Abstract.
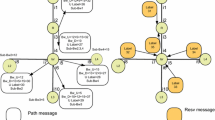
A new general theory about restoration of network paths is first introduced. The theory pertains to restoration of shortest paths in a network following failure, e.g., we prove that a shortest path in a network after removing k edges is the concatenation of at most k+1 shortest paths in the original network. The theory is then combined with efficient path concatenation techniques in MPLS (multi-protocol label switching), to achieve powerful schemes for restoration in MPLS based networks. We thus transform MPLS into a flexible and robust method for forwarding packets in a network. Finally, the different schemes suggested are evaluated experimentally on three large networks (a large ISP, the AS graph of the Internet, and the full Internet topology). These experiments demonstrate that the restoration schemes perform well in actual topologies.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: December 2001 / Accepted: July 2002
RID="*"
ID="*" This research was supported by a grant from the Ministry of Science, Israel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Afek, Y., Bremler-Barr, A., Kaplan, H. et al. Restoration by path concatenation: fast recovery of MPLS paths. Distrib Comput 15, 273–283 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00446-002-0080-6
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00446-002-0080-6