput. Appl. 14(4), 310–318 (2005)
Acknowledgements
The authors sincerely thank the anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments and constructive suggestions that are very helpful in the improvement of this paper. The authors also thank Lu et al. for sharing their experiment materials and source codes. This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under 61661031, 61362001, 61365013, 61503176, the international scientific and technological cooperation projects of Jiangxi Province (No. 20141BDH80001), and Young scientists training plan of Jiangxi province (Nos. 20142BCB23001, 20162BCB23019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Li, S., Xiong, J. et al. WpmDecolor: weighted projection maximum solver for contrast-preserving decolorization. Vis Comput 35, 205–221 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-017-1464-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-017-1464-8