Abstract
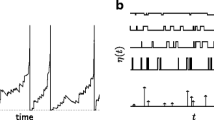
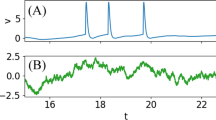
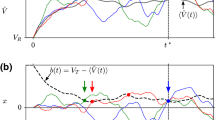
We consider a general integrate-and-fire (IF) neuron driven by asymmetric dichotomous noise. In contrast to the Gaussian white noise usually used in the so-called diffusion approximation, this noise is colored, i.e., it exhibits temporal correlations. We give an analytical expression for the stationary voltage distribution of a neuron receiving such noise and derive recursive relations for the moments of the first passage time density, which allow us to calculate the firing rate and the coefficient of variation of interspike intervals. We study how correlations in the input affect the rate and regularity of firing under variation of the model’s parameters for leaky and quadratic IF neurons. Further, we consider the limit of small correlation times and find lowest order corrections to the first passage time moments to be proportional to the square root of the correlation time. We show analytically that to this lowest order, correlations always lead to a decrease in firing rate for a leaky IF neuron. All theoretical expressions are compared to simulations of leaky and quadratic IF neurons.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alijani AK, Richardson MJ (2011) Rate response of neurons subject to fast or frozen noise: from stochastic and homogeneous to deterministic and heterogeneous populations. Phys Rev E 84(1):011919
Astumian RD, Bier M (1994) Fluctuation driven ratchets: molecular motors. Phys Rev Lett 72(11):1766
Badel L, Lefort S, Brette R, Petersen CC, Gerstner W, Richardson MJ (2008) Dynamic IV curves are reliable predictors of naturalistic pyramidal-neuron voltage traces. J Neurophysiol 99(2):656–666
Bair W, Koch C, Newsome W, Britten K (1994) Power spectrum analysis of bursting cells in area MT in the behaving monkey. J Neurosci 14:2870
Bena I (2006) Dichotomous Markov noise: exact results for out-of-equilibrium systems. Int J Mod Phys B 20(20):2825–2888
Bena I, van den Broeck C, Kawai R, Lindenberg K (2002) Nonlinear response with dichotomous noise. Phys Rev E 66(045):603
Brunel N (2000) Dynamics of sparsely connected networks of excitatory and inhibitory spiking neurons. J Comput Neurosci 8(3):183–208
Brunel N, Latham PE (2003) Firing rate of the noisy quadratic integrate-and-fire neuron. Neural Comput 15(10):2281–2306
Brunel N, Sergi S (1998) Firing frequency of leaky intergrate-and-fire neurons with synaptic current dynamics. J Theor Biol 195(1):87–95
Brunel N, Chance FS, Fourcaud N, Abbott LF (2001) Effects of synaptic noise and filtering on the frequency response of spiking neurons. Phys Rev Lett 86:2186–2189
Burkitt AN (2006a) A review of the integrate-and-fire neuron model: I. Homogeneous synaptic input. Biol Cybern 95(1):1–19
Burkitt AN (2006b) A review of the integrate-and-fire neuron model: II. Inhomogeneous synaptic input and network properties. Biol Cybern 95(2):97–112
Cowan RL, Wilson CJ (1994) Spontaneous firing patterns and axonal projections of single corticostriatal neurons in the rat medial agranular cortex. J Neurophysiol 71(1):17–32
De La Rocha J, Doiron B, Shea-Brown E, Josic K, Reyes A (2007) Correlation between neural spike trains increases with firing rate. Nature 448(7155):802–806
Fitzhugh R (1983) Statistical properties of the asymmetric random telegraph signal, with applications to single-channel analysis. Math Biosci 64(1):75–89
Fourcaud N, Brunel N (2002) Dynamics of the firing probability of noisy integrate-and-fire neurons. Neural Comput 14(9):2057–2110
Goychuk I, Hänggi P (2000) Stochastic resonance in ion channels characterized by information theory. Phys Rev E 61:4272–4280
Hänggi P, Jung P (1995) Colored noise in dynamical systems. Adv Chem Phys 89:239–326
Horsthemke W, Lefever R (1981) Voltage-noise-induced transitions in electrically excitable membranes. Biophys J 35(2):415–432
Horsthemke W, Lefever R (1984) Noise induced transitions. Springer, Berlin
Lindner B (2004a) Interspike interval statistics of neurons driven by colored noise. Phys Rev E 69(2):022901
Lindner B (2004b) Moments of the first passage time under external driving. J Stat Phys 117(3–4):703–737
Lindner B (2006) Superposition of many independent spike trains is generally not a Poisson process. Phys Rev E 73(2):022901
Lindner B, Schimansky-Geier L (2001) Transmission of noise coded versus additive signals through a neuronal ensemble. Phys Rev Lett 86:2934–2937
Lindner B, Longtin A, Bulsara A (2003) Analytic expressions for rate and CV of a type I neuron driven by white gaussian noise. Neural Comp 15(8):1761–1788
Lindner B, Gangloff D, Longtin A, Lewis J (2009) Broadband coding with dynamic synapses. J Neurosci 29(7):2076–2087
Liu YH, Wang XJ (2001) Spike-frequency adaptation of a generalized leaky integrate-and-fire model neuron. J Comput Neurosci 10(1):25–45
Markram H, Lübke J, Frotscher M, Roth A, Sakmann B (1997) Physiology and anatomy of synaptic connections between thick tufted pyramidal neurones in the developing rat neocortex. J Physiol 500(Pt 2):409
Middleton J, Chacron M, Lindner B, Longtin A (2003) Firing statistics of a neuron model driven by long-range correlated noise. Phys Rev E 68(2):021920
Moreno R, de La Rocha J, Renart A, Parga N (2002) Response of spiking neurons to correlated inputs. Phys Rev Lett 89(28):288101
Pikovsky AS, Kurths J (1997) Coherence resonance in a noise-driven excitable system. Phys Rev Lett 78:775–778
Richardson MJ, Gerstner W (2005) Synaptic shot noise and conductance fluctuations affect the membrane voltage with equal significance. Neural Comput 17(4):923–947
Richardson MJ, Swarbrick R (2010) Firing-rate response of a neuron receiving excitatory and inhibitory synaptic shot noise. Phys Rev Lett 105(17):178102
Rugar D, Budakian R, Mamin H, Chui B (2004) Single spin detection by magnetic resonance force microscopy. Nature 430(6997):329–332
Salinas E, Sejnowski TJ (2002) Integrate-and-fire neurons driven by correlated stochastic input. Neural Comput 14(9):2111–2155
Schwalger T, Schimansky-Geier L (2008) Interspike interval statistics of a leaky integrate-and-fire neuron driven by gaussian noise with large correlation times. Phys Rev E 77(3):031914
Schwalger T, Fisch K, Benda J, Lindner B (2010) How noisy adaptation of neurons shapes interspike interval histograms and correlations. PLoS Comput Biol 6(12):e1001026
Shadlen M, Newsome W (1998) The variable discharge of cortical neurons: implications for connectivity, computation, and information coding. J Neurosci 18(10):3870–3896
Shu Y, Hasenstaub A, McCormick DA (2003) Turning on and off recurrent balanced cortical activity. Nature 423(6937):288–293
Siegert AJF (1951) On the first passage time probability problem. Phys Rev 81:617–623
Softky W, Koch C (1993) The highly irregular firing of cortical cells is inconsistent with temporal integration of random epsps. J Neurosci 13(1):334–350
van den Broeck C (1983) On the relation between white shot noise, Gaussian white noise, and the dichotomic Markov process. J Stat Phys 31(3):467–483
van den Broeck C, Hänggi P (1984) Activation rates for nonlinear stochastic flows driven by non-Gaussian noise. Phys Rev A 30(5):2730
Vilela RD, Lindner B (2009) Are the input parameters of white noise driven integrate and fire neurons uniquely determined by rate and CV? J Theor Biol 257(1):90–99
Acknowledgments
We thank Tilo Schwalger and Finn Müller-Hansen for discussions and helpful comments on an earlier version of the manuscript. This work was supported by a Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung grant (FKZ: 01GQ1001A) and the research training group GRK1589/1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Droste, F., Lindner, B. Integrate-and-fire neurons driven by asymmetric dichotomous noise. Biol Cybern 108, 825–843 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-014-0621-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-014-0621-7