Abstract
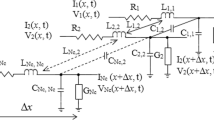
This paper presents a novel approach for an energy-aware analysis of electrically long high speed I/O links. ABCD-parameters are used to analyze the passive link model, which takes into account termination impedances at transmitter and receiver as well as the network parameters of the interconnect. Voltage transfer function and input impedance of the link model are used to carry out a combined evaluation of frequency dependent signal transmission and power consumption of the link. The combined analysis allows to carry out an optimization of the energy efficiency under the given constraints. It is applied to a realistic high speed backplane link, which is modeled using measured interconnect network parameters. Simulated interconnect network parameters are used to study the impact of link improvements on signal transmission and power consumption.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwal S, Pavankumar V, Yokesh R (2008) Energy-efficient, high performance circuits for arithmetic units. In: 21st international conference on VLSI design (VLSID 2008), January 2008, pp 371–376
Fu B, Wolpert D, Ampadu P (2009) Lookahead-based adaptive voltage scheme for energy-efficient on-chip interconnect links. In: 3rd ACM/IEEE international symposium on networks-on-chip (NoCS 2009), May 2009, pp 54–63
Venkata Kalyan T, Mutyam M, Vijaya Sankara Rao P (2008) Exploiting variable cycle transmission for energy-efficient on-chip interconnect design. In: 21st international conference on VLSI design (VLSID 2008), January 2008, pp 235–241
Hatamkhani H, Yang C-KK (2004) Power analysis for high-speed I/O transmitters. In: 2004 symposium on VLSI circuits, 2004 Digest of technical papers, June 2004, pp 142–145
Jung K, Lu Y, Alon E (2011) Power analysis and optimization for high-speed I/O transceivers. In: 2011 IEEE 54th international Midwest symposium on circuits and systems (MWSCAS), August 2011, pp 1–4
Huang G, Naeemi A, Meindl J (2005) Minimizing energy-per-bit for on-board LC transmission lines. In: Proceedings of the IEEE 2005 international interconnect technology conference, June 2005, pp 77–79
Svensson C (2001) Optimum voltage swing on on-chip and off-chip interconnect. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits 36(7):1108–1112
Gu X, Kwark Y, Liu D, Zhang Y, Fan J, Rimolo-Donadio R, Müller S, Schuster C, de Paulis F (2012) Backplane channel design optimization: recasting a 3 Gb/s link to operate at 25 Gb/s and above. In: Proceedings of the 2012 DesignCon, January 2012
Rimolo-Donadio R, Gu X, Kwark Y, Ritter M, Archambeault B, de Paulis F, Zhang Y, Fan J, Bruns H-D, Schuster C (2009) Physics-based via and trace models for efficient link simulation on multilayer structures up to 40 GHz. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 57(8):2072–2083
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank IBM Research for the provision of the original link measurement data published in [8].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, S., Duan, X. & Schuster, C. Energy-aware analysis of electrically long high speed I/O links. Comput Sci Res Dev 29, 97–102 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00450-012-0228-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00450-012-0228-y