Abstract
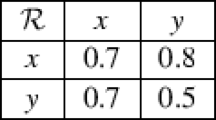
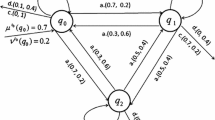
The purpose of this work is to indicate that a study of IF-automata (also called, intuitionistic fuzzy automata) can be carried out much on the same lines as the one done for fuzzy automata in Srivastava and Tiwari (Proceedings of 2002 AFSS international conference on fuzzy systems. Lecture notes in artificial intelligence, vol 2275. Springer, Berlin, pp 485–490, 2002). It is also shown that two IF-topologies (also called, intuitionistic fuzzy topologies) can be associated with the state-sets of IF-fuzzy automata whose level topologies have interesting relationships with the topologies introduced by Srivastava and Tiwari (above mentioned) for fuzzy automata.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A saturated topology is one which is closed under arbitrary intersections also.
An IF-closure operator \(c:IFS(X)\rightarrow IFS(X)\) on X is being called here saturated if the (usual) requirement \(c(u \vee v) = c(u) \vee c(v)\) is replaced by \(c(\vee u_j) = \vee c(u_j)\), where \(u, v, u_j \in IFS(X),\ j\in J\).
References
Atanassov K (1986) Intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 20:87–96
Chang CL (1968) Fuzzy topological spaces. J Math Anal Appl 24:182–189
Coker D (1997) An introduction to intuitionistic fuzzy topological spaces. Fuzzy Sets Syst 88:81–89
Das P (1999) A fuzzy topology associated with a fuzzy finite state machine. Fuzzy Sets Syst 105:469–479
Dubois D, Gottwald S, Hajek P, Kacprzyk J, Prade H (2005) Terminological difficulties in fuzzy set theory—the case of intuitionistic fuzzy sets. Fuzzy Sets Syst 156:485–491
Jun YB (2005) Intuitionistic fuzzy finite state machines. J Appl Math Comput 17:109–120
Jun YB (2006) Intuitionistic fuzzy finite switchboard state machine. J Appl Math Comput 20:315–325
Jun YB (2007) Quotient structures of intuitionistic fuzzy finite state machines. Inform Sci 177:4977–4986
Li YM, Pedrycz W (2005) Fuzzy finite automata and fuzzy regular expressions with membership values in lattice-ordered monoids. Fuzzy Sets Syst 156:68–92
Lowen R (1976) Fuzzy topological spaces and fuzzy compactness. J Math Anal Appl 56:621–633
Mac Lane S (1971) Categories for the working mathematician (Graduate Texts in Mathematics 5). Springer, Berlin
Malik DS, Mordeson JN, Sen MK (1994a) Semigroups of fuzzy finite state machine. In: Advances in fuzzy theory and technology, vol 2. Bookswrite, Durham, pp 87–98
Malik DS, Mordeson JN, Sen MK (1994b) On subsystems of a fuzzy finite state machine. Fuzzy Sets Syst 68:83–92
Mordeson JN (1999) Algebraic properties of rough set theory. NAFIPS’99, pp 56–59
Mordeson JN, Malik DS (2002) Fuzzy automata and languages: theory and applications. Chapman and Hall/CRC, London
Sheng L, Li Y (2006) Regular grammars with truth values in lattice-ordered monoid and their languages. Soft Comp 10:79–86
Srivastava AK, Tiwari SP (2002) A topology for fuzzy automata. In: Proceedings of 2002 AFSS international conference on fuzzy systems. Lecture notes in artificial intelligence, vol 2275. Springer, Berlin, pp 485–490
Srivastava AK, Tiwari SP (2003) On relationships among fuzzy approximation operators, fuzzy topology, and fuzzy automata. Fuzzy Sets Syst 138:197–204
Tiwari SP, Srivastava AK (2005) On a decomposition of fuzzy automata. Fuzzy Sets Syst 151:503–511
Yao YY (1996) Two views of the theory of rough sets in finite universes. Int J Approx Reason 15:291–317
Yao YY (1997) Combination of rough and fuzzy sets based on α-level sets. In: Rough sets and data mining: analysis for imprecise data. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 301–321
Zhang X, Li Y (2008) Intuitionistic fuzzy recognizers and intuitionistic fuzzy finite automata. Soft Comp. doi:10.1007/s00500-008-0338-4
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank the referee(s) for their observations and suggestions, which have helped them improve the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The present paper is a considerably extended version of our paper Intuitionistic fuzzy automata and associated fuzzy topologies (which contained no proofs), in the Proceedings of the Intern. Conf. on Computing: Theory and Applications (ICCTA 2007, 5–7 March 2007, ISI Kolkata, India), IEEE Computer Society, 267–271, 2007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srivastava, A.K., Tiwari, S.P. IF-topologies and IF-automata. Soft Comput 14, 571–578 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-009-0427-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-009-0427-z