Abstract
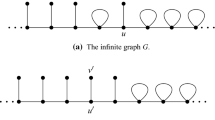
A magnet is a pair u, v of adjacent vertices such that the proper neighbours of u are completely linked to the proper neighbours of v. It has been shown that one can reduce the graph by removing the two vertices u, v of a magnet and introducing a new vertex linked to all common neighbours of u and v without changing the stability number. We prove that all graphs containing no chordless cycle C k (k ≥ 5) and none of eleven forbidden subgraphs can be reduced to a stable set by repeated use of magnets. For such graphs a polynomial algorithm is given to determine the stability number.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berge C.: Graphes. Gauthier-Villars, Paris (1983)
Butz, L., Hammer, P.L., Haussmann, D.: Reduction methods for the vertex packing problem. Proceedings of the 7th Conference on Probability Theory, Brasov, Romania 1982, VNU Science Press, Ultrecht, pp. 73–79 (1985)
Chudnovsky M., Robertson N., Seymour P., Thomas R.: The strong perfect graph theorem. Ann. Math. 164, 51–229 (2006)
Chvátal, V., Rusu, I.: A note on graphs with no long holes. Proceedings of the DIMACS Workshop on Perfect Graphs at Princeton, NJ (1993)
Fonlupt J., Uhry J.P.: Transformations which preserve perfectness and h-perfectness of graphs. Ann. Discret. Math. 16, 83–85 (1982)
Garey, M.R., Johnson, D.S.: Computers and Intractability : A Guide to the Theory of NP-Completeness. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York (1979)
Grötschel M., Lovász L., Schrijver A.: The ellipsoid method and its consequences in combinatorial optimization. Combinatorica 1, 169–197 (1981)
Hammer, P.L., Hertz, A.: On a transformation which preserves the stability number. RUTCOR research report 69-91. Rutgers University (1991)
Hayward R.: Weakly triangulated graphs. J. Comb. Theory B 39, 200–209 (1985)
Hayward R.: Generating weakly triangulated graphs. J. Graph Theory 21, 67–69 (1996)
Hayward, R., Hoang, C.T., Maffray, F.: Optimizing weakly triangulated graphs. Graphs Comb. 5, 339–349 (1989) erratum 6:33–35 (1990)
Hertz A.: On the use of Boolean methods for the computation of the stability number. Discret Appl. Math. 76, 183–203 (1997)
Hertz A.: On a transformation which preserves the stability number. Yugosl. J. Oper. Res. 10(1), 1–12 (2000)
Lévêque, B.: Coloring graphs: structures and algorithms. Ph.D thesis, Grenoble University. http://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00187797 (2007)
Lévêque, B., de Werra, D.: Graph transformations preserving the stability number. Cahier Leibniz 168, INPG Grenoble (2008)
Lovász L.: Normal hypergraphs and the perfect graph conjecture. Discret. Math. 2, 253–267 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hertz, A., de Werra, D. A Magnetic Procedure for the Stability Number. Graphs and Combinatorics 25, 707–716 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00373-010-0886-0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00373-010-0886-0