Abstract
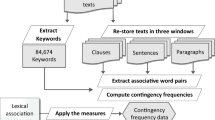
Oxymorons are combinations of contradictory or incongruous words and are typically used to draw readers’ attention to a text. This paper proposes a method to generate oxymorons using an association word corpus and a large-scale \(N\)-gram corpus. First, adjectives are fed as input into the proposed system. Then, antonym pairs are extracted from the \(N\)-gram corpus. Using the antonym pairs and the association word corpus, candidates are generated. Candidates are finalized or eliminated according to their suitability and attractiveness. To determine suitability, pointwise mutual information (PMI) is employed to exclude grammatically unnatural expressions. To determine attractiveness, PMI, gap of frequency of the oxymoron candidates, and WordNet are used. The generated combinations of oxymorons indicate the potential effectiveness of the proposed method.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbasi A, Chen H, Thoms S, Fu T (2008) Affect analysis of web forums and blogs using correlation ensembles. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 20(9):1168–1180
Akita K (2012) Scaling various kinds of stimulus words. Airi Publishing Company, Kyoto (in Japanese)
Ben-Shachar M, Dougherty RF, Deutsch GK, Wandell BA (2011) The development of cortical sensitivity to visual word forms. J Cogn Neurosci 23(9):2387–2399
Bond F, Baldwin T, Fothergill R, Uchimoto K (2012) Japanese SemCor: a sense-tagged corpus of Japanese. The 6th international conference of the global WordNet association (GWC-2012), Matsue
Croft W, Cruse DA (2004) Cognitive linguistics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gibbs RW, Kearney LR (1994) When parting is such sweet sorrow: the comprehension and appreciation of oxymora. J Psychol Res 23(1):75–89
McGinnies E (1949) Emotionality and perceptual defense. Psychol Rev 56(5):244–251
Merriam-Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary, http://www.merriam-webster.com/. Accessed July 20, 2014
Mizushima R, Yanagiya K, Kiyokawa S, Kawakami M (2011) Association word frequency chart. Nakanishiya Publishing Company, Kyoto (in Japanese)
Nishihara Y, Sunayama W (2008) Title-composing support system for reaching new audiences. IEEE international conference on data mining workshops, Pisa
Kozareva Z, Navarro B, Vazquez S, Montoyo A (2008) UA-ZBSA: a headline emotion classification through web information. In: Proceedings of the 4th international workshop on semantic evaluations
Kudo T, Kazawa H (2009) Web Japanese N-gram Ver. 1. Linguistic Data Consortium (in Japanese)
Shimizu K, Hagiwara M (2010) A method to estimate the impression of noun-verb phrases. Trans Jpn Soc Kansei Eng 10(4):505–514 (in Japanese)
Tokuhisa R, Inui K, Matsumoto Y (2008) Emotion classification using massive examples extracted from the web COLING 08. In: Proceedings of the 22nd international conference on computational linguistics, vol 1. Manchster, pp 881–888
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows (Grant No. 25-5423).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J.-W. Jung.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamane, H., Hagiwara, M. Oxymoron generation using an association word corpus and a large-scale N-gram corpus. Soft Comput 19, 919–927 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1430-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-014-1430-6