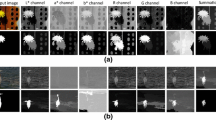
Abstract
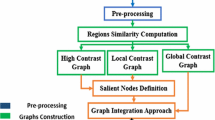
Graph-based methods have been widely adopted for predicting the most attractive region in an image. Most of the existing graph-based methods only utilize single graph to describe the image information, and thus cannot adapt for complex scenes. In this paper, a novel multi-graph framework for salient object detection is proposed. The proposed method is divided into three steps. Firstly, an image is divided into superpixels and described as a multi-graph, where superpixels are represented as nodes and their information is computed by color space and location space. Secondly, the multiple graphs are combined into a novel multi-graph-based manifold ranking propagation framework to obtain a coarse map. Finally, a map refinement model is developed to improve the quality of the coarse map. Experimental results on four challenging datasets show that the proposed method performs favorably against the state-of-the-art salient object detection methods.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borji, A., Cheng, M.M., Jiang, H., Li, J.: Salient object detection: a benchmark. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24, 5706–5722 (2015)
Ren, Z., Gao, S., Chia, L.T., Tsang, I.W.H.: Region-based saliency detection and its application in object recognition. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 24, 769–779 (2014)
Guo, C., Zhang, L.: A novel multiresolution spatiotemporal saliency detection model and its applications in image and video compression. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 19, 185–198 (2010)
Zhang, J., Feng, S., Li, D., Gao, Y., Chen, Z., Yuan, Y.: Image retrieval using the extended salient region. Inf. Sci. 399, 154–182 (2017)
Zhi, X.-H., Shen, H.-B.: Saliency driven region-edge-based top down level set evolution reveals the asynchronous focus in image segmentation. Pattern Recognit. 80, 241–255 (2018)
Maybank, S.J.: A probabilistic definition of salient regions for image matching. Neurocomputing 120, 4–14 (2013)
Yang, J., Yang, M.-H.: Top-down visual saliency via joint crf and dictionary learning. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp. 2296–2303 (2012)
Hou, X., Zhang, L.: Saliency detection: a spectral residual approach. In: 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1–8 (2007)
Li, Y., Hou, X., Koch, C., Rehg, J. M.,Yuille, A. L.: The secrets of salient object segmentation. In: 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 280–287 (2014)
Kim, J., Han, D., Tai, Y. W., Kim, J.: Salient region detection via high-dimensional color transform. In: 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 883–890 (2014)
Harel, J., Koch, C., Perona, P.: Graph-based visual saliency. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 545–552 (2007)
Wang, W., Wang, Y., Huang, Q., Gao, W.: Measuring visual saliency by site entropy rate. In: 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp. 2368–2375 (2010)
Mai, L., Niu, Y., Liu, F.: Saliency aggregation: a data-driven approach. In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp. 1131–1138 (2013)
Gong, C., Tao, D., Liu, W., Maybank, S. J., Fang, M., Fu, K., Yang, J.: Saliency propagation from simple to difficult. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2531–2539 (2015)
Zhang, Q., Lin, J., Li, W., Shi, Y., Cao, G.: Salient object detection via compactness and objectness cues. Vis. Comput. 34, 473–489 (2018)
Qi, W., Han, J., Zhang, Y., Bai, L.: Saliency detection via Boolean and foreground in a dynamic Bayesian framework. Vis. Comput. 33, 209–220 (2017)
Yang, C., Zhang, L., Lu, H., Ruan, X., Yang, M.-H.: Saliency detection via graph-based manifold ranking. In: 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp. 3166–3173 (2013)
Mao, M., Lu, J., Zhang, G., Zhang, J.: Multirelational social recommendations via multigraph ranking. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(12), 4049–4061 (2017)
Wu, J., Pan, S., Zhu, X., Zhang, C., Wu, X.: Positive and unlabeled multi-graph learning. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(4), 818–829 (2017)
Yang, X., Wang, M., Tao, D.: Robust visual tracking via multi-graph ranking. Neurocomputing 159, 35–43 (2015)
Itti, L., Koch, C., Niebur, E.: A model of saliency-based visual attention for rapid scene analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 20, 1254–1259 (1998)
Liu, T., Yuan, Z., Sun, J., Wang, J., Zheng, N., Tang, X., Shum, H.Y.: Learning to detect a salient object. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 33, 353–367 (2011)
Achanta, R., Hemami, S., Estrada, F., Susstrunk, S.: Frequency-tuned salient region detection. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1597–1604 (2009)
Shen, X., Wu, Y.: A unified approach to salient object detection via low rank matrix recovery. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 853–860 (2012)
Cheng, M.M., Mitra, N.J., Huang, X., Torr, P.H.S., Hu, S.M.: Global contrast based salient region detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 37, 569–582 (2015)
Li, X., Zhao, L., Wei, L., Yang, M.-H., Wu, F., Zhuang, Y., Ling, H., Wang, J.: Deepsaliency: multi-task deep neural network model for salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(8), 3919–3930 (2016)
Kuen, J., Wang, Z., Wang, G.: Recurrent attentional networks for saliency detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 3668–3677 (2016)
Lee, G., Tai, Y.-W., Kim, J.: Deep saliency with encoded low level distance map and high level features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 660–668 (2016)
Hou, Q., Cheng, M.-M., Hu, X., Borji, A., Tu, Z., Torr, P.: Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp. 5300–5309 (2017)
Hu, P., Shuai, B., Liu, J., Wang, G.: Deep level sets for salient object detection. In: CVPR, vol. 1, p. 2 (2017)
Wang, Q., Zheng, W., Piramuthu, R.: Grab: visual saliency via novel graph model and background priors. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 535–543 (2016)
Sun, J., Lu, H., Liu, X.: Saliency region detection based on markov absorption probabilities. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 24(5), 1639–1649 (2015)
Li, C., Yuan, Y., Cai, W., Xia, Y., Feng, D. D. et al.: Robust saliency detection via regularized random walks ranking. In: CVPR, pp. 2710–2717 (2015)
Wang, J., Lu, H., Li, X., Tong, N., Liu, W.: Saliency detection via background and foreground seed selection. Neurocomputing 152, 359–368 (2015)
Tao, D., Cheng, J., Song, M., Lin, X.: Manifold ranking-based matrix factorization for saliency detection. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 27(6), 1122–1134 (2016)
Xia, C., Li, J., Chen, X., Zheng, A., Zhang, Y.: What is and what is not a salient object? learning salient object detector by ensembling linear exemplar regressors. In: IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4321–4329 (2017)
Zhou, D., Bousquet, O., Lal, T. N., Weston, J., Schölkopf, B.: Learning with local and global consistency. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 321–328 (2004)
Zhou, D., Weston, J., Gretton, A., Bousquet, O., Schölkopf, B.: Ranking on data manifolds. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, pp. 169–176 (2004)
Perazzi, F., Krähenbühl, P., Pritch, Y., Hornung, A.: .Saliency filters: contrast based filtering for salient region detection. In: 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, pp. 733–740 (2012)
Achanta, R., Shaji, A., Smith, K., Lucchi, A., Fua, P., Süsstrunk, S.: Slic superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 34(11), 2274–2282 (2012)
Jiang, B., Zhang, L., Lu, H., Yang, C., Yang, M.-H.: Saliency detection via absorbing markov chain. In: 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), IEEE, pp. 1665–1672 (2013)
Zhang, L., Yang, C., Lu, H., Ruan, X., Yang, M.H.: Ranking saliency. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39, 1892–1904 (2017)
Wei, Y., Wen, F., Zhu, W., Sun, J.: Geodesic saliency using background priors. In: Fitzgibbon, A., Lazebnik, S. Perona, P. Sato, Y. Schmid, C. (eds.) Computer Vision– ECCV 2012, pp. 29–42. Springer, Berlin (2012)
Wu, X., Jin, Z., Zhou, J., Ma, X.: Saliency propagation with perceptual cues and background-excluded seeds. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 54, 51–62 (2018)
Lu, S., Mahadevan, V., Vasconcelos, N.: Learning optimal seeds for diffusion-based salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 2790–2797 (2014)
Cheng, M.-M., Warrell, J., Lin, W.-Y., Zheng, S., Vineet, V., Crook, N.: Efficient salient region detection with soft image abstraction. In: IEEE ICCV, pp. 1529–1536 (2013)
Cheng, M.-M., Mitra, N.J., Huang, X., Hu, S.-M.: Salientshape: group saliency in image collections. Vis. Comput. 30, 443–453 (2014)
Shi, J., Yan, Q., Xu, L., Jia, J.: Hierarchical image saliency detection on extended cssd. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 38, 717–729 (2016)
Peng, H., Li, B., Ling, H., Hu, W., Xiong, W., Maybank, S.J.: Salient object detection via structured matrix decomposition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 39, 818–832 (2017)
Margolin, R., Zelnik-Manor, L.,Tal, A.: How to evaluate foreground maps? In: The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) (2014)
Zhai, Y., Shah, M.: Visual attention detection in video sequences using spatiotemporal cues. In: Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, MM ’06, pp. 815–824. ACM, New York (2006)
Zhu, W., Liang, S., Wei, Y., Sun, J.: Saliency optimization from robust background detection. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR ’14, IEEE Computer Society, pp. 2814–2821. Washington (2014)
Tang, C., Wang, P., Zhang, C., Li, W.: Salient object detection via weighted low rank matrix recovery. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 24, 490–494 (2017)
Zhao, R., Ouyang, W., Li, H., Wang, X.: Saliency detection by multi-context deep learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1265–1274 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 61602244.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Zhou, K., Wu, X. et al. A novel multi-graph framework for salient object detection. Vis Comput 35, 1683–1699 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01637-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-019-01637-2